cell wall
advertisement

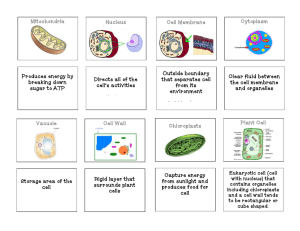
Catalyst #3: November 14th, 2013 1. What part of the cell synthesizes proteins? 2. What is the function of the rough ER? 3. What part of the cell destroys and eliminates waste from the cell? 4. What is the function of the Golgi apparatus? Agenda • Catalyst (6 minutes) • Plant vs. Animal Cells (10 minutes) • Class Questions/Venn Diagram (15 minutes) • Review Worksheet(10 minutes) • Exit Ticket (3 minutes) • Homework: – Finish the Plant vs. Animal Cell Worksheet – Study for a quiz on cellular organelles Agenda: Honors • • • • • Catalyst (6 minutes) Plant vs. Animal Cells (10 minutes) Class Questions/Venn Diagram (15 minutes) Review Worksheet(10 minutes) Exit Ticket (3 minutes) • Homework: – – – – Finish the Plant vs. Animal Cell Worksheet Study for a quiz on cellular organelles Honors Project The Cell as A ___________________ Announcements • Mastery slips • Discovery letters The Cell as a _____________ Project: Due Monday • Create your own analogy for the cell organelles we discussed (similar to our factory analogy) • At the top of your paper, list the entity that you are comparing the cell to. (i.e. School, Military, Government) • List each organelle, its function, and its analogous role • EXTRA CREDIT: Include a drawing or diagram of your analogy with each portion labeled Unit 2: Guiding Questions • What are all living organisms made up of? • What does each part of the cell do? • What different types of cells exist and how are they different? Today’s Objectives • SWBAT compare and contrast plant and animal cells in terms of their structural features • • SWBAT explain the unique functions of the plant-specific organelles and identify these organelles on a diagram Plant vs. Animal Cells Review • What three features do all cells have? – Cell membrane, cytoplasm, genetic material • What type of cells contain a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles? – Eukaryotic cells • What are some organelles in the eukaryotic cell? – Mitochondria, lysosomes, rough and smooth ER, Golgi apparatus Plant and Animal Cells • Key Point 1: Plant cells and animal cells are both eukaryotic cells • Therefore, they share many of the same structures. • Both plant and animal cells have: – Cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, lysosomes, ribosomes, rough and smooth ER, and Golgi apparatus • What is the function of each of these? Plant and Animal Cells Plants vs. Animals • Clearly, plants and animals are very different, though they are both made up of cells. • Their cells have a few key differences also Plant vs. Animal Cells Key Point 2: Plant cells have three key structures that are not found in the animal cell because they are not necessary. Do you notice any differences in the picture below? Cell Wall • Key Point 3: Plant cells have a cell wall around the cell membrane that provides an extra layer of support, strength, and protection for the cell. – Cell wall gives plant cells a more square shape – Animal cells do not have a cell wall, only a cell membrane Cell Wall Why? • Plant cells need this extra support and protection because plants are constantly exposed to physical forces from wind, rain, animals, and other factors Chloroplasts Key Point 4: Plant cells contain chloroplasts, which are the location of photosynthesis. Chloroplasts use energy from the sun to produce food for the plant The food produced during photosynthesis is glucose Chloroplasts Why? • Plant cells need chloroplasts because they cannot find and consume food the way that animals do – Therefore, they must make their own food Central Vacuole • Key Point 5: Plant cells also contain a large, central vacuole that stores water and nutrients for the plant cell. – Looks like a water balloon inside the cell – Animal cells only have small vacuoles Central Vacuole Why? • The pressure from the water in the vacuole helps plants support heavy structures such as leaves and flowers. – Animals have other support structures and do not need the extra water storage The Plant Cell Plant Cell Centrioles • There is one key structure that animal cells have but plant cells do not • Key Point 6: Animal cells have centrioles, but plant cells do not. • Centrioles organize proteins known as microtubules involved in cell division and structural support Class Question 1 • Which of the following structures is found only in the plant cell? A. B. C. D. Central Vacuole Cell wall Chloroplasts All of the above • Answer: D. All of the above Class Question 2 • What part of the plant cell is labeled by the arrow? • Answer: Cell Wall Class Question 3 • What part of the plant cell stores extra water and nutrients and supports the leaves and stems of the plant? • Answer: Central vacuole Class Question 4 • What is the function of the cell wall in the plant cell? • Answer: Provides extra support, strength, and protection Class Question 5 • Why do only plant cells have chloroplasts? A. Plants need to grow more quickly than animals B. Plant cells cannot find and consume their own food like animals can C. Plants are green and so are chloroplasts D. Plants need more energy than animals do • Answer: B. Plants cannot find and consume their own food like animals can Class Question 6 • What is one structure found in animal cells but NOT in plant cells? • Answer: Centrioles Plant and Animal Cell Foldable • Label one flap “Plant Cells”. Label the other flap “Animal Cells.” • On the inside, list the similarities on the back of the flap. • List the differences on the other flap. • BONUS: Draw a plant and animal cell under their respective flaps. Venn Diagram • Place each of the structures below in the proper section of the Venn diagram: – – – – – – – – – Mitochondria Nucleus Cell wall Cell membrane Centrioles ER Chloroplasts Ribosomes Large Vacuole Exit Ticket • Answer the questions below without using your notes: 1. What are two structures found only in plant cells? 2. What is the outer layer of the plant cell that provides extra support called? 3. What part of the plant cell produces food for the plant during photosynthesis? 4. What does the central vacuole do?