Iran PPT - Scott County Schools
advertisement

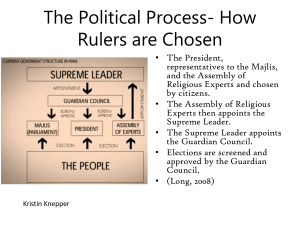
Iran Modified from Mr. Caroddo’s Education Website at http://caroddoapclasses.com/id4.html ISLAM FIVE PILLARS OF ISLAM Declaration of Faith (“There is no God but God [Allah] and Muhammad is his messenger”) Prayer (5 times a day) Alms to the poor Pilgrimage to Mecca (once in one’s lifetime) Fasting during the holy month of Ramadan. 1953 Coup In 1953, the Shah, with the support of the CIA, overthrew the democratically elected prime minister, Mossadegh Pahlavi – “White Revolution” “White” to counter influence of “red” communists Land reform – government bought land from large absentee owners and sold it to farmers at affordable prices Encourage agricultural entrepreneurship with irrigation canals, dams, & tractors Women’s rights (secularization) Suffrage Restricting Polygamy Women allowed to work outside the home Pahlavi - OIL & the Rent-seeking state Iran transformed into rent-seeking state under Pahlavi’s because of increasing income from oil Rentier Economy: heavily supported by state expenditure, while the state receives “rents” from other countries Iran received increasing revenue from exporting oil and leasing oil fields to foreign countries Although shah promoted import substitution policies by 1979 oil & associated industries provided 97% of foreign exchange and majority of Iran’s GNP Oil revenue became so great government did not have to rely on internal taxes to generate income, paid expenses from oil profits The people become unnecessary to the government in a rentier state OIL Abandoned gas pumps in a U.S. city 1973 Line at gas station in the U.S. 1979 OIL Highway in Tehran Oil Refinery in Tehran SOURCE OF U.S. OIL IMPORTS Oil Production 2004 Million Barrels per Day Former Soviet Union Saudi Arabia United States Iran Mexico 3.8 China Norway 2.9 Venezuela Iraq 9.1 8.8 5.4 3.9 3.3 2.7 1.5 Khomeini, Fundamentalism, & Revolution Islamic Fundamentalism Literal interpretation of Islamic texts Social conservatism Political traditionalism Resentment towards elites, US, and the Western world US was the “Great Satan” Velayat-e faqih (jurist’s guardianship) Senior clergy given authority over entire Shi’ia community Khomeini & the Islamic Republic Clerics consolidate power Popular support for regime high World oil prices rise again, allowing for social programs, improvements in medicine & housing Iraq invades Iran, people rally around the government Charisma of Khomeini inspired faith in the government Khomeini dies in 1989, constitution amended Ali Khamenei succeeds Khomeini, does not have the same political charisma as the Ayatollah Iran/Iraq war ends in 1988, country war-torn Oil prices drop in 1990’s Population begins to question authoritarian rule of the clerics IRAN-IRAQ WAR (1980-1988) Iraqi President Saddam Hussein OIL Khuzestan Province – Iran-Iraq War 1980-1988 Iraq’s Invasion of Kuwait – Gulf War 1991 Constitution of 1979 Document & 40 Amendments (Some added in 1989) Mixture of theocracy and democracy Preamble reflects importance of religion Velayat-e faqih (Jurist’s guardianship) Gave broad authority to Khomeini and the clerics Constitutional Amendments of 1989 On April 24, 1989, while on his death bed, Khomeini appointed a 25- member Reform Council (first Assembly of Religious Experts) to appoint his successor and amend the constitution Khomeini died in June 1989 The council named Ali Khamenei as Khomeini’s successor and made several amendments to the constitution Amendments of 1989 They eliminated the need for the Supreme Leader to be a marja, or senior cleric, Khamenei was not a marja Eliminated the post of Prime Minister Created the Supreme National Security Council Increased the size of the Assembly of Religious Experts to 86 members Gave Assembly of Religious Experts authority to meet once a year & determine if Supreme Leader was “mentally & physically” capable of carrying out their duties Made the Expediency Council a permanent institution Constitution amendments approved by Iranian voters in national referendum with 97% yes vote on July 28, 1989 Religion 89% of Iranians are Shi’a Muslims 10% are Sunni Muslim The constitution does not mention Sunnis and their legal status is therefore unknown 1% are combination of Jews, Christians, Zoroastrians, and Baha’i Constitution recognizes rights of religious minorities, many religious minorities have left country since Islamic Revolution Baha’i considered unholy offshoot of Islam and they have been persecuted by Shi’ite governments. Baha’i leaders have been executed, imprisoned, tortured, their schools closed and property confiscated Political Culture Authoritarianism (not totalitarianism) – leaders claim to be all powerful, but do not interfere with every aspect of the citizens lives Union of political & religious authority Shi’ism & Sharia – key components of everyday life Escape from European Colonialism and Western influence Influence of Ancient Persia Women & the Political System “Equality-with-difference” policy – instituted by the Islamic Republic slants law favorably towards men on issues such as divorce and custody Women must wear scarves and long coats in public Women can not leave country without consent of male relatives Women can be stoned for committing adultery Women allowed to get education in Iran and entrance into some occupations Expectations for better jobs and increased political rights among educated women Half of college students in Iran are women Women make up 27% of the labor force WOMEN IN IRAN ISLAMIC DRESS CODES Hijab (Head Scarf) Worn in the West and Iran Chador Iran Abaya Saudi Arabia Burqa Afghanistan Jilbab Indonesia Political Parties Islamic Coalition Party- conservative Alliance of Builders of Islamic Iran – member of the conservative alliance, party of current president Mahmoud Ahmadinejad, who secured office in presidential election of 2005 Islamic Society of Engineers-conservative Executives of Construction Party-centrist/reformist Elections Citizens over 15 allowed to vote until 2007 In 2007, eligibility age for voting changed to 18 National elections held for the following: Assembly of Religious Experts Representatives to the Majlis President Elections to Majlis and President are by plurality, winner-take all Elections are done over two rounds First round narrows field down to 2 candidates Iranian Presidential Election - 2009 Only 4 candidates out of 476 men & women who applied were approved by Guardian Council Election held on June 12, 2009 with incumbent Mahmoud Ahmadinejad running against three challengers: Mir-Hossein Mousavi Mohsen Rezaee Mehdi Karroubi Turnout was unexpectedly high, well over 50% and polls had to be kept open until midnight Ahmadinejad announced as winner the next morning with 62% of vote to Mousavi’s 34% Protest immediately erupted (the Green Revolution) in favor of Mousavi and claiming election fraud Election of 2009 Iranian Presidential Election June 14, Mousavi files formal appeal of results with Guardian Council June 15, Supreme Leader Khamenei announces investigation of electoral results June 16, Guardian Council announces it will recount votes, however, Mousavi states that 14 million ballots were missing, allowing for a chance to manipulate the results June 29, Iran’s electoral board completes partial recount, and concludes that Ahmadinejad won the election – this leads to more protests Interest Groups Islamic Association of Women Green Coalition Workers’ House Interest group for factory workers, have a political party as well, Islamic Labor Party Hold a May Day rally every year, turned into protest in 1999 against conservative policies to water-down labor laws Velayat-e faqih (Jurist’s guardianship) The principle instituted by Khomeini of overarching authority for different government institutions: Supreme Leader Guardian Council Assembly of Religious Experts Expediency Council This authority is all-encompassing and is over whole community based on their ability to understand shari’a and their commitment to champion the rights of the people Supreme Leader Position created for Khomeini, currently held by Ali Khamenei Powers of Supreme Leader: Elimination of presidential candidates Dismissal of the president Command armed forces Declares war & peace Appointment and removal of major administrators and judges Nominates six members of Guardian Council Appoints many non-governmental directors, such as radio/TV and semi-public foundations Responsibilities of Supreme Leader: faqih – he is the leading Islamic jurist to interpret shari’a and religious documents Links three branches of government together “Determining the interests of Islam” IRAN’S GOVERNMENT SUPREME LEADERS Ayatollah Khomeini (r. 1980-1989) Ayatollah Khamenei (r. 1989-present) PRESIDENTS Mohammed Khatami (r. 1997-2005) Mahmoud Ahmadinejad (r. 2005-present) GRAND AYATOLLAH ALI KHAMENEI (Supreme Leader 1989-present) Guardian Council 12 members All Male 6 members appointed by Supreme Leader 6 members nominated by chief judge, approved by Majlis Serve 6-year terms Responsibilities They represent theocratic principles within the government Review bills passed by Majlis to ensure they conform with shari’a Guardian Council and Supreme Leader together exercise principle of jurist’s guardianship (Make sure all democratic bodies adhere to Islamic laws & beliefs) Power to decide who can compete in elections Assembly of Religious Experts Expanded in 1989 to an 86 man house Directly elected by the people 8 year terms Members originally required to have seminary degree equivalent to a master’s, 1998 revision now allows nonclerics to stand for Assembly – candidates still subject to approval by Council of Guardians Responsibilities Broad constitutional interpretation Elected Khomeini’s successor (Khamenei) Reserve right to remove supreme leader Expediency Council Created by Khomeini Main purpose to “referee” disputes between the Guardian Council and the Majlis Exerts authority over executive, legislative, & judicial branches of gov’t 1989, Expediency Council passes some bills, and is institutionalized by constitutional amendments Currently consists of 40 permanent members It may originate its own legislation Not all members are clerics Appointed by Supreme Leader for five-year terms Collectively most powerful men in Iran President & the Cabinet Iran is not a presidential system, therefore the executive branch does not have the same authority as presidents in presidential systems such as U.S., Mexico, and Nigeria President does represent highest official representing democratic principles in Iran Chief executive, highest state official after Supreme Leader Directly elected every 4 years for a maximum of two terms Constitution still requires the president to be a Shi’ite and uphold Islamic principles There have been six presidents of the Islamic Republic since the Revolution, three have been clerics. MAHMOUD AHMADINEJAD (President 2005-present) President’s Power Devising the Budget Supervising economic matters Proposing legislation to the Majlis Executing policies Signing of treaties, laws, and agreements Chairing the National Security Council Selecting deputies and cabinet ministers Appointing provincial governors, town mayors, and ambassadors Semipublic Institutions Usually called “foundations” (bonyads), an Islamic charity organization Foundation of the Oppressed Martyrs Foundation Foundation for the Publication of Imam Khomeini’s Works Foundations are tax exempt Reputed to have a great deal of wealth Most property they supervise was confiscated from pre1979 elite Legislature: MAJLIS Unicameral legislature Created by Constitution of 1906, however Constitution of 1979 and 1989 amendments weakened the Majlis power 290 seats All directly elected through single member districts by citizens over 18 years old Majlis Authority Powers of the Majlis Enacting or Changing Laws, qanun (with approval of Guardian Council) The constitution uses the term qanun (statutes) rather than shar’ia (divine law) to avoid the question of whether laws come from God or the people It accepts the rationale that God formulates divine law (shar’ia), but elected representatives can draw up statutes (qanun) Interpretation of legislation (as long as it does not contradict judicial authorities) Appointment of 6 of 12 Guardian Council members from list made by chief judge Investigation of the cabinet ministers and public complaints against the executive and judiciary Removal of cabinet ministers, but not the president Approval of budget, cabinet appointments, treaties, & loans Majlis elections Election of 2000 (6th Majlis) Reformists fill seats through coalition of reformist parties (Khordad Front) Reformists win 80% of the vote, most secular voters whose parties were banned supported the reformists. Participation was over 70% of the electorate Election of 2004 (7th Majlis) Guardian Council bans thousands of reformist candidates Overwhelming victory for conservatives Control of the Majlis flips from the reformists to the conservative faction Many Iranians were disappointed in failure of Khordad Front to initiate reforms Participation of the electorate dropped to around 50% 2008 Majlis Elections The 2008 elections for the 8th Majlis turned into a repeat performance of 2004 The Guardian Council, assisted by the Interior Ministry, disqualified more than 3,000 potential candidates, including some of the leading reformers who held seats in the 7th Majlis The conservatives, led by Ahmadinejad’s Principalist’s Party, took 190 seats, although many were critical of Ahmadinejad’s populist rhetoric The reformers, mostly supported by Khatami’s Islamic Iran Participation Front and Rafsanjani’s Servants of Reconstruction, took 40 seats Judiciary Distinction between two types of law: sharia & qanun Judicial review does not exist in Iran Principle of jurist’s guardianship means that the Supreme Leader, the Guardian Council, and the Assembly of Religious Experts have final say regarding interpretation of law Ultimate legal authority does not rest in the constitution, but in sharia law itself Because interpreting shari’a is difficult it has been applied in different ways at various times Because of Ayatollah Khomeini’s approach, interpretation of shari’a came to be the standard that would influence all succeeding Iranian leaders Judiciary Islamic Republic Islamicized the judiciary code to interpret shari’a strictly Retribution Law Permitted families to demand “blood money” – compensation to the victim’s family from those responsible for someone’s death Mandated the death penalty for actions such as adultery, homosexuality, drug dealing and alcoholism Set up unequal treatment between men & women, and Muslims & non-Muslims Banned interest rates on loans, viewed as usury, which means lenders take advantage of people seeking loans Law & Justice Khomeini realized that despite the influence of sharia judges, the regime did need a centralized judicial system to tend to matters of justice in an orderly manner The interpretation of sharia was broadened so that the harsh penalties of the Retribution Law are rarely carried out Modern methods of punishment are more common than harsh public retribution Regime retained the shah’s court structure Appeals system Hierarchy of state courts Central government’s right to appoint and dismiss judges Military Revolutionary Guard – established by Khomeini after the revolution, a parallel military force to the shah’s traditional armed forces that were the 5th largest at the time Commanders of the Revolutionary Guard are appointed by the Supreme Leader According to the constitution, the regular army defends the borders, the Revolutionary Guard protects the republic Both were greatly strained during the Iran-Iraq War of the 1980’s Basij – volunteer militia of those to young to serve created during Iran-Iraq War. Martyred by Khomeini against the invading Iraqi troops After the war they became the Supreme Leader’s private militia Currently serve as the Islamic Republic’s “morality police” (Comparable to Hitler Nazi Youth) Iran’s armed forces currently have over 500,000 active troops making it the 8th largest military in the world Theocratic & Democratic Elements of Iran’s Government Structure Structure Theocratic Characteristics •Supreme Leader •Jurist •Guardian Council •Jurist guardianship; interpreter of shari’a; six members selected by the Supreme Leader •Six •Assembly of Religious •Jurist •Directly Experts Democratic Characteristics guardianship; ultimate interpreter of shari’a; appointed for life guardianship; interpreter of shari’a members selected by the Majlis; which is popularly elected, indirect democratic tie people elected by the Theocratic & Democratic Elements of Iran’s Government Structure Structure Theocratic Characteristics Democratic Characteristics •Appointed by the Supreme Leader; most members are clerics •Some •Majlis •Responsibility •Directly •Judiciary •Courts •Expediency Council shari’a to uphold held to shari’a law; subject to the judicial judgments of the Supreme Leader, Guardian Council clerics members are not elected by the people; pass non religious laws •Court structure similar to those in democracies; “modern” penalties, such as fines and imprisonment Public Policy: Policy-Making Factions Conservatives Created by often contradictory influences of theocracy & democracy Conservatives uphold principles of regime established in 1979 Against modernization because it threatens Shi’ism Wary of western influence Political & religious decisions should be one in the same Support right of clerics to run the political system Reformists Believe political system needs reform (but disagree on what reforms) Advocate some degree of international involvement with western countries Believe Shi’ism is important basis of Iranian society Support idea that political leaders do not have to be clerics Public Policy: Policy-Making Factions Statists Government should take active role in the economy Not necessarily communists Policy goals include: Redistribute land Redistribute wealth Eliminate unemployment Finance Social Welfare Programs Price restrictions on Consumer goods Free-marketers Similar market principles to the US, but in a theocratic/democratic state Liberal Economic Policies Remove price controls Lower business taxes Encourage private enterprise Balance the budget NUCLEAR WEAPONS NUCLEAR POWER: Peaceful or Aggressive Intentions? Energy Demand for energy outpacing supply Reserve of oil for export Technical developments Permitted according to terms of the NPT Weapons Iran has enough natural gas Aggressive rhetoric of Iran’s President, Ahmadinejad Secret construction of nuclear power plants Relations with terrorist organizations FUTURE Iran’s government may be losing legitimacy Iranians are Muslim, support religious rule. Tension with the West continue.