AICE Marine Unit 4 - Nutrient Cycles in Marine Ecosystems Part I Fill
advertisement

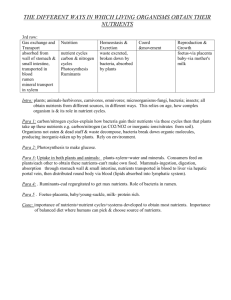
AICE Marine Unit 4 - Nutrient Cycles in Marine Ecosystems Part I Fill-In Notes I. Detritus What is it? _______________________________________________________________ How does it fit in to a food web/chain? ________________________________________________________________________ Who/what consumes it? ___________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Detritus is broken down and released as chemical elements into the ____________, _________, & _________ where P.P. can recycle them into organic compounds Without detritivores, life would cease! Essential nutrients would be _______________ & ___________________ to the ecosystem II. Chemical Cycling Nutrients move between ____________ and ________________ parts of the ecosystem in ______________________________ cycles. Cycles may be _____________ or _____________. Nutrient cycles with a gaseous component (_____________, ________________, and ________________________) are global whereas phosphorus, potassium and calcium cycle more locally (at least on short time scales). - 2 Major Types of Biogeochemical Cycles: **Based on the Primary Source of nutrient input** o Gaseous cycles—____________________ & _________________ (global circulation patterns) o Sedimentary cycles—___________________________________________; these vary from one element to another, but essentially each has two abiotic phases: ______________ phase _____________ phase Draw me! III. o o IV. o o o o o V. o o o o o o VI. o o VII. General Structure of Nutrient Cycles Nutrients can move from __________________________________ by a variety of processes Some examples: a. Photosynthesis (_________________________________________________) b. Respiration (makes inorganic nutrients available from organic) c. ___________________________ (makes inorganic nutrients available from organic) d. ____________________ (makes inorganic nutrients available from organic) Decomposition and nutrient cycling rates Rate of nutrient cycling is affected by _________________________________ In the tropics, _________________________________________ cause organic material to decompose __________________________ than it does in temperate regions! In aquatic ecosystems decomposition in ____________________ sediments can be very slow (50 + years) As a result, sediments are often a __________________ and only when there is upwelling* are _______________________________________________. (*Upwelling ___________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________) Human effects on nutrient cycles: Recent studies suggest that human activities (________________________________________________) have approximately doubled the supply of __________________ available to plants. Fertilizers that are applied in amounts greater than plants can use or that are applied when plants are not in the fields leach into groundwater or run off into streams and rivers therefore getting to the ocean. A major problem with intensive farming is _______________________________. The ________________________________________ causes blooms of algae and cyanobacteria as well as explosive growth of water weeds. Because respiration by plants depletes the oxygen levels at night this process of _____________________________ can cause fish kills. Eutrophication of Lake Erie, for example, wiped out commercially important populations of fish including lake trout, blue pike and whitefish in the 1960’s. Limits on primary productivity ____________________________________________________ affecting NPP in aquatic biomes. In marine environments the nutrients limiting primary productivity are usually ________________ and __________________________, which are scarce in the photic zone. 5 Nutrient Cycles 1. ________________________________ 2. _______________________________ 3. ______________________________ 4. _______________________________ 5. ______________________________ VIII. o o o o o o Carbon Cycle Carbon forms _________________________________________ (organic chemistry is the study of carbon chemistry). ________________________________________ etc. all contain carbon. Photosynthetic organisms take in _______________________________ and using energy from sunlight join carbon atoms ________________________ (energy is stored in the chemical bonds). Major reservoirs of carbon include: ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________. Photosynthesis removes ______________________________________ An approximately equal amount of CO2 is returned to atmosphere by cellular respiration. _______________________________________ adds large amounts CO2 to the atmosphere. IX. Nitrogen Cycling o N is an essential element in o Protein: ____________________________________________ o Nucleic acids: nitrogenous bases o N2 makes up about _________________________________________ o N2 is only usable by prokaryotes with the enzyme nitrogenase o Cyanobacteria like Anabaena carry their nitrogenase in a low oxygen package, the heterocyst. - Fixation - Converts N2 to o ________________________________ NH4 : o N2 --> 2N o 2N + 3H2 --> 2NH3 o Rhizosphere bacteria: mutualistic, some nodule formers o Free-living bacteria (+cyanobacteria) ~ 12,000 species o Nitrate (high energy discharge, like lightning) - NO3 o NO3 in atmosphere + water vapor = H2NO3 o Atmospheric fixation low: 8.9 kg N/ha/yr - Mineralization (ammonification) o Major step in ______________ o Biomolecules (proteins, nucleic acids) from ___________________________________________________________ and fungi to amino acids then to CO2 + H2O + NH4 + energy o Fate: dissolved in H2O, trapped in soil, fixed in clay X. Nitrification - Nitrosomonas bacteria use __________________________ as sole E source - Nitrobacter bacteria use the remaining E in nitrite ion and oxidize it to nitrate - _________________________________ if nitrates build up in aquatic ecosystems - Denitrification • Nitrates reduced _______________________________________ • Denitrifiers are _______________________________ – Bacteria: Pseudomonas – Fungi Phosphorus Cycle: Terrestrial & Aquatic Nitrogen Cycle