Agriculture Review ANS
advertisement

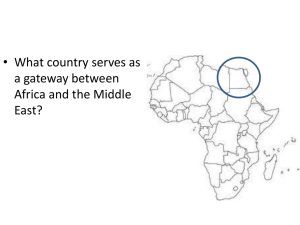
Warmup • A model is useful in that it A. Conveys the whole truth about a phenomenon B. Eliminates the complexity associated with the world C. Provides a comprehensible and limited view of a phenomenon D. Relies completely on empirical data for confirmation or refutation E. Eliminates the need to use math or quantifiable data What is this chart illustrating? Secondary activities Primary activities Most of these are located in __________________. ???? Review How did agriculture first develop? 1. 2. 3. 4. People were hunter-gatherers Gatherers dropped fruit Locations with dropped seeds produced fruit Hunter-gatherers noticed this process Which gender was probably the first to discover agriculture? • Females because they were the gatherers What is the difference between subsistence and commercial agriculture? • Subsistence – food produced for self and family; labor intensive • Commercial – food produced to sell for profit; capitol intesive What is the commercial farming practiced in MDCs known as? • Agribusiness Describe the process of slash-and-burn agriculture. 1. Cut sections of forest 2. Burn it to ash 3. Let the ashes seep in to the ground (swidden) 4. Plant crops What is swidden? Is it sustainable? Describe the soil of the rain forests. Nutrient poor What is shifting cultivation? • Slash and burn agriculture How much of the world’s land area is covered by shifting cultivation? • 36 million square kilometers • 14 million square miles How does pastoral nomadism relate to transhumance? Describe the relationship between intensive subsistence and crop rotation. How many crops do plantations usually grow? • 2 cash crops (cotton, tobacco, sugarcane, rubber) How did plantations play a role in American history and when did they decline? Explain the location of dairy farms in MDCs. • Can be located farther from the market due to transportation, refrigeration, and pasteurization. • Up to 300 miles from market. Who is the largest producer of grain in the world? What is the most important crop grown, and why is it important? How is ranching in MDCs different from pastoral nomadism? • Ranching is commercial, sedentary. • Pastoral nomadism is subsistence, nomadic. How does the farm subsidy system work in the United States? • Government money to help farmers if there is under- or over-production. Why do environmental advocates push for the limited use of chemical pesticides? Pesticides, if overused, can seep into the soil and into the water table Where are most drugs produced? To whom are they sold? Give an illustration of desertification. How has modern technology and population affected the world’s oceans? For each of the following causes, list the effect (this is based on your book and class discussion) 1970s: Studies show that beef is fatty 1990s: The Atkins diet craze (anti-carbohydrate) 2000s: Genetically modified foods are widespread 1930-2012 Food Pyramid 2015 Food Pyramid Fully define the Green Revolution • The invention and rapid diffusion of more productive agricultural techniques during the 1960s through the 1980s. • These techniques involved higher-yield (high production) seeds and chemical fertilizers, new irrigation techniques, and machinery such as the reaper and the combine. • Founded by Norman Borlaug Explain increases in rice production • In many regions in Asia, from 1970-1995, rice production doubled. • GR seeds went from 0% of planted rice in the 1960s to over 80% of planted rice today in many parts of Asia. Sources: http://countrystudies.us/philippines/62.htm http://www.highbeam.com/doc/1G1-16514368.html Negative Effects of the GR • Decreased crop variations. • Requires heavy machinery, therefore excluding many poor farmers. • Many new crops are resistant to traditional pesticides. • LDC farmers enter a cycle of dependence on multinational corporations like Monsanto. • Does not address economic inequality. Positive Effects of the GR • More food = more people who can be fed. • New crops are more responsive to irrigation and to petrochemical fertilizers. • Postpones the predictions of Thomas Malthus. • Reduction in poverty in many regions, particularly Asia. Gender Effects of the GR • Women's wage-earning opportunities have decreased because of mechanization. Source: http://www.fao.org/FOCUS/E/Women/green-e.htm Food Security • Access to and availability of food, • Resource distribution to produce food • Purchasing power to buy food where it is not produced. Source: http://www.fao.org/FOCUS/E/Women/Sustin-e.htm Sustainable Agriculture • Agricultural practices that preserve and enhance environmental quality. • GR is not focused on sustainability. • Intensive GR farming could lead to soil exhaustion. • Fertilizers in the GR may hurt local ecosystems. Food Distribution: Two Arguments • 1 – The GR increased crop yields across the world, driving up the supply of food and driving down to costs. As a result, the poor had food and more job opportunities in agriculture. Food Distribution: Two Arguments • 2- The GR drove many poor farmers out of business because they could not afford GR seeds. Additionally, LDCs are still poor, and it does not matter how much food is produced if the poor cannot afford it. Label von Thunen’s model below. According to von Thunen, what is the regional geography of agriculture determined by? RENT How does relative location affect each of the following categories in von Thunen’s model? -Horticulture and dairy- Spoils quickly, most value per acre. -Logging- High transport cost due to weight, medium value per acre -Crops and grazing- Requires enormous amounts of land, low value per acre.