document
advertisement
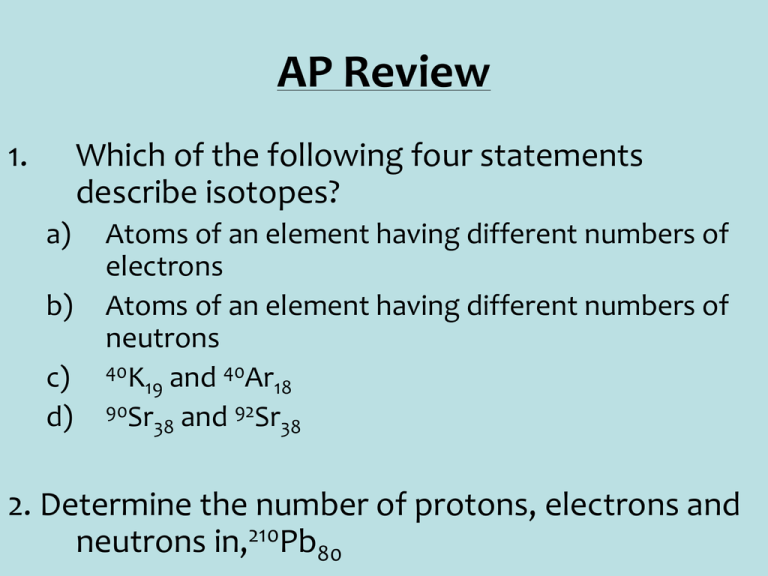
AP Review 1. Which of the following four statements describe isotopes? a) b) c) d) Atoms of an element having different numbers of electrons Atoms of an element having different numbers of neutrons 40K and 40Ar 19 18 90Sr and 92Sr 38 38 2. Determine the number of protons, electrons and neutrons in,210Pb80 AP Review 3. Neon has three isotopes of masses 22, 21 and 20. If the isotopes have the abundance 8%, 2% and 90% respectively, what is the average relative atomic mass of neon? Review 4. What are the formulae for the following ionic compounds? a) b) c) d) e) f) Ammonium nitrate Copper (II) bromide Copper (I) bromide Zinc hydrogensulfate Aluminum sulfate Sodium perchlorate Review 5. Write formula or names for the following molecular compounds. a) b) c) d) e) Dinitrogen tetroxide N2O5 PCl3 Phosphorous pentachloride SF6 Review 6. Write the electronic configuration of the following elements using the noble gas core method. a) b) Cu Ca 2+ Review 7. A hydrocarbon (a compound containing only hydrogen and carbon) has the following composition by mass, hydrogen 7.69% and Carbon 92.31%. Calculate its empirical formula. 8. The same compound as in question 7 has a molar mass (RMM) of 26, what is the molecular formula? Review 9. A 8.512g sample of copper (II) sulfate pentahydrate is dissolved in 500mL of water. A 25mL portion completely reacts with 20cm3 of a 0.1702 M solution of iodide ions. In what ratio do Cu2+ and lreact? 10. Calculate the molality of a sulfuric acid solution containing 48.8 g of sulfuric acid in 1980 g of water. 11. Calculate the volume of 3.25M nitric acid that must be diluted with water to produce 500mL of 1.25M nitric acid. Review • 12. When caffeic acid is analyzed by combustion analysis, a 0.300 g sample produces 0.6595 g CO2 and 0.1200 g H2O. Caffeic acid contains only carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. What is the empirical formula of caffeic acid? • 13. Nitrobenzene contains C, H, N and O. A 0.286 g sample gives 0.614 g CO2 and 0.105 g H2O when combusted. In another experiment, 0.358 g sample of nitrobenzene yields 0.0495g of NH3. What is the molecular formula of nitrobenzene? (Assume RMM of nitrobenzene is 123 g/mol and in the second experiment all nitrogen present in the nitrobenzene is converted to NH3). Review 14. Samples of the following hydrates are weighed, heated to drive off the water of crystallization, cooled and reweighed until constant mass is achieved. Calculate the values of a-c. a) 8.69g of CuSO4.aH2O left a residue of 5.56g b) 11.73g of CoCl2.bH2O left a residue of 6.41g c) 18.86g of CaSO4.cH2O left a residue of 14.92g Review 15. 5.9g of aspirin, C9H8O4, are made from 5.0g of 2-hydroxybenzoic acid, C7H6O3, and 7.5g of ethanoic anhydride, C4H6O3. The reactants react in a 1:1 ratio to form 1 mole of aspirin. Calculate the percentage yield of aspirin. Review • 16. Predict if a reaction takes place between the following solutions. If it does, write a net ionic equation for the reaction. • LiOH(aq) + MgCl2(aq) • BaS(aq) + NiSO4(aq) • (NH4)2SO4(aq) + ZnCl2(aq) • AlCl3(aq) + NaOH(aq) Review 17. What is the oxidation number of each of the atoms listed in the following species? a) b) c) d) e) Carbon in CO2 Oxygen in NaO2 Nitrogen in NH4+ Barium in BaF2 Aluminum in AlF63- Review 18. Write half-equations for the following redox reactions and use them to balance the full equations. • IO3- + I- I2 Review 19. 3.335g of iodine and some potassium iodide were dissolved in 200cm3 of water. (The iodide ions are there simply to help the iodine dissolve—they are not involved in the reaction at all). A 20.0 cm3 portion of this solution is reacted with 17.7 cm3 of sodium thiosulfate solution. Calculate the concentration of the thiosulfate solution. 2Na2S2O3(aq) + I2(aq) 2NaI(aq) + Na2S4O6(aq) Review 20. Consider the following successive ionization energies (kJ/mol) of element X. 1st 737 2nd 1450 3rd 7732 4th 10540 5th 13360 6th 17995 What is the most likely formula of X's chloride? Why is the value for the 2nd ionization energy greater than the 1st? Review 21.Arrange the following species in order of increasing size. Ar, K+, Ca2+, S2-, Cl- Review 22. Draw Lewis structures clearly indicating the arrangement of outer electrons, the overall shape and the bond angles of the following species: • PCl6• ICl3 • BrF5 Review 23. Calculate the standard enthalpy change in the reaction below, given the standard enthalpies of formation of lead (II) oxide, carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide are -219, -111 and -394kJmol-1, respectively. PbO(s) + CO(g) Pb(s) + CO2(g) Review 24. Use Bond energies to calculate the standard enthalpy of the reaction CH2=CH2 + H2 CH3CH3 25. 7.82g of compound Y in 299g of benzene causes its freezing point to drop by 1.05ºC. What is the RMM of Y given Kf for benzene = 5.12ºC/m? 26. At 25ºC the osmotic pressure of a 0.01M solution of a compound is 0.466atm. Calculate the van't Hoff factor.



![[1] , ramegowda.rb [2] , phani konide](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007232622_1-484c205d524e137367bdbb76b981f60c-300x300.png)