Chapter 11 – Carbon Chapter 11 Goals
advertisement

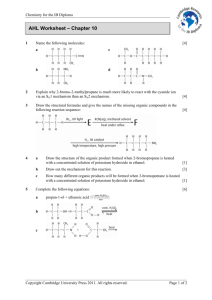
Chapter 11 – Carbon Chapter 11 Goals: 1.Classify organic compounds. 2. Recognize structural isomers and steroisomers. 3. Name and draw structures of common organic compounds. 4. Know the common reactions of organic functional groups. 5. Identify common polymers. Isomerism Isomers have identical ___________ but different ______________ Two forms of isomerism Constitutional (or structural) Stereoisomerism Constitutional Same empirical formula but different atomto-atom connections Stereoisomerism Same atom-to-atom connections but different _______________________. Structural Isomers Stereoisomers: geometrical Cis-2-butene Trans-2-butene Stereoisomers: optical • Optical isomers are molecules with non-superimposable mirror images. • Such molecules are called _________ • Pairs of chiral molecules are _______________. • Chiral molecules in solution can rotate the plane of plane polarized light. Stereoisomers Chirality generally occurs when a C atom has 4 different groups attached. Lactic acid Chirality These molecules are nonsuperimposable mirror images. Chirality Right- and lefthanded seashells The DNA here is right-handed Hydrocarbons • Compounds of C and H • Subgroups: – Alk____: C-C single bonds – Alk____: C=C double bonds – Alk____: carbon-carbon triple bonds – ________: based on benzene Hydrocarbons CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7CO2H Trans Fatty Acids tend to raise total blood cholesterol Functional Groups Amides Acids + Amines --> AMIDES N-methylacetamide Peptides and Proteins O H 3N OŠ H CH3 Alanine HOCH 2 H 3N + H OŠ O Serine peptide bond H HOCH2 H H 3N O N H O OŠ CH3 Polymers • Giant molecules made by joining many small molecules called monomers • Average production is 150 kg per person annually in the U.S. Polyamide: Nylon-6,6 Polyamides •Each monomer has 6 C atoms in its chain. •A polyamide link forms on elmination of HCl •Result = nylon 66 •Proteins are polyamides Remember • OWL end-of-chapter assignment is required.