CIRC and RESP system BOOKLET - Coristines
advertisement

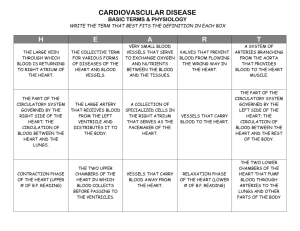
Circulation – Bill Nye the Science Guy 1. Your heart is about as big as your _______________________________________________ 2. How many drums of blood does a heart pump each day? ______________________________ 3. Why does your foot fall asleep when it’s in a weird position for a long time? ______________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 4. What are two kinds of blood cells in your body? _____________________________________ 5. What is the function of white blood cells? __________________________________________ 6. Your body makes _________________________ blood cells every day. 7. White blood cells live for _________________________________________ 8. Red blood cells live for ___________________________________________ 9.Capillaries are so small, they have a unique way of traveling. It is _______________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 10. What is Bill’s blood pressure? ____________________________________________________ 11.How long does it take blood to make a complete trip around your body when you’re watching TV? _____________________________ How about when you’re exercising? ____________________ 12. Where do arteries take your blood? __________________________________________________ 13. Where do veins take your blood? ____________________________________________________ 14.What does blood do for your muscles? ________________________________________________ 15. How does a flight suit (G suit) keep your blood circulating? _______________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ 16. DID YOU KNOW??? Blood cells are made in ____________________________. During your lifetime your heart will beat __________________ times. 17. What color is the girl’s headband? __________________________________________________ 18. The song tells us you blood stream runs through your ___________________________________. 19. What is Bill wearing in the final scene? ______________________________________________ The Circulatory System 1 1) View the introduction video of the circulatory system and take the quiz 2) View the video in Activity 6D to help you fill in the blanks below. ____________________ is an anatomical model. Keith’s ________________ is his cardiac muscle. The ______________ ______________ + ______________= cardiovascular The heart’s job is to _________________________________________________ How many chambers does the heart have ______________? The right side of the heart collects ____________________(oxygenated/deoxygenated) blood in the right ____________and pumps blood using the _____________ out the pulmonary artery where it goes to the _______________ to receive _______________. The left side of the heart receives _________________ (oxygenated/deoxygenated) blood from the left ______________________ which moves it to the left _________________ and is then pumped out the ______________. There are three blood vessels 1) ______________ carry blood away from the _____________ at _________ pressure. 2) ______________ are very ________________ and allow oxygen and nutrients to reach body cells. 3) ______________ carry blood toward the ______________ and have valves so _____________________________. Class note: The purpose of the circulatory system in any organism is to _____________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ The circulatory system is made of _____ parts: 1) Heart – _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 2) ________________ – thick walled blood vessels that carry oxygen rich blood to away to the cells of the body 2 3) Veins_______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 4) ______________ – very thin walled blood vessels that allow cells to get oxygen and nutrients and give up waste. 5) Blood _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _____________________ 3 4 5 6 7 8 Activity 6A – Review the circulatory system by completing the on-line crossword. Show your teacher when you are done. _______ What is Blood? Activity 6B – View the video and answer the questions below: What is blood ? It is a mixture of __________________ floating in a yellowish liquid called _____________________. _________________ is made mostly of _______________ but it also contains _____________, proteins, and ____________. There are three different types of blood cells 1. ___________________________ or erythrocytes 2. ___________________________ or leukocytes 3. ___________________________ or thrombocytes Description Cell type 1 Defend the body against infection Red 2 Shaped like a doughnut white 3 Small pieces of cell material platelet 4 Are red in colour 5 Plug up holes 6 Fight viruses 7 Carry oxygen to the cells of the body 8 Eat invading germs 9 Remove carbon dioxide waste 10 Clot holes but break down after 24 hrs 11 Made in the bone marrow Make a drawing to show what each looks like by using the computer to find a picture. A) 9 erythrocytes or _________________ B) leukocytes or _________________ C) thrombocytes or ________________ 10 11 12 13 14 Donating Blood Can anyone use your blood? Watch the video in Activity# 6C (up to the 4 ½ minutes) on the wiki and answer the questions below. A transfusion is ____________________________________________________________________. 1. What are blood types? They are based on the type of __________________ on the surface of our _____________________________. 2. What are the different blood types in the ABO system? Use the diagrams to help you draw the different antibody types. 3. These types of bloods are important when we move blood from ______________________ to ______________________ because of our immune response. 4. Antibodies are part of our immune system and they are used to fight against diseases. We have antibodies that fight against all kinds of proteins except ___________________________________________. Why? 5. What type of antibody would people with each of the following blood types make? 15 Blood type Antibody (protein) 1 2 3 4 6. If a person were in an accident or needed an operation, they would likely need a blood transfusion. Who could receive blood without being killed by the transfusion? A person with Blood type Could receive blood from a person with type: 1 2 3 4 At about 4:30 min, You are now done viewing this video as it goes on about the genetics of blood typing (we don't need this info). Answer the following questions: 1. Which blood type is called the universal donor? ________________________________ 2. Which blood type is able to receive blood from everyone else? ________________________________ 3. What type of antibodies (attackers) does type A blood make? ________________________________ 4. What type of antibodies does type O blood make? __________________________________________ 16 The Heart Your heart is _______________________________________________ in your body It is hard wired to your _____________________________ so you do not have to __________________ to keep it beating. Like all other muscles it must be fed _________________ and _______________ to keep working. These are delivered to the heart through the ____________________________. If these arteries get ______________ over time, this can cause a _________________________. Bill Nye: “Heart” Video Listening Guide 1. Your heart is a __________________ that is about as big as your ____________________. 2. Your heart has _____________ sides and it has _____________ chambers. 3. ____________________ are structures that keep the blood flowing in one direction. 4. The normal heart beats between ___________________ beats per minute. 5. Exercise makes your heart beat faster because the muscles need more _________________________. 6. In the right side of your heart wall is a patch of nerves called the ______________________ that sends electrical signals to your heart. 7. The muscles in your arms and legs have ______________________ that look like stripes. 8. Heart muscle looks like a combination of ___________________ and ____________________ muscle. 9. You can make your heart muscle stronger by ____________________________. 17 10. When you cut a blood vessel, your body forms a __________________ to prevent blood from leaking out. 11. How is the blood pumped in the body during heart surgery? _____________________________________ 12. When you stand up quickly you sometimes feel “light-headed” because: 13. The kind of fat that is bad for you is __________________________ because it can clog your arteries. 18 Use Activity 6E on the wiki to help you label the parts of the heart on the following diagram. 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 Blood Pressure Go to activity 6G on the wiki Read the graph on blood pressure to answer the following questions. Blood pressure readings are written as fractions of systolic/diastolic 1. Is a blood pressure of 130/60 ideal or pre-high blood pressure? ______________________________ 2. Is a reading of 80/50 good? Explain ___________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 3. What classification would you be given for each of the following blood pressure readings? A) 160/80 _________________ B) 80/50 __________________ C) 90/95 __________________ D) 110/70 _________________ 4. What is the highest systolic pressure a person can have before they are in the high blood pressure category? _______________________ 5. What is the lowest diastolic pressure a person can have before they are in the low blood pressure category? __________________________ 6. What is you classification (go to Shoppers/Sobeys and get you blood pressure read) 27 Use the words in the box to fill in the blanks. veins transport circulatory arteries oxygen lungs nutrients energy carbon dioxide capillaries dark bright away heat to blood heart pumped intestine atmosphere All animals need to ________________ materials around to the different parts of their body. This is the job of the ________________ system. The circulatory system consists of a liquid called _______________, a pump called the ________________ and a series of vessels called _________________ and ________________. One thing that must be transported around is a gas called _____________. Oxygen enters the blood through the ______________. It is then ____________ through the heart and around the body where it is used along with food to make ______________. The body produces another gas called _______________, which is a waste product. This gas is carried back to the heart and then to the lungs where it is released back into the _______________. The vessels that transport blood _________ from the heart are called arteries. The blood in arteries is _____________ red because it is rich in oxygen. The vessels that transport blood _______________ the heart are called veins. The blood in veins is ______________ red because it is low in oxygen. ________________ are small vessels that join the arteries and veins. _______________ from food are also transported around the body by the circulatory system. They enter the blood from the small _________________. The circulatory system also helps to regulate temperature by transporting _________________ around the body. 28 Bill Nye: Introduction to Respiration 1) In your upper body there is a strong muscle called the ________________________. 2) When you inhale, your diaphragm goes ___________________. 3) _____________________ is the same material that makes candles burn and iron rust. 4) We combine the oxygen with our __________________ to get the energy we need to live. 5) Your ____________________ are full of tiny little passageways like sponges. 6) These __________________ ______________________ allow you to take it the oxygen. 7) Your lungs have as much surface area as a ___________________ ________________. 8) ___________________ _________________ is how spread out something is. 9) Your lungs have little passages, little ________________________ called alveoli. 10) Your _______________ lung is bigger than your _____________ ________________. 11) Your right lung is divided into ______ parts, and your left lung is divided into _____ parts. 12) Cellular ______________________ occurs when our cells combine chemicals and food with oxygen to store energy called ATP. 13) Your body uses _________ as a sort of _____________________ _______________. The Respiratory System 29 The purpose of the respiratory system is to exchange used air from inside the body with fresh air from outside the body. Used air contains large amounts of carbon dioxide. The chemical formula is ________. Fresh air contains large amount of oxygen. The chemical formula is ___________. Every cell in the body must undergo _____________________ which is the __________________________________ in the presence of __________________to produce _________________________________________. _________________+ _______________----> _______________ + ___________ How does the respiratory system work? Use activity #7 on the wiki to fill in the blanks below Help Emma to breath! 1. Click on the nose: The purpose of the nose is to do three things. The nose ____________air to remove ___________________. It _______________ the air up and lastly it gives us our sense of _________. 2. The _______________ is a muscular tube that carries ______________ to the __________________ and __________________ to the ________________. 3. The _________________________ is a _____________ shaped flap at the top of the l________________ that covers the top of the voice box so we do not get food into the windpipe. 4. The Larynx is also called the __________________. It sits on top of the __________________ (trachea) and has a thick cartilage backbone called the ___________________ _______________. 5.The _________________ or windpipe takes in ____________________ and delivers it to the _____________. It is held open by rings of ________________. 30 6. Two smaller tubes break off the trachea. These are called ________________. These tubes break up into smaller ___________________ tubes because they look like tree ________________. They deliver ________________ to the bottom of the _______________________. 7. There are grape-like sacs at the end of the bronchial tubes. These sacs are called ____________________________. Their walls are ______________, allowing ___________________ from inhaled air to pass into the blood vessels where it is picked up by _______ _____________ __________. Alveoli also allows _____________ to pass through the thin walls and leave the lungs when you _____________________. Use activity 7B to assist you in labeling the diagram below. Note on Organs of The Respiratory System 31 Structure Description Nose Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli What is the pathway out of the body for a carbon dioxide molecule that must be breathed out? List the structures in order of which the molecule must past through from beginning to end. ___________________--> _____________________--> _____________________--> ___________________--> _____________________--> _____________________ ___________________. How Much Hot Air Do You Hold? 32 Let's test your lung capacity – the amount of air you lungs can hold. Purpose: To compare the lung capacity of males and females. Hypothesis: __________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ Materials: rubber tubbing alcohol water jug Procedure: 1) Measure out 100 mL of water and pour it into an empty water jug. Use a marker to mark the water level. 2) Measure out another 100 mL of water and again pour it into the jug. Mark the new water level as 200. Create a scale on the water jug by continuing this process until it is full. 3) Fill a sink ½ full with water and turn the jug upside down into the sink without spilling the water. 4) Place a rubber hose into the opened mouth of the jug. 5) Get a sterile piece of tubing from your teacher and attach it to the end of the rubber hose. 6) Take a deep breath and blow into the tube to see how much water you can blow out. 7) Read the level from the scale and record in your data chart. 8) Repeat for each member of the group making sure they each get their own sterile tubing. Observations table: Name of Girl Volume of water (L) Average volume of water _______________ Name of Boy 33 Volume of water (L) Average volume of water _______________ 1. Create a bar graph of your average results. 2. Which group had the largest lung capacity? Provide your evidence. __________________________________________________________________ 3. What other comparisons could you make with lung capacity besides males vs females? __________________________________________________________________ 34 35 36 37 Use the words in the box to fill in the blanks. air oxygen inhale lungs trachea respiratory carbon dioxide yawn bronchi hiccup diaphragm water vapor mouth sneeze blood 38 exhale cough pharynx nose All animals need ________________ to make energy from food. We get this oxygen from the _____________ that we breathe. In order to get the oxygen into the blood where it can be transported to the rest of the body, the air travels through a system of organs called the _______________ system. When you ________________, air enters the body through the _______________ or the ____________. From there it passes through the ______________, which forces air into the _______________ and food into the esophagus. The air travels down the trachea into two branching tubes called ________________ and then on into the ________________. In the lungs oxygen from the air enters the _______________. At the same time, the waste gas ____________________ leaves the blood and then leaves the body when you ___________________. Some __________________ also leaves the body when you exhale, which is why mirrors get foggy when you breathe on them. The ______________ is the muscle that controls the lungs. It is important to keep the respiratory system clear so oxygen can keep flowing into your body. If something gets in your nose and irritates it, you ___________________. If something gets in your trachea or bronchi and irritates it, you _________________. If something irritates your diaphragm, you _________________. Finally, if the brain thinks you are not getting enough oxygen, then it forces you to _________________. Research and presentation Assignment Choose a disease/illness from below: Sickle cell anemia, high blood pressure, heart attack, ulcer, irritable bowel syndrome, Crohn's disease, Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) , diverticulitis, lactose intolerance, atherosclerosis 1. Describe the symptoms of the disease (how would a person know they had this sickness?) 39 2. Describe what has gone wrong with the body as a result of this disease. What would the body normally be doing and what is the disease causing it to do instead? 3. What organs does this disease affect? You must have a diagram that labels every organ affected. 4. Can the disease kill you? 5. What is the treatment for the disease? Dissection of the Rat Rats belong to the class Mammalia. Rats are among the most commonly studied organisms in biology. Although many differences exist between humans and rats, the basic body plans are similar. Humans and rats both belong to the class Mammalia. By studying the anatomy of the rat, you will be better able to understand your own body. The outside of the rat: 40 Look at your rat and observe the general characteristics. 1. The rat's body is divided into six regions: Find each on your rat and stick a labeled pin at each location. Your teacher will check your accuracy. 1) head 2) neck 3) pectoral region - area where front legs attach 4) thoracic region - chest area 5) abdomen - belly 6) pelvic region - area where the back legs attach 7) also label the following with pins i) the vibrissae (sensory hairs or whiskers) located on the rat's face. ii) The incisors iii) The nictitating membrane found at the inside corner of the eye. This membrane can be drawn across the eye for protection. iv) The pinna (ear flaps) v) Nares - Paired openings leading into the nose; the nostrils. vi) The anus Your Mark _______ 12 2. Place all of the above labels on the diagram below as well. 1. How many digits do the forepaws have? _____ 2. How many digits do the hind paws have? _____ 3. Is your rat a male or female? (Females will have 3 sets of nipples for feeding young offspring.) Males will not. Internal Rat Investigation 1. You must now cut the rat open. Use scissors and gently poke the lower edge through the skin and muscle of the rat near its mouth. Make cut # 1 (the long cut, 41 as seen in the diagram from head to tail). Keep the cut shallow by pulling up on the bottom edge. This will prevent hurting the organs below. 2. Make three cuts perpendicular to the first. Cut # 2 from ear to ear Cut #3 below the arms Cut #4 at the back legs 3. Pull back the skin between cuts 3 and 4 as if you were opening a book. Draw what the muscles look like in the space below: 4. Examine the rats tongue. Describe the surface of it. _____________________________________________________________ 5. Open up the thoracic cavity (upper chest). Using a probe, stick it into the mouth until you can see it in the esophagus. Label the esophagus 6. Find and label the liver. How many sections does the liver have?__________. 7. Trace the esophagus until it reaches the stomach. Cut the stomach open lengthwise and open it up. Clean out anything in it. What food might it have been? ________________________________________________________________ 42 ____Look at the intestine walls. Describe what you see. ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________ What happens in the stomach? ___________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ____ Label the stomach. 8. Gently tease apart the small intestine. Using a ruler measure its length in centimeters. How long is it? _________________. Make a lengthwise cut along a section of the small intestine so you can look inside. Describe what the inside wall looks like. ________________________________________________________________ ____ Label the small intestine 9. Measure the length of the large intestine. How long is it? ______________ There are two sections to the colon. The ascending (goes up), transverse (goes across), the descending part is the rectum. Label these three on the rat 10. Find and label the pancrease. Your teacher will come around and mark your dissection and labels up to this point Your mark = __________ 13 Respiratory systems The heart is in the thoracic cavity under cuts #2-#3. You will need to open these up like a book and pin them back. 1. Look for the tube that has cartilage rings connected to the back of the mouth. This is the Trachea – Label it on your rat. Why does the trachea have rings? _____________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ___ 43 2. The Larynx – is the voice box at the top of the trachea; it contains the vocal cord. Label this on the rat. How is sound made? ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ________ 3. Follow the trachea down to where it branches into two smaller tubes. Each one is a Bronchus – Do these still have cartilage? ____________________________ Label the bronchus. 4. Each bronchus leads to a Lung - spongy structures located in the thoracic cavity. The right lung consists of ________ (how many lobes or sections?), whereas the left has ______ lobes. Label the lung on your rat. 5. The Diaphragm - A thin muscular sheet, seen earlier, that separates the abdominal and thoracic cavities. It draws air into the lungs. Label the diaphragm. The Circulatory System The Pericardium -is a tough membrane that forms a sac around the heart. You must gently cut through it to get to the heart. Pull up with the tweezers and cut with the scissors 1. The right and left Atria - are visible as dark flaps on top of the heart. Label them What is the purpose of the atrium? ________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 2. Ventricles – Cut open the bottom of the heart. How many chambers are present? _____ What is the purpose of the ventricles? _________________________________________. ______________________________________________________________________ __ Label the ventricle. 3. Coronary vessels - Arteries and veins supplying the heart are visible on its surface. Label the coronary vessels. Your teacher will mark your dissection of the Respiratory and Circulatory system. Your mark = __________ 9 44 45 46