Osmosis Lab
advertisement

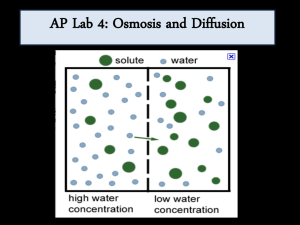
OSMOSIS LAB Osmosis: the movement of water molecules from a region of lower solute concentration to a region of higher solute concentration. SOLUTION CONCENTRATIONS: Isotonic: two solutions have the same concentration of solutes. (iso- same, toncondition, -ic pertaining to) Two solutions of different concentration: The one with more solute is hypertonic to the solution with less solute. (hyper- more than) The solution that has less solute is hypotonic to the one with more solute. (hypo- less than) Semi-permeable membrane IN WHAT DIRECTION WILL NET H2O MOVEMENT OCCUR? SET UP: Six dialysis tubing bags are filled with (15-25mL) six solutions of differing sucrose concentrations and placed in beakers of distilled water. 0M 0.2M 0.4M 0.6M 0.8M 1.0M Sucrose solution Distilled water Reminder: Molarity (M) = mol/L ex. 1 mole of sucrose per liter of water = 1.0M RQ: HOW DOES THE MOLARITY OF A SOLUTION EFFECT THE RATE OF OSMOSIS THROUGH A SEMI PERMEABLE MEMBRANE? Independent Variable: Dependent Variable: PREDICTIONS? Change Initial Final Contents in Dialysis Bag in Mass Mass (g) Mass (g) (g) a) 0M (distilled water) 26.0 b) 0.2M sucrose 26.2 c) 0.4M sucrose 26.1 d) 0.6M sucrose 26.4 e) 0.8M sucrose 26.3 f) 1.0M sucrose 26.4 RESULTS: Contents in Dialysis Bag Initial Final Mass Change in Mass (g) (g) Mass (g) a) 0M (distilled water) 26.0 26.3 0.3 b) 0.2M sucrose 26.2 27.0 0.8 c) 0.4M sucrose 26.1 28.1 2.0 d) 0.6M sucrose 26.4 29.3 2.9 e) 0.8M sucrose 26.3 30.2 3.9 f) 1.0M sucrose 26.4 31.2 4.8 Explain the relationship between the change in mass and the molarity of sucrose within the dialysis tubing bag. RELATIONSHIP? Change in Mass vs. Molarity 6.0 Change in mass (g) 5.0 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 0.0 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 Molarity (M) Predict what would happen to the mass of each bag in this experiment if all the bags were placed in a 0.4M solution instead of distilled water.