measurement
advertisement

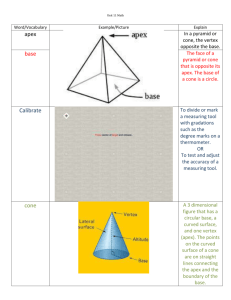
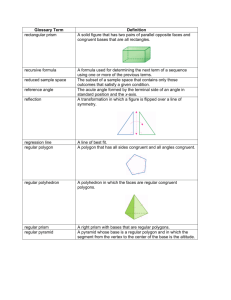
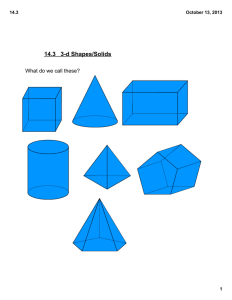
CHAPTER 5 MEASUREMENT SECTION 5-1 Ratios and Units of Measure MEASUREMENT– is a process used to find size, quantities, or amounts COMPASS – is used for drawing curved lines and circles for measuring distances. PROTRACTOR – is an instrument for measuring and drawing angles. SCALES or RULERS – devices for measuring distance. CALIPERS and MICROMETERS – devices used for making precise measurements PRECISION – is related to the unit of measure used. GREATEST POSSIBLE ERROR – is ½ the smallest unit used to make the measurement. RATIO – is a quotient of two numbers that compares one number with the other. RATE – is a ratio that compares two different quantities UNIT RATE – compares a quantity to one unit of that quantity SECTION 5-2 Perimeter, Circumference and Area PERIMETER – is the distance around a polygon. CIRCUMFERENCE – is the distance around a circle. AREA – the amount of surface a figure covers. Circle C = d or 2r 2 A =r Rectangle or Square P = 2l + 2w A = lw Triangle A = ½bh Parallelogram A = bh Trapezoid A = ½h(b1+b2) SECTION 5-3 Probability and Area PROBABILITY – the likelihood that an event will occur. P(any event) = number of favorable outcomes ÷ number of possible outcomes SECTION 5-4 Problem Solving Skills: Irregular Shapes SECTION 5-5 Three-dimensional Figures and Loci POLYHEDRON– is a three-dimensional figure in which each surface is a polygon and The surfaces are called faces. Two faces intersect at an edge, and a vertex is a point where three or more edges intersect. PRISM - a polyhedron with two identical parallel faces. Each of these faces is called a base and a prism is named by the shape of its bases. PYRAMID - a polyhedron with only one base. The other faces are triangles that meet at a vertex and a pyramid is named by the shape of its base. LATERAL FACES - are those faces that are not bases. LATERAL EDGES - are the edges of lateral faces and can be parallel, intersecting,or skew. CYLINDER - a threedimensional figure having a curved region with two parallel congruent circular bases. Its axis joins the centers of the two bases. CONE - a three-dimensional figure having a curved surface and one circular base. Its axis is a segment from the vertex to the center of the base. SPHERE - is the set of points in space that are the same distance from a given point called the center of the sphere. SECTION 5-6 Surface Area of Threedimensional Figures SURFACE AREA - The sum of the areas of all the faces of a threedimensional figure. FORMULAS Square base A= 2 s Square prism SA = 2 6s Rectangular Prism SA = 2(lw + lh + wh) Triangular face A = ½bh Circular base A= 2 r Curved surface A = 2rh Cylinder SA = 2rh + 2 2r Cone SA = rs + 2 r S is the slant height Sphere SA = 2 4 r SECTION 5-7 Volume of Threedimensional Figures FORMULAS Prism V = Bh where B = area of the given base Pyramid V = 1/3Bh where B = area of the given base Cylinder V= 2 r h Cone V= 2 1/3r h Sphere V= 3 4/3r END