Liver, Biliary Tract, & Pancreas Problems

Liver, Biliary Tract, & Pancreas Problems
Nur 302 Unit I
Liver, Biliary Tract & Pancreas Problems
Jaundice Hemolytic jaundice Hepatocellular Jaundice Obstructive jaundice
Viral Hepatitis
Inflammation of the liver.
Types: A,B,C,D,E,G Epstein-Barr, herpes, cytomegalovirus, coxsackievirus, rubella Presence of antigens & antibodies Outbreaks of hepatitis – type A, 50% type B, 20% type C, 30% type A
Hepatitis A
Fecal-oral route, outbreaks caused by fecal contaminated food or drinking water.
Crowded conditions, poor sanitation & hygiene, undeveloped countries, shellfish from contaminated water Most infectious 2 wks before s/s & 1wk after s/s start.
No chronic carrier
Hepatitis B
Percutaneous, permucosal, or perinatal exposure, sexually transmitted disease.
100X more infectious than HIV; can live on dry surface for 7 days Carrier state - antigen HBsAg for 6-12 mo.
Immunity – antigen anti-HBs-Ag
Hepatitis C
Transmission- pericutaneous At risk: IV drugs, bld transfusion, hemodialysis, tattooing, hi risk sexual behavior, organ transplants, health care workers
Hepatitis D
Delta virus Transmission - percutaneous Can turn mild or chronic hepB into severe, chronic, progressive, active hepatitis & cirrhosis Can occur as coinfection with hepB or as superinfection
Hepatitis E
Transmission – fecal-oral route, esp contaminated drinking water.
Enteric non-A, non-B hepatitis Occurs in developing countries, epidemics in India, Asia, Mexico, Africa. In US rarely, only after a person traveled.
Hepatitis G
Recently discovered.
Found in blood donors & transmitted by transfusion.
Co-exists with other hepatitis viruses.
Not associated with chronic hepatitis or cirrhosis.
Pathophysiology
Inflammation of liver -> Cell degeneration & necrosis Proliferation & enlargement of Kupffer cells Interrupted flow of bile & cholestasis If no complications, liver cells regenerate, resume normal appearance & function.
Rash, angioedema, arthritis, fever, malaise
Collaborative Care
Rest, well balanced diet Antiemetics, Benadryl, NO phenothiazines Immunoglobulin for hepB or hepA Alpha inferon wks after exposure, hepA vaccine –pre exposure prophylaxis HepB vaccine prophylaxis, post exposure hepatitis B immune globulin
Nursing Care: Hepatitis
Health Promotion Assessment of jaundice Adequate nutrition Rest Home Care
Toxic, Drug-induced & Idiopathic Hepatitis
Ingestion, inhalation, parenteral injection of chemicals Systemic poisons- carbon tetrachloride, gold compounds, converted toxic metabolites (acetaminophen) Drugs – Halothane, INH, Diuril, Aldomet Elderly, previous liver diseased Idiopathic - autoimmune
Cirrhosis of the Liver
Degeneration & destruction of liver cells Abnormal bld vessel & bile duct relationships from fibrosis Lobules of irreg size & shape & impeded bld flow from overgrowth of new & fibrous tissue Insidious, progressive, chronic disease
Types of Cirrhosis
Alcoholic, portal or nutritional cirrhosis: fat accumulation in liver cells, scar formation.
Post necrotic- re: hepatitis, broad bands scar tissue.
Biliary: due to chronic biliary obstruction or infection. Jaundice, diffuse fibrosis.
Cardiac: R heart failure, constrictive pericarditis, tricuspid insufficiency Cell necrosis, scar tissue, nodules, decr cellular nutrition, hypoxia-> decreased functioning of liver
Clinical Manifestations
Insidious- anorexia, dyspepsia, n/v, flatulence, diarrhea or constipation, dull, heavy feeling in RUQ, enl liver & spleen Jaundice Skin lesions – spider angiomas, palmer erythema Hematologic – thrombocytopenia, anemia, leukopenia, coagulation disorders Endocrine disturbances – hormone inactivation Peripheral neuropathy – deficiency in folic
Diagnostic Studies
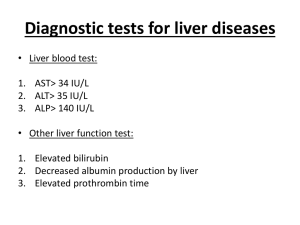
Liver enzymes elevated, PT prolonged Cholesterol & Protein levels decreased Serum & urine bilirubin increased, stool decreased Liver scan,biopsy, analysis of ascitic fluid Esophagogastroduodenoscopy, angiogram Lytes, CBC, ammonia level
Peripheral Edema & Ascites
Peripheral edema @ ankle & presacral area decr. albumin -> decr colloidal osmotic pressure. Increased portalcaval pressure from portal hypertension.
Ascites- hypertension in liver->proteins move bld via capillaries to lymph->leak into peritoneal cavity-> osmotic pres pulls water. Lo albumin & hyperaldosteronism adds to ascites formation.
S/S- abd distention, wt gain, distended abd wall veins, dehydration, decr output, hypokalemia.
Collaborative Care
Na restriction: 250-500mg Na/day Salt poor albumin Diuretics: Aldactone, Dyrenium, Midamor, Lasix Fluid removal via paracentesis or retroperitoneal shunt Monitor lytes and fluid balance
Portal Hypertension & Esophageal Varices
Compression, destruction of hepatic & portal veins & sinusoids-> obstruction portal bld flow-> portal hypertension.
Collateral circulation – lower esophagus, parietal peritoneum, rectum-> varices where collateral & systemic circulation meet.
Esophageal varices, fragile, tolerate hi pressure poorly, tortuous, bleed easily. Life threatening complication.
Hepatic Encephalopathy
Ammonia in systemic circulation without liver detoxification.
Ammonia from metabolism of P shunted past liver or liver unable to convert ammonia to urea-> lg amt ammonia-> crosses blood-brain barrier->neuro s/s S/S: LOC changes from lethargy to coma, disorientation, asterixis, writing impairments, hyperventilation, hypothermia, grimacing, grasping, fetor hepaticus
Collaborative Care
Protein restriction Neomycin po or enemas Lactulose (Cephalac) Control GI blding, remove bld from intestinal tract, treat lyte & acid/base imbalance Liver transplant
Nursing Care: Encephalopathy
Neuro assessment q2h - LOC, reflexes, pupils, sensory & motor Check lytes, acid/base balance, ammonia Decrease ammonia with lactulose, enemas Possible tube feeding- lo-no protein, hi CHO & flds
Hepatorenal Syndrome
Renal failure- possibly due to redistribution of blood flow from kidneys or hypovolemia Follows diuretic therapy, GI hemorrhage or paracentesis Tx: salt poor albumin, salt & water restrictions, diuretic therapy
Nursing Care: Cirrhosis
Health Promotion Bed rest & prevent complications Nutrition- oral hygiene, supplements Assess: jaundice, edema, ascites, bleeding, LOC, dyspnea Skin care Altered body image Monitor lytes, liver & coag studies, ammonia, CBC
Home Care
Written instructions- fluid & diet restrictions Teach pt & family- s/s complications, meds & side effects, observe for bleeding, skin care, protection from infection Counseling & referral to community health nurse
Liver Cancer
Metastasis, h/o cirrhosis, chronic hepB or C Malignant cells enlarge & mis-shape liver Hemorrhage or necrosis common Dx: hard to differentiate bet cirrhosis & Ca Rx: palliative, lobectomy, chemo, poor prognosis, death in 4-7 months Nsg care: same as advanced liver disease
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography
ERCP The scope is brought in through the esophagus, the stomach and into the bile ducts. A contrast fluid is injected. The gallbladder does not become visible. The hepatopancreatic duct does not show signs of obstruction.
Conclusion: No signs of obstruction of the hepatopancreatic duct, obstruction in the gallbladder or the cystic duct cannot be excluded. Nursing Care???
ERCP Nursing Care
Explain procedure & get consent NPO 8 hours before ERCP Sedation before & during ERCP Antibiotics if ordered Post ERCP – check perforation, infection, s/s pancreatitis, VS, check gag reflex
Cholecystitis & Cholelithiasis
S/S cholecystitis: indigestion, moderate-> severe pain, URQ tenderness, referred to R shoulder & scapula, n/v, restless, diaphoretic S/S cholelithiasis: none, s/s depend if stones are moving or not, spasms can be severe, tachycardia, diaphoresis, 3-6 hr after meal, when lie down, s/s bile blockage Dx: ultrasound, cholangiogram, cholecystogram
Collaborative Care
Cholecystitis: control pain, antibiotics, flds Cholelithiasis: cholesterol solvents, lithotripsy, endoscopic sphincterotomy, surgery Surgery: cholecystectomy, laparoscopic cholecystectomy Transhepatic biliary catheter Meds: anticholinergics, analgesics, fat soluble vitamins, bile salts, Demerol, Questran, diet
Nursing Care: GB Disease
Health promotion Acute GB attack: relieve pain, n/v, assessment of progression of s/s & s/s obstruction bile duct, observe s/s bleeding at mucous membranes, assess for infection Post endoscopy; assess s/s pancreatitis, perforation, bleeding Post-op: referred pain to shoulder, place in Simm’s position, prevent resp complications, care of T-tube
Cancer of the Gallbladder
Uncommon Relationship bet Ca GB & chronic cholelithiasis or cholecystitis S/S: insidious, same as GB disease, later s/s biliary obstruction Rx: surgery, symptomatic, supportive Nursing care: supportive, pain relief, skin care, hydration, comfort
Chronic Pancreatitis
Progressive destruction & fibrotic replacement of tissue Chronic obstructive pancreatitis Chronic calcifying pancreatitis S/S: pain, malabsorption with wt loss, jaundice, dark urine, steatorrhea, DM Dx: secretin stimulation test
Collaborative Care
Diet, pancreatic enzyme replacement, control of diabetes Antacids, anticholinergic meds, H2 blockers, bile salts, insulin Surgery if obstruction Nursing Care: health promotion: diet, pancreatic enzymes, diabetic teaching, avoid alcohol, referrals for narcotic or alcohol dependence
Pancreatic Cancer
Over 50% tumors @ head of pancreas-> obstruction of common bile duct->jaundice S/S: pain, rapid wt loss, anorexia, nausea, jaundice Dx: CEA, CA19-9, ultrasound, CT, ERCP-> samples for cytology & biopsy Rx: Whipple’s procedure, radiation, chemo Nursing Care: supportive, comfort, help pt & family grieve