Unit 2 Table: Acts
advertisement

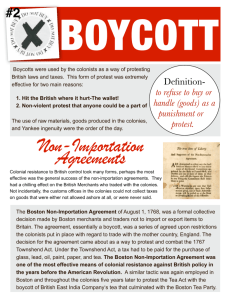
Act Proclamati on of 1763 Sugar Act Currency Act Mutiny Act Stamp Act Quebec Act Year 1763 1764 1764 1765 1765 Reason for Instati ng To prevent escalation of fighting btw white s and NAs that would threaten trade Eliminate the illegal sugar trade btw the colonies , the French, and the Spanish West Indies British navy ships were assigned to patrol American waters and search for smugglers Forbid settlers to advance beyond a line drawn along the App. Mtns. Strengthene d the enforcemen t of the duty on sugar Required colonial assembly to stop issuing paper $$$ lowered the duty on molasses Phase out colonial $$ NAs (esp. Cherokee) initially liked agreement Damaged the market for sugar grown in the colonies FAILED bc white settlers did not listen Est. new admiralty courts in America to try accused smugglers Said… Conse quence s Mainly affected merchants Townshend / Revenue Act Intolerable Acts 1774 1767 1774 Effort to reapply the old principles of mercantilism Direct attempt to raise revenue in the colonies After F&I War, English had Quebec Region; bc of cultural difference, English had dilemma… designed to raise $$$ exclusively for England combo of 4 Coercive Acts, meant to punish the colonists after Boston Tea Party & unrelated Quebec Act Colonists were required to assist in provisioning and maintaining the army Imposed a tax on newspapers, almanacs, pamphlets, deeds, wills, licenses allowed French customs & Catholicism from Quebec to Ohio River put a light import duty on such things as glass, lead, paper, and tea considered unfair because they were designed to discipline Boston Colonial manufacturin g was restricted so it would not compete with the expanding industry of GB Affected ALL Americans created more tension between the colonists and the British met slight protest from the colonists, effected all the colonies by the Boston Port Act which closed Boston Harbor until damages were paid Stamps not expensive rather, set precedent Sparked upset in VA House of Burgesses, Patrick Henry lead to the American Revolution Tea Act NOT to regulate trade btw America & GB repealed in 1770, except for the tax on tea. tax on tea was kept to keep alive the principle of Parliamentary taxation. Led to First Continental Congress Chapter 4 People/Groups Name: Benjamin Franklin Charles Townshend Committees of Correspondence Significance: Proposed the Albany Plan to unify the states Control of the British ministry; nicknamed "Champagne Charley" for his brilliant speeches in Parliament while drunk; Daughters of Liberty First Continental Congress George Grenville American's resp. to Intolerable Acts; redressed colonial grievances; all colonies - GA; JA persuaded toward rev; wrote Declaration of Rights; called for boycott of English goods British Prime Minister from 1763-1765; delegate to Constitutional Convention crucial in drafting Constitution persuaded Parliament in 1767 to pass the Townshend Acts Samuel Adams started in Boston 1772 to spread propaganda; used to oppose British policy; extremely effective almost every colony had one; example of the colonies breaking from Europe to bc American Name: Lord North Patrick Henry Samuel Adams Sons of Liberty Stamp Act Congress 1765 William Pitt Significance: George III's stout prime minister (governor during Boston Tea Party) in the 1770's. lawyer during Rev "give me liberty, or give me death!" propagandist and an engineer of rebellion; strong politician and leader that was very aware and sensitive to the rights of the colonists; organized the local committees of correspondence in MA, starting with Boston in 1772 organization est. in 1765; met in NYC w/ 27 delegates from 9 colonies; helped toward colonial unity; caused an uprising bc there was no one to sell the stamps/ British did not understand why Americans could not pay for their own defense; act repealed in 1766 British leader from 1757-1758; Rev War served as ambassador to France Lord North's rule fell in March of 1782, which therefore ended the rule of George III for a short while. served two terms as governor of VA instrumental in the development of the Bill of Rights members resisted the Stamp Act of 1765. combined with the Daughters of Liberty remained active in resistance movements. ordered the Navy to enforce the Navigation Laws; got Parliament to pass the Sugar Act; brought about the Quartering Act leader in the London government; "Organizer of Victory"; won a war against Quebec. Pittsburgh was named after him Legislation Year Sugar Act 1764 - Placed duty on imported sugar, greater regulation to suppress smuggling. - goal: Eliminate the illegal sugar trade btw the colonies, the French, and the Spanish West Indies - Strengthened the enforcement of the duty on sugar - lowered the duty on molasses - Damaged the market for sugar grown in the colonies - Est. new admiralty courts in America to try accused smugglers - Mainly affected merchants Stamp Act 1765 Declaratory Act 1766 Asserted authority of Parliament to make laws for colonies “in all cases, whatsoever.” Townshend Acts 1767 Import duties on lead, glass, paper, and tea; Repealed 1770 Tea Act 1773 Gave East India Company total monopoly on all tea imports to America Intolerable Acts 1774 Called “Coercive Acts” by Parliament Boston Port Bill Closed the Port of Boston Massachusetts Government Act Annulled the Massachusetts colonial charter, ending self-rule in the colony of Massachusetts Administration of Justice Act Protected British officials from colonial courts by sending them home for trial if arrested Quartering Act Legalized housing of British troops in private homes Quebec Act Created highly centralized government in Canada