It's a Gas (2) - Sayers-ONeill

Graphing Relationships
Learning Check
Write in your spiral whether the following slides show direct or inverse relationships.
Graph 1
Height of mountain
Graph 2
Minutes of cardiac activity
Word Problem
The more trees that are cut down in a forest, the fewer the number of animals that can live there.
Number of trees cut down increases
Number of animals decreases
Inverse relationship
Inverse Relationships
As one variable increases, the other decreases .
Inverse relationship
Height of mountain
Direct Relationship
As one increases, the other increases
Direct relationship
Minutes of cardiac activity
Gases have mass.
• Gases seem to be weightless, but they are classified as matter, which means they have mass.
• The density of a gas – the mass per unit of volume – is much less than the density of a liquid or solid, however
.
Gases have mass
.
It’s this very low density that allows us to be able to walk through the room without concerning ourselves with air resistance.
Since it is so easy to “swim” across the room we don’t put much thought into the mass of a gas.
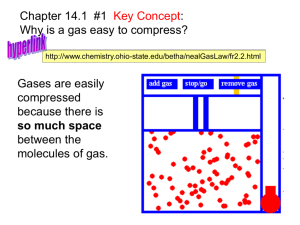
Gases can be compressed
A gases low density means there to is a lot of empty space between gas molecules
If you squeeze a gas
(increase pressure), its volume can be reduced considerably
Engine
We can use this ability of a gas to do work for us.
Think of a shocks on a car. You really are riding on a pillow of air.
A bump in the road compresses the gas in the shocks until the bump’s energy is absorbed.
Gases fill their containers
Gases expand until they take up as much room as they possibly can.
Gases spread out to fill containers until the concentration of gases is uniform
(the same) throughout the entire space.
This is why that nowhere around you is there an absence of air.
Gas particles are in constant random motion.
Gas particles move in a straight line until they collide with other particles or the sides of the container, which causes them to change directions until they collide with something else.
This bouncing off of everything around them spread the particles out until they are uniform throughout the entire container.
Motion states of matter
Gases diffuse
If I opened up a bag of popcorn in front of the class you would soon be able to smell it in the back.
The popcorn smell is a high energy molecule or group of molecules that is in the gas state.
Gases diffuse
Gases can move through each other rapidly.
The movement of one substance through another is called diffusion .
Because of all of the empty space between gas molecules, another gas molecule can pass between them until each gas is spread out over the entire container.
Diffusion
Why do gases diffuse?
Ordered systems have low entropy (S) – the more order, the lower a system’s entropy;
Disordered systems have high entropy – the more disorder, the higher system’s entropy.
Change in entropy is shown by ΔS.
ΔS = S before
– S after
S ice
< S water
< S steam
Why do gases diffuse?
The Second Law of Thermodynamics says that changes leading to greater disorder are favored over changes that produce greater order.
So if there are no other influences in any spontaneous change, entropy increases.
Quantuum Casino
Gases diffuse
Gas molecules are in constant random motion; they will mix with other gases uniformly (evenly).
Some gases diffuse faster then other gases based on their size and their energy.
Diffusion explains why we can all breath oxygen anywhere in the room.
It also helps us minimize potential odoriferous problems.
Effusion
Gases effuse
Gases can move through very small spaces in “solid” surfaces. This is called effusion.
Latex balloons have small microscopic holes in them. Invisible to the human eye, but 1000 times larger than Helium atoms. The Helium atoms can escape relatively easily.
Why do Mylar balloons stay inflated longer?
Effusion
Gases effuse
Graham’s Law of Effusion states that the rate at which a gas effuses (or diffuses) is inversely proportional to its molar mass.
Translation: Bigger molecules move more slowly.
ν = speed m = molar mass
Learning Check
What are the values for STP?
1 atm pressure; 0°Celsius
If 142 grams of chlorine gas are in an expandable container, what volume will be occupied by the gas? 44.8 liters
Which is a possible density value for a gas?
1.380 g/ml 1.43 g/L 19.3 g/ml
Learning Check
How much faster will hydrogen travel than oxygen?
Call hydrogen gas 1 and oxygen gas 2.
Molar mass of H
2
Molar mass of O
2 is 2grams/mole is 32 grams/mole
Velocity H
2
Velocity O
2
= 32 = 4
2
Hydrogen moves four times faster then oxygen
Learning Check
When you pass by a pizza place and smell the pizza, what is this an example of?
Diffusion
What property of gas is the reason you should check the firmness of an air raft before setting out onto a lake or pool?
Effusion
Gases exert pressure
Gas particles exert pressure by colliding with objects in their path.
The sum of all of the collisions makes up the pressure the gas exerts.
Imagine a gas in a container as a room of hard rubber balls.
The collisions of the balls bouncing around exert a force on the object that with which they collide.
The definition of a pressure is a force per unit area – so the total of all of the tiny collisions makes up the pressure exerted by the gas.
The gases push against the walls of their containers with a force.
The pressure of gases is what keeps our tires inflated, makes our basketballs bounce, makes hairspray come out of the can, etc.
Kinetic Molecular Theory
A theory used to explain the behaviors and characteristics of gases.
KMT Assumptions
1) A gas is made up of many small particles that move constantly and randomly in straight lines.
2) The molecules in a gas occupy no volume.
3) When gas molecules collide, they don’t lose energy due to friction or gain energy either.
4) Gas molecules are not attracted to each other at all.
5) The kinetic energy of gas molecules depends only on the temperature of the gas.
KMT Assumptions
Ideal gases would be exactly like the description on the previous slide. It is useful to use them as a model.
However, they do not actually exist.
Real gases :
1) really are small, constantly moving particles
2) but, the molecules do have some volume
3) and, they do lose energy due to friction in collisions
4) and, they are slightly attracted to each other
5) their energy is really only dependent on temperature
If a Real gas is at a high temperature and low pressure, it behaves very much like an Ideal gas .
Ideal Gas
At high temperatures, the molecules have a lot of energy – hard to notice really small losses and they can escape any attraction to another molecule.
At low pressures, the molecules are not forced close to each other
– so volume doesn’t matter and they are not close enough to be attracted very much to each other.
Real Gas
Gas Variables
The amount (moles not volume) of a gas.
The volume (in liters).
The pressure
The temperature
Amount (n)
The quantity of gas in a given sample is expressed as moles of gas.
1 mole = molar mass = 6.02 x 10 23 molecules
Volume
The volume of the gas is simply the volume of the container it is contained in.
The metric unit of volume is the liter (L)
Pressure
The pressure of a gas is the force exerted on the wall of the container a gas is trapped in.
There are several units for pressure depending on the instrument used to measure it including:
Atmospheres, kiloPascals, and millimeters of Mercury
Pressure Units
Atmospheres – atm kiloPascals – kPa millimeters of Mercury – mm Hg
1 atm = 101.3 kPa = 760 mm Hg
Temperature
The temperature of a gas is generally measured with a thermometer in Celsius.
All calculations involving gases should be made after converting the Celsius to
Kelvin temperature .
Kelvin = C° + 273
Gas Laws
Combined Gas Law
PV nT
PV nT
The four gas variables are related through this equation.
Boyle’s Law
Pressure and Volume
Robert Boyle determined the relationship between pressure and volume of a gas.
Moles of gas and temperature of the system were kept constant
What happens to the air in a bicycle pump if you push down?
As the pressure increases
Volume decreases
Boyle’s Law
PV nT
PV nT
Moles and temperature were kept constant during the experiment.
How do Pressure and Volume of gases relate graphically?
Inverse relationship
PV = k
Pressure
Guy Lussac’s Law
Pressure and Temperature
Guy Lussac determined the relationship between temperature and pressure of a gas.
Moles and volume were kept constant during the experiments.
What happens if you heat up the gas in a closed container?
Today’s temp: 35°F
Pressure
Gauge
Today’s temp: 85°F
Guy Lussac’s Law
Pressure and Temperature
PV nT
PV nT
Moles (n) and volume are constant
The pressure increases when temperature increases because the molecules are moving with greater speed and colliding against the sides of their containers more often.
Therefore, the pressure inside that container is greater, because there are more collisions.
How do Pressure and Temperature of gases relate graphically?
P/T = k
Temp
Charles’s Law
Jacques Charles determined the relationship between temperature and volume of a gas.
During his experiments pressure of the system and amount of gas were held constant.
If you have a balloon that is beginning to deflate, what would happen if you put it in a hot car?
Volume of balloon at room temperature
Volume of balloon at 5°C
Charles’s Law
Volume and Temperature
PV nT
PV nT
Moles (n) and pressure are constant
How do Temperature and Volume of gases relate graphically?
Direct relationship
V/T = k
Temp
Ideal Gas Law
PV nT
PV nT
At STP, 1 mole of gas will take up 22.4 L of the volume of the container
Ideal Gas Law
(1atm)
(22.4L)
(1mole) (273K)
PV n T
Substitute these values for one side of the equation.
Ideal Gas Law
R 0.082
atm ∙L mole∙K
PV nT
Calculate; this is the Gas Constant.
Take a careful look at the units.
Ideal Gas Law
PV n R T
Rearrange. This is the form most commonly used. Use the Ideal Gas
Equation to solve a problem when the amount (moles)of gas is given
Dalton's Law of Partial
Pressures
At constant volume and temp., the total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures.
P total
= P
1
+ P
2
+ P
3
......