Bond Energies - The Ossett Academy Website
advertisement

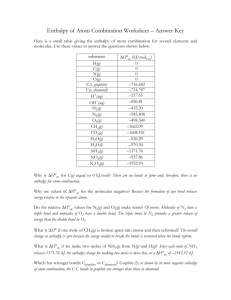
Year 11 Taster day – Chemistry A-Level homework task Bond Energies Objective: That bond energies can be used to calculate energy changes in a reaction. Success Criteria: All students should be able to: State a definition of bond energy. Most students should be able to: Use a data table to get a bond energy Some students should also be able to: Calculate the energy transferred in reactions using supplied bond energies During the Chemistry session at Ossett Academy, you carried out a practical to find the enthalpy change of a reaction, complete the following worksheet. Test yourself on the key ideas Aim To help you to understand the ideas and conventions that underlie bond energy calculations. 1 When you use mains gas for cooking or heating, you are using methane, CH4. Here is the equation for burning methane: CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O ΔH = 890 kJ a) Which substances are the reactants? b) Is this reaction exothermic or endothermic? c) What is the sign for ΔH? d) If you burn 1 mole of methane, how many moles of i) CO2 ii) H2O are produced? 2 When completed, the diagram should show molecules being broken up and put together. Complete both the diagram and the key. You will need to fill in all the blank key cells. Key to diagram Pictogram Meaning Pictogram Meaning 3 Complete and label the energy diagram. Energy of the reactants Before reaction 4 After the reaction Complete the equation using structural formulae. H H C H + 2 O=O H 5 Complete the following table. Bond breaking Bond making Bond Number Bond energy ΔH (kJ) Bond Number Bond energy ΔH (kJ) C–H 4 413 kJ +1652 C=O 2 805 kJ –1610 O=O 2 498 kJ + 0000 O–H Total ΔH = 464 kJ Total Answer the following exam question, you will have to look up the structure of some of the compounds in order to work out the enthalpy. 1. (a) Use the bond enthalpy data provided below to work out an enthalpy change for the reaction in the equation below. 2H2S(g) 3O2(g) 2SO2(g) 2H2O(g) f) bond enthalpy/kJ mol–1 e) bond g) H–S h) 364 i) S=O j) 525 k) SO l) 265 m) H–O n) 464 o) O=O p) 498 Clearly lay out all your working using the grid below. bonds broken enthalpy change total for breaking bonds overall enthalpy change/kJ mol–1 bonds formed enthalpy change total for forming new bonds