Reframing Project Presentation
advertisement

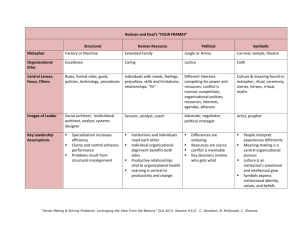
REFRAMING PROJECT Sara Mills EDSE 843 Spring 2008 Human Resources Frame “The key challenge is to tailor organizations to individuals – to find a way for people to get the job done while feeling good about what they are doing.” (Bolman and Deal, 2003, p. 14) Addressing the Need Argyris and Schon’s Theories for Action – Model II Assumptions: 1. 2. 3. Emphasize common goals and mutual influence. Communicate openly, and publicly test assumptions and beliefs. Combine advocacy with inquiry. (in Bolman and Deal, 2003, pg. 163-168) Addressing the Need Fullan’s (2001) focus on “Relationships, relationships, relationships”: Leadership in schools must be instructional leadership Collaborative cultures are powerful, but must be focused on right things Effective leaders have emotional intelligence Appreciating resistance Making the Change Bolman and Deal (2003) highlight importance of investing in employees by creating a learning organization, which requires: 1. Good mentors who teach others, 2. Management system that allows people to try new things, and 3. Good exchange with the environment. Making the Change Knowledge Building (Fullan, 2001) • Sharing local knowledge – converting tacit knowledge to explicit knowledge in the local context so that it is specific and useable • Two interrelated responsibilities of a “caring expert”: – – Reaching level of personal mastery in tacit and explicit knowledge, and Understands that she is responsible for sharing it (Van Krogh et al., 2000, in Fullan) Structural Frame “If employees are unclear about what they are supposed to be doing, they often shape their role around personal preferences instead of organizational goals, frequently leading to problems.” (Bolman and Deal, 2003, pg. 70) Structure of the School Central Office technostructure Schoolbased Admin Support staff Teachers “Lateral communication works best when a complex task is performed in a turbulent, fast-changing environment.” (Bolman and Deal, 2003, pg. 56). Structure of the Team Regular Education Special Education Structure of the Team Regular Education Third Grade Team Special Education New Learning Responsibility charting – “a social contract among members that relates to their purposes and guides and obligates how they will work together” (Katzenback and Smith, 1993, in Bolman and Deal, 2003, pg. 106) Move toward idea of “commando team”, where structure varies in response to changes in tasks and circumstances. Political Frame “[Instructional] design . . . . can be viewed not as a rational expression of an organization’s goals but as a political embodiment of contending claims.” (Bolman and Deal, 2003, p.225) Manager as Politician Four key skills: Agenda setting Mapping the political terrain Networking and forming coalitions Bargaining and negotiating (Bolman and Deal, 2003, p. 205) The Political Terrain High Principal GE Teachers Power SE Teacher Mentor Low Pro-change Opposed to Change Interest Forming Coalitions Third grade team spoke to the principal about their concerns Principal talked to me rather than directly to Tracy I did not tell Tracy that the principal talked to me The principal and Tracy did not have a fully trusting relationship Bargaining and Negotiating Deciding when students would be in the general education classroom Revising program students would receive when in special education classroom Moral Judgment Bolman and Deal (2003) identify four principals of moral judgment: Mutuality Generality Openness Caring This case lacked openness New Learning Making the change a win-win situation for Tracy Working with the third grade team as a whole Symbolic Frame “The structure of public schools is largely symbolic.” (Bolman and Deal, 2003, pg. 275) Inclusive Practice as Symbolic “Correct appearance, rather than efficient production, is the prevailing measure of effectiveness.” (Bolman and Deal, 2003, p.274) We hold this view based on: Myths, values and vision, which relate to our past, present and future Stories about student successes and exceptional teachers Rituals like IEP process, and grade-level team meetings New Learning Focus on building the “spirit” of the third-grade team to improve performance. Strategies could include: Example, rather than command – Modeling Use of metaphor Developing ceremonies to celebrate co-teaching successes Discussion What can administrators do to facilitate inclusive practices and co-teaching in schools? Human resources frame Structural frame Political frame Symbolic frame References Bolman, L. & Deal, T. (2003). Reframing organizations: Artistry, choice and leadership (3rd ed.). San Francisco: Jossey-Bass. Fullan, M. (2001). Leading in a culture of change. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.