Grating X-ray Phase Contrast Imaging for Density Diagnostic of High
advertisement

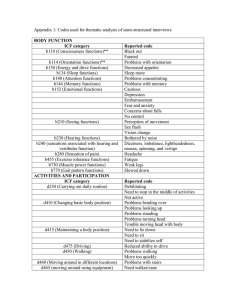
Grating Phase-Contrast Imaging for Diagnostic of High Energy Density Plasmas D. Stutman, M.P. Valdivia, M. Finkenthal Department of Physics & Astronomy Johns Hopkins University, USA Work supported by US DoE/NNSA Grant DENA0001B35 Presented at the 2014 International Workshop on X-ray and Neutron Phase Imaging with Gratings Garmisch-Partenkirchen, January 22 2014, Germany High Energy Density Plasmas are extreme state of matter Energy density> 105 J/cm-3 (p>1 Mbar ) Temperature (K) 108 ICF compression ICF ignition Solar core 106 104 102 1020 Planetary cores Solids 1022 1024 1026 Electron density (cm-3) HEDP in Inertial Confinement Fusion 300 TW laser power for 4 ns Ablation Compression Ignition Nuclear burn (100x energy gain) D-T fuel 6mm Be shell 200µm 600 g/cm3 108 K Density is fundamental plasma parameter in HEDP Electron density N at mid-compression in ICF (cm-3) 2 1024 Density -> Confinement Gradient-> Stability 1 1024 0 0.6 1.2 2 1024 • 10-1000 µm scales 1 1024 • 10 µm resolution 0.53 0.54 0.55 0.56 R (mm) Koch et al JAP 2009 Plasma turbulence makes gradients also on the µm scale Capsule mixing (HYDRA computation) Burn possible Burn not possible 50 µm Clark et al LLNL report 2011 Density (g/cm-3) X-ray radiography for density diagnostic in HEDP Pinhole backlighters for <10 keV radiography 10 µm Main laser Backlighter pinhole laser Hot V-Ge plasma Target plasma 2 cm 100 cm Gated X-ray detector Micro-foil backlighters for 20-75 keV radiography 10µm High-Z foil 100ps/1 kJ (1 petawatt) laser K-a • Poor attenuation contrast in low-Z plasmas • Density gradient hard to diagnose Refraction angles in the 100 µrad range expected in HEDP Refraction angles for 8 keV photons in ICF (µrad) 200 100 0 -100 0.53 0.54 0.55 R (mm) Koch et al JAP 2009 0.56 Talbot-Lau radiography has great potential for HEDP Attenuation radiograph T-L Moiré deflectometry 3 mm Be rod M=25x 25kVp Mo tube 1 mm • Much more sensitive than attenuation • Direct density gradient diagnostic How to implement Talbot-Lau interferometry in HEDP Removable X-ray tube G0 G1 G2 shield P≈2.5 cm Detector • Small G0 ≤ 2.5 µm (A=G0/P≈100 µrad) • High Talbot magnification, Talbot order • Moiré deflectometry with ≥10% contrast for 10s of µm fringe period at object • In-situ phase background Good fringe contrast achieved at high Talbot magnification G0=2.4 µm, G1=3.8 µm, G2=10 µm (MT=5.2) E~17 keV (Mo anode 25 kVp), A=80 µrad 100 µm fringe period at object M.P. Valdivia et al JAP 2013 m=3 SNR fringe period limit of ~30 µm Accurate, high resolution density profiles Density gradient in 3 mm Be rod Mo anode 25 kVp, M=20x Areal density profile • Remarkable accuracy for angles << interferometer angular width Simultaneous density gradient and attenuation maps 1.5 mm Al rod, 17 keV, M=20x Refraction Attenuation • Simultaneous density and Zeff diagnostic Scatter imaging also works Plastic doped with micro-particles Scatter image 1.5 mm • µ-turbulence diagnostic without µm spatial resolution • T-L Moiré deflectometry at 8 keV also very encouraging High magnification interferometry below 10 keV Au grating on membrane Free-standing phase grating 4 µm 40 mm MICROWORKS INC • Early ICF stages, smaller HEDP experiments Moiré deflectometry at 8 keV (Cu anode) Be rod Fruit-fly Wax drop • >30% fringe contrast with free-standing grating Will G0 survive long enough to produce useful images? Pinhole closure experiments Pinhole aperture (µm) Backlighter Reighard et al RSI 2008 • 1 GW/cm2 soft X-rays on G0 • Few ns lifetime for G0 on Si substrate + photoresist Alternate G0 solutions explored Micro-layered backlighter Micro-periodic mirror Pt 100 ps laser Si 1 µm SUMMARY • Talbot-Lau method has great potential for HEDP diagnostic • G0 survival, 2-D gratings, phase-retrieval without Moiré fringes • High M interferometry for biomedical, material applications Moiré deflectometry demonstrated in low density plasmas Moiré deflectometry of 1020 cm-3 plasma jet using soft X-ray laser Grava et al 2008 Resolution improves with smaller source size M=20 80 micron 58 µm 40 micron 30 µm 10 micron 8 µm MO = 8-25 Weff = 80 µrad