Assessment of Student Learning Outcomes
advertisement

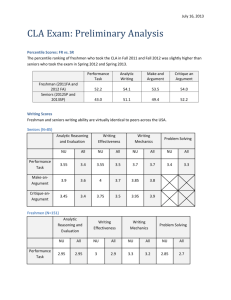
University of Pittsburgh Assessment of General Education Patricia E. Beeson Vice Provost for Graduate and Undergraduate Studies February 11, 2008 Two Approaches to Assessment of General Education Establish overarching learning outcomes and assess progress toward those Establish goals for specific General Education Requirements and assess those University-Wide Learning Goals Exhibit mastery of their discipline Think critically and analytically Gather and evaluate information effectively and appropriately Understand and be able to apply basic, scientific and quantitative reasoning Communicate clearly and effectively Use information technology appropriate to their discipline Understand and appreciate diverse cultures (both locally and internationally) Work effectively with others Have a sense of self, responsibility to others, and connectedness to the University Available Assessment Instruments National Survey of Student Engagement CLA, CAAP, MAPP Standardized Assessment of Information Literacy Skills Intercultural Development Inventory Foreign Language Assessment National Survey of Student Engagement Indirect Evidence (self assessment) Freshmen and Seniors (value added) Comparative Data Available For More Information: http://nsse.iub.edu/ National Survey of Student Engagement To what extent has your college experience contributed to your ability to write clearly and effectively? (percent responding quite a bit or very much) 2002 Freshmen: 56% 2006 Seniors: 72% Value Added - 16 percentage points Mapping NSSE to Outcomes Outcome: Communicate clearly and effectively Outcome Assessment (1) Writing clearly and effectively Outcome Assessment (2) Speaking clearly and effectively Process Assessments Prepared two or more drafts of a paper or assignment before turning it in Number of written papers or reports of 20 pages or more, between 5 and 19 pages, and fewer than five Asked questions in class or contributed to class discussions Made a class presentation Collegiate Learning Assessment Direct Assessment of Analytic Writing Critical Thinking Information Literacy(?) Freshmen and Seniors Tested Comparative Data Available For More Information: http://www.cae.org/content/pro_collegiate.htm Collegiate Learning Assessment Analytic Writing: Make an Argument Break an Argument Evaluated on Presentation, Development, Persuasiveness, Mechanics, Interest Performance Task Critical Thinking Information Literacy CLA Performance Task - Document Library Research Brief Memo from Investigator Web Search Results News Story Data Tables Crime Stats Chart CLA Performance Task Designed to Assess Ability to: Evaluate, Analyze and Synthesize Evidence Draw Conclusions Acknowledge Alternative Viewpoints Collegiate Assessment of Academic Proficiency - CAAP Direct Evidence Freshmen and Seniors (value added) Comparative Data Available For More Information: http://www.act.org/caap/ CAAP CAAP offers six independent test modules: Reading Writing Skills Writing Essay Mathematics Science Critical Thinking CAAP Critical Thinking Test Critical Thinking Test is designed to measure ability to clarify, analyze, evaluate, and extend arguments. Includes four passages representative of the kinds of issues commonly encountered in a postsecondary curriculum. Multiple Choice questions about passages Measure of Academic Proficiency and Progress - MAAP Direct Evidence Freshmen, Sophomores, and Seniors (value added) Comparative Data Available For More Information: www.ets.org MAAP Four integrated tests assessing four core skill areas in the context of humanities, social sciences and natural sciences: Critical thinking Reading Writing Mathematics MAPP The MAPP intended to measure skills developed versus subject knowledge acquired in general education courses Multiple Choice format Institution can add additional questions including optional essay Standardized Assessment of Information Literacy Skills – SAILS Direct Evidence Pre- and Post-Testing is Available Comparative Data Available For More Information: https://www.projectsails.org/ SAILS Test of information literacy skills, based on Information Literacy Competency Standards for Higher Education including ability to : Access information effectively and efficiently Critically evaluate sources and content Incorporate information into knowledge base Use information effectively to accomplish specific purpose Understand economic, legal and social issues surrounding use of information Intercultural Development Inventory Indirect and Direct Evidence Fifty items or statements, answered as the extent to which a person agrees or disagrees with the statement IDI measures both one’s self-perceived and actual place on the Developmental Model of Intercultural Sensitivity continuum Can be Administered at any Level Comparative Data Available For More Information: http://www.hammerconsulting.org/idi_what.php Intercultural Development Inventory The Intercultural Development Inventory (IDI) measures how a person tends to think and feel about cultural difference IDI measures how a person construes and organizes events, guided and limited by their cultural patterns Foreign Language Assessment Under development by language departments in cooperation with European Union Center