Prof. Snyder's Powerpoint-Indian Religious Tradition
advertisement

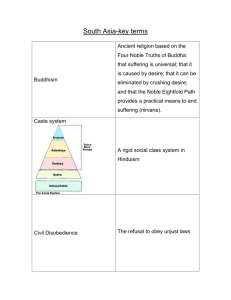
Comparison of Religious Traditions Middle Eastern (J-C-I) Indian (Hindu) Anthropomorphic Monotheism Polymorphic Pantheism God is transcendent The One is immanent Revealed—the Word of God Nonrevealed—human insights Outer search Inner search Catechismal Experimental Congregational Individualistic Exclusive Inclusive Proselytizing Non-proselytizing The Indian Religious Tradition: Hinduism The Indian Religious Tradition: Hinduism Early Period: Rig Veda and Brahmanas Religion = priests + rituals (mechanical approach) The Upanishads: spirituality, mysticism The Nature of reality: Maya (illusion): ignorance vs. sin Brahman-atman (the “world soul”, ultimate reality) eternal, unchanging, everywhere the same, one The nature of life: Atman (individual “soul”, eternal Self) Samsara (reincarnation)—The human being: physical body, outer self, inner Self (atman) The Law of Karma (cause and effect) “As ye sow so shall ye reap” Caste hierarchy Dharma (cosmic order; caste duty; right action) The Indian Religious Tradition: Hinduism The Goal of Life: moksha (release from samsara) Paths to the goal: yoga (union with the One) Unlimited possibilities Some types: Jnana yoga: wisdom, enlightenment Karma yoga: work, dharma Bhakti yoga: devotion The key is selflessness Indian Religious Tradition: Hinduism The full development of Hinduism: New Popular deities: the Trimurti Brahma: the Creator Vishnu: the Preserver Shiva: the Destroyer The Doctrine of Avatars (incarnations) Hinduism absorbs all deities The Ideal Pattern of Life: Student Householder Forest dweller (sadhu) Sannyasin The Indian Religious Tradition: Hinduism (Shiva Nataraja) Indian Religious Tradition: Jainism & Buddhism Jainism: ahimsa (non-harm, non-injury) Buddhism: Siddhartha Gautama (the “Buddha”) His life as a model (tathagata) The four sights His Enlightenment: the Four Noble Truths 1. Dukkha—pain, suffering, unsatisfactoriness 2. Cause of dukkha—attachment, wanting 3. Elimination of dukkha—non-attachment 4. The Eightfold Path—leads to Nirvana Monasticism—separation from the world Indian Religious Tradition: Hinduism and Buddhism Similarities and differences: Both agree that: Life involves pain and suffering This is caused by attachment Relief comes from non-attachment There is reincarnation Happiness can be found in this life Buddhism disagrees: There is no Brahman There is no Atman Rejects the caste system People (including women) are equal Indian Religious Tradition: Images