Expository Vocabulary Terms
advertisement

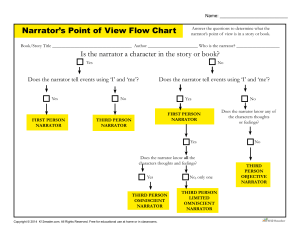
Expository Vocabulary Terms Compare and Contrast • To identify the similarities and differences of two or more subjects Extraneous information • Not relating directly or significantly to the matter or subject at hand • irrelevant Author’s Purpose These are all examples of what? • • • • To express feelings or thoughts To inform or explain To persuade To entertain Patterns of Organization (the way ideas and information is arranged and organized) These are all examples of what? • • • • • Cause and Effect Chronological Order Compare and Contrast Classification Problem-Solution • Combination of ideas, values, feelings, and beliefs that influence the way a writer looks at a topic Main Idea • Central or most important idea about a topic that a writer or speaker conveys. • Expressed in the topic sentence Problem-Solution Order • Problem is stated and analyzed and then at least one solution is proposed and examined Topic Sentence • States the paragraph’s main idea Conclusion • Statement of belief based on evidence, experience, and reasoning • This valid statement logically follows from the facts or statements upon which it is based and helps bring together the information Text features • Elements of a text that help organize and call attention to the important information • Briefly retell the main ideas of a piece of writing in one’s own words Inference • A logical guess that is based on facts and one’s own background knowledge and experience Index • An alphabetized list of important topics covered in the book and the page numbers on which they can be found • It can be used to quickly find information about a topic Cause and Effect • Two events are related when one event brings about, or causes, the other Bibliography • List of related books and other material used to write a text • Can be good sources of further study on a subject Graphic Organizers • “word picture” or visual illustration of a verbal statement that helps a reader understand a text • Examples include: charts, tables, webs, and diagrams Point of View • Method of narration used in a short story, novel, narrative poem, or work of fiction • Examples: – 1st person: narrator is a character – 3rd person: narrator is outside the action (not a character) – 3rd person omniscient: all knowing (narrator sees into the minds of the characters and knows what they are thinking) – 3rd person limited: narrator only knows what one character thinks, feels, and observes Sidebar • Additional information set in a box alongside or within a news or feature article Footnotes • An explanatory or documenting note or comment at the bottom of a page, referring to a specific part of the text on a page