accommodatingdiverselearners
advertisement

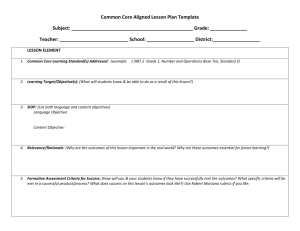
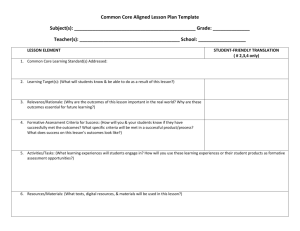
“Kevin is so engaged while investigating the mock rocks. It’s remarkable! He’s usually not so focused.” - Resource teacher overhead talking to the general ed teacher about her SPED student performance in the inclusive science classroom. Accommodations, Modifications and Strategies for Students with Learning Differences Goals • To understand several accommodations, modifications, and strategies for diverse learners. • To examine accommodations, modifications, and strategies for diverse learners in Make It and Take It. Relationship to RIPTS • Standard 3: How Children Learn and Develop • Standard 4: Respect for Diversity * Link to Rhode Island Professional Teaching Standards. Turn and Talk Describe a diverse learner. What are Learning Differences? • Multiple Intelligences • Learning Styles (tactile; visual; auditory; multi-sensory) • Students with Individual/504 Education Plans – – – – – – – Dyslexia, autism, developmentally delayed Emotional or behavioral impairments (e.g., depression, fears) Sensory Impairment (e.g., deaf, blind, deaf-blind) Neurologic Impairment (e.g., use of memory) Health (e.g., ADHD, leukemia) Physical impairments (e.g., cerebral palsy, Congenital anomaly) Gifted (creative and academically talented) • English language barriers (ESL/ELL) • Cultural • General lack of interest or engagement What is Universal Design for Learning? UDL is a blueprint for creating flexible goals, methods, materials, and assessments that accommodate learner differences. http://www.cast.org/research/udl/index.html UDL Origins and Definition UDL Origins and Definition Drawbacks of Retrofitting • Each retrofit solves only one local problem • Retrofitting can be costly • Many retrofits are UGLY! UDL Origins and Definition Architect, Ron Mace “Consider the needs of the broadest possible range of users from the beginning” UDL Origins and Definition Accessible design improves access for everyone, not only those individuals from whom each affordance is made. Accommodations The support that special needs students require to successfully demonstrate learning. Accommodations should not change expectations to the curriculum grade levels. Modifications Changes made to curriculum expectations in order to meet the needs of the student. Modifications are made when the expectations are beyond the students level of ability. Strategies Skills or techniques used to assist in learning. They are individualized to suit the student’s learning style and developmental level: Turn and Talk What accommodations, modifications, and strategies are you including in your MITI planning and teaching? Accommodations The support that special needs students require to successfully demonstrate learning. Accommodations should not change expectations to the curriculum grade levels. Examples: • Extra time • Preferred seating • Taped books • Flexible grouping Modifications Changes made to curriculum expectations in order to meet the needs of the student. Modifications are made when the expectations are beyond the students level of ability. Examples: - Include student in same activity but individualize expectations and materials - Include student in same unit but provide different task and expectations. Strategies Skills or techniques used to assist in learning. They are individualized to suit the student’s learning style and developmental level: Examples: - Color coding - Visual cues - Word Walls - PowerPoint Slides Modifications: Pyramid PlanningWhat some What most students will know and be able to do What ALL students will know and be able to do students will know and be able to do TASK: Use “Pyramid Planning” to develop 3 learning outcomes for a lesson: MOST What most students will know and be able to do SOME What some students will know and be able to do ALL What ALL students will know and be able to do Students will be able to [verb of cognitive process] [noun – procedural knowledge] by ……(observable behaviors/performance, qualities of product). The students will be able to • SOME …..record observations in data chart independently, with little guidance. • MOST ….record observations in data chart with structure and guidance. • ALL ….collect data by observing and comparing the colors of beads in the control and treatment groups. What is Universal Design for Learning? UDL is a blueprint for creating flexible goals, methods, materials, and assessments that accommodate learner differences. UDL includes three principles for designing curriculum: recognition, strategy, and affect. http://www.cast.org/research/udl/index.html Solutions for RECOGNITION Represent information in multiple formats and media METHODS • Electronic version of the text (varying text sizes, read aloud with text-to-speech) • CD ROM or online encyclopedia with images and spoken text • Links to Spanish web sites on the subject • Printed and electronic concept map with images, text & hyperlinks • E-text outline of lecture content with main ideas highlighted • Tool to translate words or connected text into other languages • Text-to-speech utility to read e-text aloud (English and Spanish) • Video(s) on subject • Graphic highlighting of important ideas (on screen or on paper) • Digital photograph collection • Links to web sites with primary sources, images, sounds, and video・Additional background knowledge Solutions for STRATEGY Provide multiple pathways for students' action and expression METHODS • Printed and electronic text-based outline to structure composition • Cheat sheet with clear steps for library research • Library mentor lined up to help • Set of pre-chosen links to relevant web sites • Digital collections of images and information to narrow search • Option to create multimedia report rather than written • Option to use computer slide show for presentation • Option to work in collaborative groups • Talking word processor with spell check • Voice recognition software to scaffold writing • Teacher made e-templates Solutions for AFFECT Provide multiple ways to engage students' interest and motivation METHODS • Option to create a graphic report with minimal text • Use of graphics program which supports drawing (e.g. Kid Pix) • Electronic concept map with parts filled in & limited content choices as scaffold • Option to use Internet instead of library • Voice recognition software to scaffold writing • Collaborative learning groups with different roles • Build class library of digital photographs with students • Links to web sites with primary sources, images, sounds, and video • Alternative content for lessons focused on processes • Teacher made e-templates • Web sites/software with leveled management system