ACCOUNTING
advertisement

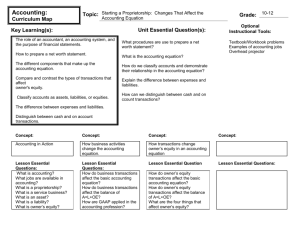
ACCOUNTING Chapter 1 Accounting Terms LESSON 1-1 • The Accounting Equation • What is accounting? – – – – Planning Recording Analyzing Interpreting financial information • The language of business! ACCOUNTING SYSTEM • A planned process for providing financial information that will be useful to management ACCOUNTING RECORDS • Organized summaries of a business’s financial activities FINANCIAL STATEMENTS • Financial reports that summarize the financial condition and operations of a business. • Used by: – Suppliers that are considering extending credit to a business – Institutions that are considering extending loans to a business – Business owners and managers SERVICE BUSINESS • A business that performs an activity for a fee. – Accounting – Doctor – Stylist – Lawn care – Daycare – Car Wash PROPRIETORSHIP • A business owned and controlled by one person – Advantages • Ease of formation • Total control by the owner • Profits that are not shared – Disadvantages • • • • • Limited resources Unlimited liability Limited expertise Limited life Obligation to follow the laws of both the federal government and the state and city in which the business is formed. ASSET • Anything of value that is owned – Cash – Supplies – Accounts Receivable – Prepaid Insurance – Equipment Equities • Financial right to the assets of a business • Two types – Equity of those to whom money is owed – Liabilities – Equity of the owner Liabilities • An amount owed by a business – Accounts payable – Notes payable OWNER’S EQUITY • The amount remaining after the value of all liabilities is subtracted from the value of all assets. ACCOUNTING EQUATION • An equation showing the relationship among assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity. • ASSETS = LIABILITIES + OWNER’S EQUITY • A = L + OE ETHICS • The principles of right and wrong that guide an individual in making decisions. BUSINESS ETHICS • The use of ethics in making business decisions. REVIEW OF 1-1 • What is accounting? • Give two examples of a service business. • What is a proprietorship? • State the accounting equation. LESSON 1-2 • How Business Activities Change the Accounting Equation TRANSACTION • A business activity that changes assets, liabilities, or owner’s equity. • Example – A business pays cash for supplies • After each transaction, the accounting equation must remain in balance. ACCOUNT • A record summarizing all the information pertaining to a single item. ACCOUNT TITLE • The name given to an account. ACCOUNT BALANCE • The amount in an account. CAPITAL • The account uses to summarize the owner’s equity in a business. • The capital account is an owner’s equity account REVIEW OF 1-2 • What must be done if a transaction increases on the left side of the accounting equation? • How can a transaction affect only one side of the accounting equation? • To what does the phrase on account refer? LESSON 1-3 • How Transactions Change Owner’s Equity in an Accounting Equation REVENUE • An increase in owner’s equity resulting from the operation of a business. • Money from a sale. SALE ON ACCOUNT OR A CHARGE SALE • A sale for which cash will be received at a later date. EXPENSE • A decrease in owner’s equity resulting from the operation of a business. – Utilities – Repairs – Miscellaneous – Rent – Salaries WITHDRAWALS • Assets taken out of a business for the owner’s personal use. REVIEW OF 1-3 • How is owner’s equity affected when cash is received from sales? • How is owner’s equity affected when services are sold on account? • How is owner’s equity affected when cash is paid for expenses. GAAP • Generally Accepted Accounting Principles • Why is GAAP necessary? – By requiring the financial statement preparers to consistently follow certain standards and rules such as GAAP, the users are able to compare the financial statements of several companies and to track the results of one company over several time periods. SEC • Security and Exchange Commission – Has the authority to establish GAAP – Allowed a series of private organizations to determine GAAP FASB • Financial Accounting Standards Board – The organization that the SEC has given the authority to set accounting standards. – Established in 1973. ACCOUNTING CONCEPTS FOR CHAPTER 1 • Business Entity – Applied when a business’s financial information is recorded and reported separately from the owner’s personal financial information. • Unit of Measurement – Applied when business transactions are stated in numbers that have common values. – Example – in the US transactions are recorded in dollars. ASSIGNMENT • Applications: – 1-1 – 1-2 – 1-3 – 1-4 – mastery – 1-5 - challenge