Economic Assessment of colombia, 2013
advertisement

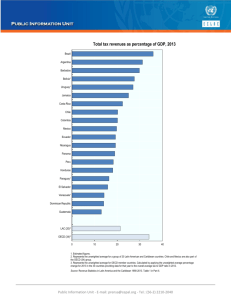
INTEGRATING SECURITIES MARKETS TO BOOST COMPETITIVENESS The Latin American Integrated Market – MILA DAY 2015 Sebastián Nieto Parra Economist LAC Unit Development Centre OECD October 2015 Contents 1 Key Challenge: Tackling the Middle Income Trap (MIT) 2 Market Integration: a key asset to avoid the MIT 3 Crucial role of Capital Markets 4 Conditions and Benefits of Capital Markets Integration Contents 1 Key Challenge: Tackling the Middle Income Trap (MIT) 2 Market Integration: a key asset to avoid the MIT 3 Crucial role of Capital Markets 4 Conditions and Benefits of Capital Markets Integration The Middle Income Trap: A common challenge in the MILA countries GDP per capita (1990 USD ) 2013 1980 1950 40000 35000 30000 25000 20000 HI 15000 10000 UMI 5000 0 LMI LI CHL URY ARG VEN CRI MEX COL Source: OECD-CAF-ECLAC Latin American Economic Outlook , 2014 BRA PER DOM OECD average A disappointing progress compared to different OECD countries Evading the middle income trap China South Korea Japan Portugal Israel Spain LAC avg MILA avg GDP per capita constant 1990PPP dollars 12000 High-income > 11 750 USD 10000 8000 6000 Middle-income 7250 USD 4000 2000 Low-income > 2 000 USD 0 1950 1955 1960 1965 1970 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 Source: Author's calculation based on Felipe, Abdon and Kumar (2012). Data extracted from International Monetary Fund, World Economic Outlook Database (April 2015) and Madison (2010) Sources of GDP per capita differences: low level of productivity Percentage of GDP per capita difference compared with the upper half of OECD countries % 0 -20 -40 -60 -80 Peru China Colombia South Africa Brazil Mexico Chile Korea OECD Australia Percentage difference in labour resource utilisation and labour productivity Labour productivity % Labour resource utilisation 40 20 0 -20 -40 -60 -80 -100 Peru China Colombia South Africa Brazil Mexico Chile Korea Source: OECD National Accounts Database, World Bank (2015), World Development Indicators (database), Washington, DC, ILO (International Labour Organization), Key Indicators of the Labour Market (KILM) OECD Australia Economic complexity indicator, 1990-2012 ECI ranks how diversified and complex a country’s export basket is Index 2 2012 1990 1.5 1 0.5 0 -0.5 -1 Source: Hausmann et al. (2012), The Atlas of Economic Complexity, Puritan Press, Cambridge, MA; Simoes and Hidalgo (2012), “The Economic Complexity Observatory: An analytical tool for understanding the dynamics of economic development”, Workshop at the Twenty-Fifth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, August, 2011, Cambridge, MA. Contents 1 Key Challenge: Tackling the Middle Income Trap (MIT) 2 Market Integration: a key asset to avoid the MIT 3 Crucial role of Capital Markets 4 Conditions and Benefits of Capital Markets Integration Intra-trade remains poor in the region Share of intra-regional trade in intermediate and final goods, by region, 2011 Final goods Intermediates 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 EU27 Asia LAC Source: OECD Latin American Economic Outlook 2016 based on United Nations (2015), United Nations Commodity Trade Statistics Database, (COMTRADE) More can be done in the participation to Global Value Chains Backward GVC participation in selected regions and countries, 2011 (%) 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 Colombia Peru LAC 6 Chile EU27 Asia Source: Latin American Economic Outlook 2016 based on 2015 OECD/WTO TiVA data. Mexico China Korea Business expenditure on research and development Business expenditure on research and development 2013 Number of Patent Cooperation Treaty 2010-2011 average (% of GDP) 250 3.5 3 200 2.5 150 2 1.5 100 1 50 0.5 0 0 Source: OECD (2015), Main Science and Technology Indicators Database and OECD calculations based on Red de Indicadores de Ciencia y Tecnología Iberoamericana e Interamericana (RICYT) Source: OECD Indicators on Patent (database) Effectiveness of investment infrastructure and logistics: more important than FTAs Ratio of freight costs to tariffs, 2012 and 2014 Ratio of freight costs to tariffs (2014) Ratio of freight costs to tariffs (2012) 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 Source: Based on data from the US Census Bureau. FT920: U.S. Merchandise Trade. Contents 1 Key Challenge: Tackling the Middle Income Trap (MIT) 2 Market Integration: a key asset to avoid the MIT 3 Crucial role of Capital Markets 4 Conditions and Benefits of Capital Markets Integration Policies to escape the middle income trap Priorities for productivity and higher income (coefficients) Low income countries 5 Low middle income countries Upper middle income countries 4 3 2 1 Fuente: Izquierdo et al. (2015), In Search of Larger Per Capita Incomes: How to Prioritize Across Productivity Determinants?, IDB mimeo. Telecommunication Labor Markets Trade Innovation infrastructure Health Education -1 Stock Markets 0 0 Switzerland Chile United States United Kingdom Canada Sweden Korea, Rep. Australia Spain Colombia Denmark France OECD avg Japan OECD median Finland Belgium Brazil Peru Norway Ireland Mexico LAC median China Germany LAC avg Turkey Poland Portugal Italy Czech Republic Greece Hungary Bolivia Venezuela, RB Argentina Uruguay Market capitalization remains high… Market Capitalization (% GDP, 2012) 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 Source: World Bank, World Development Indicators (2012) 0 Japan Spain United States Canada Poland Australia United… Korea, Rep. Argentina Uruguay Germany Greece OECD avg France Italy Turkey Brazil Venezuela, RB Slovenia OECD median Peru Norway Sweden Hungary LAC avg Mexico Belgium Denmark Bolivia LAC median Finland Chile Portugal Switzerland Netherlands Colombia Czech… Ireland Jamaica But with high market concentration Listed companies (% Market capitalization-GDP, 2012) 60 50 40 30 20 10 Source: World Bank, World Development Indicators (2012) Productivity growth and stock markets: listed companies Annual growth of labor productivity per worked 2000-15 Labor productivity per hour worked annualized growth 2000-15 0.04 0.035 PER 0.03 CHL 0.025 0.02 COL y = 0.0072ln(x) + 0.164 R² = 0.2978 0.015 BRA 0.01 0.005 MEX ARG 0 VEN -0.005 -0.01 0 5E-10 1E-09 1.5E-09 2E-09 Listed companies (% PIB) average 1995-12 Source: World Bank, 2014 / The Conference Board , 2015 2.5E-09 3E-09 3.5E-09 0 Italy Korea, Rep. United States Turkey Spain Japan OECD avg Germany United Kingdom Australia Finland OECD median Brazil Netherlands Sweden France Canada Switzerland Norway Hungary Denmark LAC avg Portugal Poland Belgium Greece Czech Republic Mexico Chile Colombia Slovenia Peru LAC median Argentina Jamaica Uruguay Bolivia Venezuela Liquidity: an important challenge for market development in the region Stock traded (% market capitalization, 2012) % 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 Source: World Bank, World Development Indicators (2012) Liquidity is associated with productivity Labor productivity per hour worked and stocks traded 70 Labor productivity per hour worked avg 2000-15 60 50 y = 4.7609ln(x) + 22.417 R² = 0.2404 40 30 20 VEN CHL URG ARG MEX BRA COL 10 PER 0 0 50 100 Stocks traded (% GDP) avg 1995-12 Source: World Bank, 2014 / The Conference Board , 2015 150 200 250 Differences in terms of debt composition in MILA countries Domestic Debt Market Composition (%, 2012) Central Government Cource: BIS, 2012 Financial intermediaries Non-Financial intermediaries Contents 1 Key Challenge: Tackling the Middle Income Trap (MIT) 2 Market Integration: a key asset to avoid the MIT 3 Crucial role of Capital Markets 4 Conditions and Benefits of Capital Markets Integration 0 Argentina LAC avg El Salvador Dominican… Costa Rica Russia Cyprus Guatemala Uruguay Indonesia South Africa Turkey Colombia Peru Malaysia Panama MILA avg Portugal Mexico Hungary Iceland Thailand Philippines Slovenia China Italy Chile Spain Israel Poland Qatar Singapore OECD avg Slovak… Korea Estonia Czech… Ireland New Zealand Belgium France Japan United… Finland Netherlands Austria Norway Denmark Sweden Germany Enhanced macroeconomic discipline CDSs – Credit Default Swap Spreads 10 years (Basis Points, annual average 2015) 500 2.287 450 400 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 Source: Bloomberg Market integration attracts further international investors • The top investors that own shares in the companies listed on the member exchanges of the CEE Stock Exchange group are primarily international investors from US, UK, Austria, France, Germany Note: Stocks included in the CEE Stock Exchange Group are Budapest (Hungary), Ljubljana (Slovenia), Prague (Czech Republic), and Vienna (Austria). Others category includes the following countries Canada, Czech Republic, Denmark, Hungary, Slovenia, Sweden Source: CEE Stock Exchange report /Ipreo. Economies of scale: increases efficiency and new issuers Listed domestic companies, 2012 Stock exchange merger and liquidity: The case of Euronext 1000 900 800 700 600 500 400 300 200 Source: World Bank, World Development Indicators (2012) Jamaica Bolivia Venezuela Colombia Argentina Mexico Peru Chile Brazil MILA 0 OECD avg 100 Source: Nielsson, (2012) Stock exchange merger and liquidity The case of Euronext, Journal of Financial Markets, Vo.. 12, Issue 2, 2009, 229-267 Conclusions - Pacific Alliance countries have a common challenge: to boost productivity and competitiveness To tackle the Middle Income Trap. - A key actor to facilitate improvements in these areas: Capital Markets. - In particular MILA: to increase the number of listed companies, the liquidity, and to attract new investors. - A key pillar: credibility of macroeconomic policies. - OECD supports regional integration in Latam and in particular close work/collaboration with MILA/Pacific Alliance countries: - Chile and Mexico: OECD members - Colombia: Accession Process to join the OECD - Peru: OECD Country Programme INTEGRATING SECURITIES MARKETS TO BOOST COMPETITIVENESS The Latin American Integrated Market – MILA DAY 2015 Sebastián Nieto Parra Development Centre OECD October 2015