Name the Organelle
advertisement
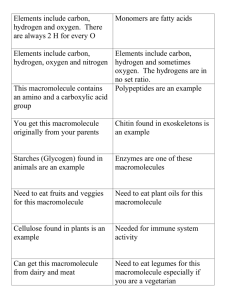
Benchmark 2 Review Any number 2 through 103 3. 1. 2. 6. 5. 4. What is a species? A. groups of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area. B. a group of organisms so similar to one another that they can breed and produce fertile offspring. C. assemblages of different populations that live together in a defined area. D. is a collection of all the organisms that live in a particular place, together with their nonliving, or physical, environment. E. is a group of ecosystems that have the same climate and similar dominant communities What is a population? A. groups of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area. B. a group of organisms so similar to one another that they can breed and produce fertile offspring. C. assemblages of different populations that live together in a defined area. D. is a collection of all the organisms that live in a particular place, together with their nonliving, or physical, environment. E. is a group of ecosystems that have the same climate and similar dominant communities What is a community? A. groups of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area. B. a group of organisms so similar to one another that they can breed and produce fertile offspring. C. assemblages of different populations that live together in a defined area. D. is a collection of all the organisms that live in a particular place, together with their nonliving, or physical, environment. E. is a group of ecosystems that have the same climate and similar dominant communities What is a community? A. groups of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area. B. a group of organisms so similar to one another that they can breed and produce fertile offspring. C. assemblages of different populations that live together in a defined area. D. is a collection of all the organisms that live in a particular place, together with their nonliving, or physical, environment. E. is a group of ecosystems that have the same climate and similar dominant communities What is an ecosystem? A. groups of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area. B. a group of organisms so similar to one another that they can breed and produce fertile offspring. C. assemblages of different populations that live together in a defined area. D. is a collection of all the organisms that live in a particular place, together with their nonliving, or physical, environment. E. is a group of ecosystems that have the same climate and similar dominant communities What is biome? A. groups of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area. B. a group of organisms so similar to one another that they can breed and produce fertile offspring. C. assemblages of different populations that live together in a defined area. D. is a collection of all the organisms that live in a particular place, together with their nonliving, or physical, environment. E. is a group of ecosystems that have the same climate and similar dominant communities Autotrophs • Autotrophs - use energy from the environment to fuel the assembly of simple inorganic compounds into complex organic molecules (Producers) • Processes- photosynthesis and chemosynthesis. Heterotrophs • Heterotrophs - organisms that rely on other organisms for their energy and food supply (Consumers) • Herbivores • Carnivores • Omnivores • Scavengers • Detritivores • Decomposers Food Chains and Food Chains • Food Chain - a series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten • Food Web - links all the food chains in an ecosystem together Trophic Levels Ecological Pyramids 1. Energy – 2. Biomass – 3. Numbers - Energy Pyramid Biomass Pyramid Numbers What is a community? • • • • • groups of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area. a group of organisms so similar to one another that they can breed and produce fertile offspring. assemblages of different populations that live together in a defined area. is a collection of all the organisms that live in a particular place, together with their nonliving, or physical, environment. is a group of ecosystems that have the same climate and similar dominant communities Question 2. A. C. B. What is a species? • • • • • groups of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area. a group of organisms so similar to one another that they can breed and produce fertile offspring. assemblages of different populations that live together in a defined area. is a collection of all the organisms that live in a particular place, together with their nonliving, or physical, environment. is a group of ecosystems that have the same climate and similar dominant communities Question 4. A. C. B. What is an ecosystem? • • • • • groups of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area. a group of organisms so similar to one another that they can breed and produce fertile offspring. assemblages of different populations that live together in a defined area. is a collection of all the organisms that live in a particular place, together with their nonliving, or physical, environment. is a group of ecosystems that have the same climate and similar dominant communities C. Question 6. B. A. What is biome? • • • • • groups of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area. a group of organisms so similar to one another that they can breed and produce fertile offspring. assemblages of different populations that live together in a defined area. is a collection of all the organisms that live in a particular place, together with their nonliving, or physical, environment. is a group of ecosystems that have the same climate and similar dominant communities C. Question 8. B. A. A group of organisms of a certain species that is in one area at a given time is known as A. an ecosystem B. a community C. a population D. a trophic level Question 10. A. B. C. Organisms in an ecosystem are linked together by A geochemical pathways B greenhouse effects C food webs D water cycles Which of the following fields of biology focuses on the interactions among various species with each other and their environment? A anatomy B genetics C biochemistry D ecology Which of the following is an abiotic factor in an ecosystem? A grass B a fox C a rock D a worm Predators often feed on weak or sick animals in an ecosystem. The role of the predator is described as its A community B habitat C niche D population In the food chain below, which population will most likely decrease if snakes are removed from the food chain? grass grasshopper frog snake hawk • • • • A grass B grasshopper C frog D hawk Of the following, which is considered a living organism? A bacterium B mitochondrion C nucleus D abiotic factor Biology is the study of A science B molecules C life D animals True or False Autotrophs - use energy from the environment to fuel the assembly of simple inorganic compounds into complex organic molecules Autotroph or Heterotroph? Autotroph or Hetertroph? True or False Heterotrophs - organisms that rely on other organisms for their energy and food supply. In a scientific experiment, how many independent variables should be tested at the same time? A none B one C two D three or more Which of the following is the smallest unit as shown on the metric ruler below? A centimeter B kilometer C millimeter D hectometer A student named Lu is about to leave the lab area where she has been working with chemicals. What is the last activity she should perform before she leaves the lab area? A put away her equipment B wash her hands C wash the tabletop D clean the glassware Homeostasis is the maintenance of stable conditions within the body. Which of the following is a method of maintaining homeostasis in the human body? A working in air conditioning B shivering when cold C eating balanced meals D sleeping regularly As energy flows through an ecosystem, at each trophic level it A increases B decreases C fluctuates D remains the same The total mass of living tissue at each trophic level can be shown in a(an) A.energy pyramid. B.pyramid of numbers. C.biomass pyramid. D.biogeochemical cycle Predators often feed on weak or sick animals in an ecosystem. The role of the predator is described as its A community B habitat C niche D population Organisms in an ecosystem are linked together by A geochemical pathways B greenhouse effects C food webs D water cycles In the food chain below, which population will most likely decrease if snakes are removed from the food chain? grass grasshopper frog snake hawk A grass B grasshopper C frog D hawk Autotrophs are organisms that A. rely on other organisms for their energy and food supply. B. consume plant and animal remains and other dead matter. C. use energy they take in from the environment to convert inorganic molecules into complex organic molecules. D. obtain energy by eating only plants. Question 7 All of life on Earth exists in a region known as A. an ecosystem. B. a biome. C. the biosphere. D. ecology. Which choice below has the correct trophic levels in the correct order? a. Producer, 1st Level Consumer, 2nd Level Consumer, 3rd Level Consumer. b. 3rd Level Consumer, 2nd Level Consumer, 1st Level Consumer, Producer. c. 3rd Level Consumer,1st Level Consumer, Producer, 2nd Level Consumer. How much energy is transferred to the next trophic level in an energy pyramid that is available for use? a. 5% b. 10% c. 15% d. 100% Groups of different species that live together in a defined area make up a(an) A. population. B. community. C. ecosystem. D. biosphere. Name? Macromolecule? Contains Adenine, Thymine, Guanine and cytosine Stores Genetic Information Double Stranded Name? Macromolecule? C, H, O Structural component for insulation and long term energy storage. Fat Cells Name? Macromolecule? C, H, O, N, S Anti-body Major part of the immune system that helps education white blood cells on potential pathogens. Name? Macromolecule? C,H, O Cellulose Major structural component in plant cell walls Name? Macromolecule? C, H, O, N, S Major structural component found in egg white Macromolecule? Name? Macromolecule? C, H, O, N, S Biological catalyst that speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy. Name? Macromolecule? C, H, O Major structural component of fungi cell wall and in the exoskeleton of arthropods. Macromolecule? Name? Macromolecule? C, H, O Complex sugar – polysaccharide Source of Energy Name? Macromolecule? C, H, O Wax Waterproofing function in some organisms The leaves of rutabaga plants are smooth, waxy, and divided into lobes. The leaves are edible and can be used and prepared in the same manner as turnip leaves. Name? Macromolecule? C, H, O, N, S Insulin Major component of the blood that helps convert glucose into a useable form (hint: diabetes) Help regulate other body functions as well. Name? Macromolecule? C, H, O Oils Name? Macromolecule? C, H, O, N, S Keratin Major structural component of skin, hair and fingernails. Name? Macromolecule? C, H, O C6H12O6 Simple sugar Source of energy Name? Macromolecule? C, H, O Fat Soluble hormone Examples: estrogen, progesterone, corticosteroids, testosterone, and Vitamin D. Name? Macromolecule? Contains Adenine, Uracil, Guanine and cytosine Stores genetic information for making proteins Single Stranded Macromolecule? Macromolecule? Name? Macromolecule? C, H, O, N, S Major structural component found in muscles (actin and myosin). Name? Macromolecule? C, H, O Complex sugar – polysaccharide Source of Energy Can be a structural component Nucleotides are the monomer for what macromolecule? Monosaccarides are the monomer for what macromolecule? Fatty Acids and Glycerol are the monomers for what macromolecule? Amino Acids are the monomer for what macromolecule? Identify the bond • A water molecule is __________ because there is an uneven distribution of electrons between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms. • Attraction of two different molecules? – Adhesion • Attraction of two of the same molecule? – Cohesion • Material composed of two or more elements or compounds? – Mixture • Examples? • Mixture with Water? – Solutions and Suspensions. • All components are evenly distributed throughout? – Solution • Substance being dissolved? – Solute • Substance doing the dissolving? – Solvent • Mixtures of water and material that is not dissolved? – Suspension • Solution or Suspension? • Gatorade – Solution • Quick Sand – Suspension • Saltwater – Solution • Blood – Both!!! • What does pH measure? • Acids (H+ ions) and Bases (OH- ions) • What is the pH scale range? • 0-14 • Acid or Base? • Orange Juice with a pH of 2 – Acid • Soap with a pH of 10 – Base • Human Blood with a pH of 7 – Neutral • Bleach with a pH of 13 – Base • Stomach Secretions with a pH of 1 – Acid • How do scientists (or cells) adjust pH levels? – Buffers (weak acids or bases) • What are the six most common element found in living things? – Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Sulfur, Nitrogen • What are the four macromolecules? • Grab your PeNCiL! – – – – Proteins Nucleic Acids Carbohydrates Lipids • What is the monomer? • Proteins – Amino Acids • Nucleic Acids – Nucleotides • Carbohydrates – Monosaccharide • Lipids – Fatty Acids Hint: C6H12O6 OR -NH2 + -COOH + R Amino Acids • What is the function? • Proteins – Structure and Functions • Nucleic Acids – Store Genetic Information • Carbohydrates – Energy and Structural • Lipids – Store Energy and Structural • Name examples? • Proteins • Nucleic Acids • Carbohydrates • Lipids • All Organic Compounds Contain? – Carbon • Identify Reactant or Product? • CO2 + H20 H2CO3 • Identify Reactant or Product? • CO2 +H20 H2CO3 • Energy that is needed to get a reaction? – Activation Energy • Substance that speeds up a chemical reaction? – Catalyst • Protein that is a biological catalyst (by lowering activation energy)? – Enzyme • Identify the part of an enzymatic reaction ? Question 34 • Identify the part of an enzymatic reaction ? • Identify the part of an enzymatic reaction ? • Identify the part of an enzymatic reaction ? • Identify the part of an enzymatic reaction ? • Some Enzymes are physically changed by extreme temperature or pH this is called? – Denaturation • What is the optimum temperature for this enzyme? oC • What is the optimum pH for Enzyme B? A B C Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic? Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic? Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic? Plant Cell or Animal Cell? Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic? Plant Cell or Animal Cell? Name the Organelle? Found in Plant Cells, Animal Cells or Both? Name the Organelle? Found in Plant Cells, Animal Cells or Both? Name the Organelle? Found in Plant Cells, Animal Cells or Both? Name the Organelle? Found in Plant Cells, Animal Cells or Both? Name the Organelle? Found in Plant Cells, Animal Cells or Both? Name the Organelle? Outside the Cell Found in Plant Cells, Animal Cells or Both? Inside the Cell Name the Organelle? Inside the Cell Enlarged Found in Plant Cells, Animal Cells or Both? Outside the Cell Name the Organelle? Found in Plant Cells, Animal Cells or Both? Name the Organelle? Found in Plant Cells, Animal Cells or Both? Name the Organelle? Found in Plant Cells, Animal Cells or Both? Name the Organelle? ? Found in Plant Cells, Animal Cells or Both? What is it? What is it? DNA Proteins like this one are carrier ______________ proteins. Integral peripheral Carbon dioxide and oxygen move across membranes in cells by diffusion _________________ Kind of endocytosis used to take in large particles or whole cells. phagocytosis Putting a plant cell in a HYPOTONIC solution will cause a(n) ____________ increase increase decrease in osmotic pressure when water enters the cell. This diagram represents a animal cell in a _______________ hypertonic solution. shrink It will probably ________________ shrink swell & burst stay the same size crenation This process is called _________________ Kind of transport used by glucose to move across cell membranes Facilitated diffusion with a channel Kind of transport that can move sodium and potassium ions AGAINST the concentration gradient fast Sodium-potassium pump When you sit in the bathtub, your fingers get wrinkly because of the water entering your skin cells. The bathtub water is a ____________ hypotonic solution compared to your skin cells Hypotonic isotonic hypertonic This type of transport is called endocytosis _______________ http://academic.brooklyn.cuny.edu/biology/bio4fv/page/cell-movement.html Diffusion continues until the concentration of molecules is equal throughout the space. This is called equilibrium ___________________ ACTIVE ____________ transport can move molecules AGAINST the concentration gradient. Active Passive This diagram represents an animal cell in a _______________ hypotonic solution. swell & burst It will probably ________________ shrink swell & burst stay the same size Passive transport does NOT ___________ require energy to move molecules. Kind of transport used by ions like Ca+ + , Cl - , Na+ , and K + to move across cell membranes Facilitated diffusion with Ion channels (Na+ and K + can also move by the Na+ - K + pump) Give some examples of membrane proteins that help move molecules across cell membranes Carriers, ion channels, pumps Name a kind of transport that uses membrane proteins to help molecules move across membranes Facilitated diffusion with carriers, Facilitated diffusion with ion channels, Na+-K+ pump proton pump A membrane that lets certain molecules pass through and not others is called _______________ Semi permeable OR selectively permeable Image from: http://www.d.umn.edu/~sdowning/Membranes/membraneImages/jpegimages/diffusionmedium.jpg Name a kind of transport that uses vesicles to move substances across a membrane Pinocytosis, phagocytosis, Exocytosis, endocytosis Name the kind of transport that moves WATER across cell membranes OSMOSIS (Facilitated diffusion with aquaporins) A freshwater fish has about 1% salt in his body. Freshwater is close to 0% salt. Will water move into or out of this kind of fish? More solute molecules inside the fish’s cells than in the freshwater. (HYPOTONIC) Water will move INTO the fish http://www.lionden.com/cell_animations.htm Which organelle makes the ATP used to run the Na + -K+ pump? mitochondria Type of endocytosis in which cells take in small molecules or fluids pinocytosis The white circles stand for oxygen molecules. Use what you know about diffusion of molecules to predict which way the oxygen will move. From the lungs into the blood (Move from a High concentration to low concentration) The shrinking away of the cell membrane from the cell wall in a plant cell when placed in a HYPERTONIC environment plasmolysis An INTEGRAL MEMBRANE PROTEIN that moves molecules PASSIVELY across cell membranes by attaching, CHANGING SHAPE, and flipping to the other side like a revolving door carrier protein http://bio.winona.edu/berg/ANIMTNS/facdifan.gif This diagram represents an animal cell in a ___________ solution. isotonic It will probably __________________ stay the same size Undergo cytolysis Undergo plasmolysis stay the same size Tell if the transport is ACTIVE or PASSIVE Facilitated diffusion ___________________ Osmosis ____________________ Na + - K+ pump ____________________ Diffusion ____________________ Endocytosis _______________________ Exocytosis ________________________ Ion channels ________________________ PASSIVE PASSIVE ACTIVE PASSIVE ACTIVE ACTIVE PASSIVE This diagram represents an plant cell in a _______________ hypotonic solution. The osmotic pressure in this cell will increase _______________ increase decrease Tell if the transport uses Vesicles membrane proteins Needs NO HELP Facilitated diffusion ___________________ Osmosis ____________________ Na + - K+ pump ____________________ Diffusion ____________________ Endocytosis _______________________ Exocytosis ________________________ Ion channels ________________________ Proton pump _________________ membrane protein Membrane protein membrane protein Needs no help Vesicle vesicle membrane protein membrane protein This diagram represents a plant cell in a _______________ hypertonic solution. The cell membrane will probably ________________ shrink away from the cell wall shrink away from the cell wall swell & burst stay the same size The osmotic pressure in this cell will decrease ________________ increase decrease Match the picture with the kind of transport FACILITATED DIFFUSION with carrier proteins http://bio.winona.edu/berg/ANIMTNS/facdifan.gif DIFFUSION Match the picture with the kind of transport http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBooktransp.html EXOCYTOSIS INSIDE CELL OUTSIDE CELL Substance is put in a vesicle and transported up to the cell membrane and released OUTSIDE Golgi Boies Match the picture with the kind of transport http://www.lionden.com/cell_animations.htm Na+ - K + pump Name a substance that in transported in this way + + Na or K Match the picture with the kind of transport http://academic.brooklyn.cuny.edu/biology/bio4fv/page/endocytb.htm ENDOCYTOSIS Substance is transported INTO cell inside a vesicle If these green/blue dots represent small molecule or fluids this would be called __________________ PINOCYTOSIS Kind of membrane protein used by glucose to move across cell membranes Carrier protein Putting plant cells into a HYPERTONIC solution will cause water to ____________________________________ Leave cell enter cell leave cell Putting plant cells into a HYPOTONIC solution will cause water to ____________________________________ Enter cell enter cell leave cell Ocean water has a greater concentration of dissolved solutes than the organisms that live there so ocea fish live in a _______tonic HYPER environment. Will water move into or out of this kind of fish? More solute molecules outside the fish’s cells than in. Water will move leave the fish Match the picture with the kind of transport http://academic.brooklyn.cuny.edu/biology/bio4fv/page/cell-movement.html ENDOCYTOSIS Substance is transported INTO cell inside a vesicle If the green square represents a large molecule or a whole cell this would be called __________________ PHAGOCYTOSIS Tell the kind of transport used by each Glucose ___________________ Oxygen & carbon dioxide _______________ Na + and K+ ions ____________________ Facilitated diffusion with carrier proteins Na +, K+ Cl -, & Ca ++ ions_______________ diffusion Na + – K+ pump Facilitated diffusion with Ion channels Match the picture with the kind of transport WATER molecules can diffuse PASSIVELY OSMOSIS Tell the kind of transport used by cells To take in large molecules Phagocytosis & whole cells ___________________________ To take in small molecules Pinocytosis & fluid _____________________________ Used by Golgi to transport Exocytosis molecules OUT of cell ___________________________ Used by white blood cells to Phagocytosis engulf and destroy bacteria _____________________ HYPERTONIC ISOTONIC HYPOTONIC Diffusion of water is called ______________ osmosis Healthy cells work to “maintain stable internal conditions” also called ____________. If this homeostasis doesn’t happen, cells can be damaged. (That is what happens when cells shrink or swell in hypotonic or hypertonic solutions.) HOW are pumps different from facilitated diffusion carriers and channels? Pumps require energy (active transport) and carriers and channels don’t need energy (passive transport) Pumps move against the gradient (low →high) Carriers/channels move with the gradient (high → low) Name the Organelle? Name the Organelle? Identify this part Macromolecule? Name the Organelle? What are the differences between plant cells and animal cells? What is it? What is the function? Name? Macromolecule? C, H, O, N, S Major structural component found in muscles (actin and myosin). What are the differences between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells? Identify this part Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic? Plant Cell or Animal Cell? What is the function? What did a thin slice of cork seem like to Robert Hooke when he observed it through a microscope? The cork seemed to be made of tiny empty chambers, cells. Macromolecule? What is the function? Name? Macromolecule? C,H, O Cellulose Major structural component in plant cell walls Identify this part Name the Organelle? Name? Macromolecule? C, H, O Wax Waterproofing function in some organisms The leaves of rutabaga plants are smooth, waxy, and divided into lobes. The leaves are edible and can be used and prepared in the same manner as turnip leaves. Nucleotides are the monomer for what macromolecule? Name the Organelle? Inside the Cell Enlarged Outside the Cell Name? Macromolecule? C, H, O, N, S Keratin Major structural component of skin, hair and fingernails. Identify this part What is the function? Fatty Acids and Glycerol are the monomers for what macromolecule? What is the function? DNA Name? Macromolecule? Contains Adenine, Uracil, Guanine and cytosine Stores genetic information for making proteins Single Stranded Name? Macromolecule? C, H, O, N, S Anti-body Major part of the immune system that helps education white blood cells on potential pathogens. Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic? Plant Cell or Animal Cell? Identify this part Determine the total magnification if you are looking through a 10x eyepiece and 4x objective lens. 40X What is the function? Inside the Cell Enlarged Outside the Cell Name? Macromolecule? C, H, O Oils Name? Macromolecule? C, H, O Fat Soluble hormone Examples: estrogen, progesterone, corticosteroids, testosterone, and Vitamin D. What is the function? Name? Macromolecule? C, H, O Complex sugar – polysaccharide Source of Energy Can be a structural component What is the function? Identify this part What is the function? Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic? Identify this part What are the three concepts that make up the cell theory? a. All living things are composed of cells. b. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. c. New cells are produced from existing cells. Name the Organelle? Name? Macromolecule? C, H, O, N, S Major structural component found in egg white Macromolecule? Macromolecule? Identify this part Name? Macromolecule? C, H, O, N, S Insulin Major component of the blood that helps convert glucose into a useable form (hint: diabetes) Help regulate other body functions as well. Name the Organelle? Outside the Cell Inside the Cell Which organelle is found in prokayrotic and eukaryotic cells and is the site of protein synthesis? A.Chloroplasts B.ER C.Lysosomes D.Ribosomes Name? Macromolecule? C, H, O C6H12O6 Simple sugar Source of energy Monosaccarides are the monomer for what macromolecule? Identify this part Name the Organelle? Name? Macromolecule? C, H, O, N, S Biological catalyst that speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy. Identify this part Name the Organelle? What is the function? Which of the following is an example of a prokaryotic cell? A.Plant B.Protist C.Bacteria D.Paramecium Name the Organelle? Identify this part Name the Organelle? Found in Plant Cells, Animal Cells or Both? Name the Organelle? What did the German biologist Theodor Schwann conclude? He concluded that animals were also made of cells. Name the Organelle? Identify this part What is it? DNA Name the Organelle? Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic? Identify this part Name the Organelle? Name? Macromolecule? Contains Adenine, Thymine, Guanine and cytosine Stores Genetic Information Double Stranded Name? Macromolecule? C, H, O Structural component for insulation and long term energy storage. Fat Cells Name? Macromolecule? C, H, O Major structural component of fungi cell wall and in the exoskeleton of arthropods. Name? Macromolecule? C, H, O Complex sugar – polysaccharide Source of Energy What is the function? Outside the Cell Inside the Cell Name the Organelle? Function? Found in Plant Cells, Animal Cells or Both? Identify this part Amino Acids are the monomer for what macromolecule? What is the function? Name the Organelle? Identify the bond • A water molecule is __________ because there is an uneven distribution of electrons between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms. • Attraction of two different molecules? – Adhesion • Attraction of two of the same molecule? – Cohesion Name the Organelle? • Material composed of two or more elements or compounds? – Mixture • Examples? • Mixture with Water? – Solutions and Suspensions. • All components are evenly distributed throughout? – Solution • Substance being dissolved? – Solute • Substance doing the dissolving? – Solvent • Mixtures of water and material that is not dissolved? – Suspension • Solution or Suspension? • Gatorade – Solution • Quick Sand – Suspension • Saltwater – Solution • Blood – Both!!! • What does pH measure? • Acids (H+ ions) and Bases (OH- ions) • What is the pH scale range? • 0-14 • Acid or Base? • Orange Juice with a pH of 2 – Acid • Soap with a pH of 10 – Base • Human Blood with a pH of 7 – Neutral • Bleach with a pH of 13 – Base • Stomach Secretions with a pH of 1 – Acid • How do scientists (or cells) adjust pH levels? – Buffers (weak acids or bases) • What are the six most common element found in living things? – Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Sulfur, Nitrogen • What are the four macromolecules? • Grab your PeNCiL! – – – – Proteins Nucleic Acids Carbohydrates Lipids • What is the monomer? • Proteins – Amino Acids • Nucleic Acids – Nucleotides • Carbohydrates – Monosaccharide • Lipids – Fatty Acids • What is the function? • Proteins – Structure and Functions • Nucleic Acids – Store Genetic Information • Carbohydrates – Energy and Structural • Lipids – Store Energy and Structural • Identify Reactant or Product? • CO2 + H20 H2CO3 • Identify Reactant or Product? • CO2 +H20 H2CO3 • Energy that is needed to get a reaction? – Activation Energy • Substance that speeds up a chemical reaction? – Catalyst • Protein that is a biological catalyst (by lowering activation energy)? – Enzyme • Identify the part of an enzymatic reaction ? • Identify the part of an enzymatic reaction ? • Identify the part of an enzymatic reaction ? • Identify the part of an enzymatic reaction ? • Identify the part of an enzymatic reaction ? • Some Enzymes are physically changed by extreme temperature or pH this is called? – Denaturation • What is the optimum temperature for this enzyme? oC • What is the optimum pH for Enzyme B? A B C