Hemodynamic Monitoring
advertisement

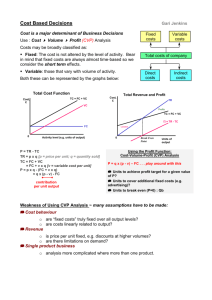
Hemodynamic Monitoring
Part I
(ABP, CVP, Ao)
MICU Competencies
2006-2007
1
What is Hemodynamic Monitoring?
• Non-invasive = clinical assessment & NBP
• Direct measurement of arterial pressure
• Invasive hemodynamic monitoring
2
Noninvasive Hemodynamic Monitoring
• Noninvasive BP
• Heart Rate, pulses
• Mental Status
• Skin Temperature
• Capillary Refill
• Urine Output
• Mottling (absent)
3
Proper Fit of a Blood Pressure Cuff
• Width of bladder = 2/3 of upper arm
• Length of bladder encircles 80% arm
• Lower edge of cuff approximately 2.5 cm
above the antecubital space
4
Why A Properly Fitting Cuff?
• Too
small
causes false-high reading
• Too
LARGE causes false-low reading
5
Indications for
Arterial Blood Pressure
• Frequent titration of vasoactive drips
• Unstable blood pressures
• Frequent ABGs or labs
• Unable to obtain Non-invasive BP
6
Supplies to Gather
• Arterial Catheter
• Pressure Tubing
• Pressure Bag
• Flush – 500cc NS
• Pressure Cable
7
Supplies to Gather
• Sterile Gown (2)
• Suture (silk 2.0)
• Sterile Towels (3)
• Chlorhexidine Swabs
• Sterile Gloves
• Mask
8
Leveling and Zeroing
• Leveling
– Before/after insertion
– If patient, bed or transducer move
• Zeroing
– Performed before insertion & readings
• Level and zero at the insertion site
9
Potential Complications
Associated With Arterial Lines
• Hemorrhage
• Air Emboli
• Infection
• Altered Skin Integrity
• Impaired Circulation
10
Documentation
• Insertion procedure note
• ABP readings as ordered
• Neurovascular checks every two hours
(in musculoskeletal assessment of HED)
• Pressure line flush amounts (3ml/hr)
• Tubing and dressing changes
11
Central Venous Pressure Assesses . . .
• Intravascular volume status
• Right ventricular function
• Patient response to drugs &/or fluids
12
Central Venous Pressure (CVP)
• Central line or pulmonary artery catheter
• Normal values = 2 – 8 mm Hg
• Low CVP = hypovolemia or ↓ venous return
• High CVP = over hydration, ↑ venous return,
or right-sided heart failure
13
Leveling and Zeroing
• Leveling
– Before/after insertion
– After patient, bed or transducer move
– Aligns transducer with catheter tip
• Zeroing
– Performed before insertion & readings
• Level and zero transducer at the phlebostatic
axis
14
Phlebostatic Axis
• 4th intercostal space, mid-axillary line
• Level of the atria
(Edwards Lifesciences, n.d.)
15
More on Leveling and Zeroing
• HOB 0 – 60 degrees
• No lateral positioning
• Phlebostatic axis with
any position (dotted line)
(Edwards Lifesciences, n.d.)
16
Dynamic Flush
Dynamic flush ensures the integrity
of the pressure tubing system.
Notice how it ascends - forms a
square pattern - and bounces below
the baseline before returning to
the original waveform.
•Check dynamic flush after zeroing
any pressure tubing system
17
System Maintenance
• Change tubing and fluid bag q 96hrs
• No pressors through CVP port
• Antibiotics, NS boluses, blood, & IV pushes
are allowed through the CVP line
18
Troubleshooting
• Improper set-up and equipment malfunction
are the primary causes for hemodynamic
monitoring problems
• Retracing the set-up process or tubing
(patient to monitor) may identify the problem
and solution quickly
• Use your staff resources: Help All, Charge
Nurse, Educator, Preceptors, MICU experts
19
Troubleshooting
Damped Waveforms
Pressure bag inflated to 300 mmHg
Reposition extremity or patient
Verify appropriate scale
Flush or aspirate line
Check or replace module or cable
20
Troubleshooting
Inability to obtain/zero waveform
Connections between cable & monitor
Position of stopcocks
Retry zeroing after above adjustments
21
Continuous Airway Pressure (Ao)
• Also known as Paw, Ao
• Purpose:
– Improves accuracy of hemodynamic
waveform measurements
– Identification of end-expiration
• Positive waveform deflections = positive
pressure ventilation
• Negative deflections = spontaneous
inspiratory effort
22
Supplies to Gather
• Pressure Cable
• Pressure Tubing
• Connector
(Edwards Lifesciences, n.d.)
23
Setting up the Ao
• Discard infusion spike end & cap port
• Connect pressure tubing to vent tubing
(using connector opposite heating cable)
• Connect cables
• Zero the tubing (leveling not necessary)
24
Troubleshooting Ao
• Do not prime tubing with fluids!
• Damping will occur with fluid or secretions
• To evacuate any fluids, disconnect pressure
tubing from vent tubing and push air through
the pressure tubing with a 10 ml syringe
connected at one end until fluid-free
25
Pressure Measurement
1) Record Ao and CVP on the same strip
2) Find end-expiration by drawing a vertical line with a
straight edge 200 ms prior to the rise or dip in Ao (1
large box) associated with a breath.
3) Draw a horizontal line through the visually assessed
average vascular pressure starting at end-expiration
going backward 200 ms (1 large box).
4) Read the pressure at the horizontal line.
15
10
5
0
-5
CVP=13
26
Assist-Control
{
CVP
{
Ao
200 ms
200 ms
27
CPAP with Pressure Support
{
{
Ao
200 ms
CVP
200 ms
28
CPAP without Pressure Support
{
Ao
{
200 ms
CVP
200 ms
29
40
30
20
10
0
-10
Incorrect method!
This point was
identified as endexpiration for a pt.
who did not have an
Ao set up.
Correct method!
30 sec after the above
tracing, Ao was added & true
end-expiration clearly
identified.
30
Same patient 20 minutes later
4040
3030
2020
1010
00
-10
-10
31
15
10
5
0
-5
CVP=13
32
Summary
•Record Ao with CVP
•Read mean CVP at end-expiration as
described. No need read vascular pressure at
any particular time in the cardiac cycle
33
Documentation of CVP
• Include on waveform strip
–
–
–
–
–
–
Position of the HOB
Vasopressors and rates
Amount of PEEP
Scale
CVP measurement
Signature of the nurse
(post in green chart behind graphics tab)
34
References & Resources
Burns, S. M. (2004). Continuous airway pressure monitoring. Critical Care Nurse, 24(6), 70-74.
Chulay, M., & Burns, S. M. (2006). AACN Essentials of critical care. McGraw-Hill: New York.
Edwards. (2006). Pulmonary Artery Catheter Educational Project. http://www.pacep.org
Edwards Lifesciences. (n.d.) Educational videos. www.edwards.com
MICU Routine Practice Guidelines. www.vanderbiltmicu.com
MICU Bedside Resource Books
MICU Education Kits (Red cart in conference room)
MICU Preceptors, Help All Nurses, & Charge Nurses
VUMC policies. http://vumcpolicies.mc.vanderbilt.edu
35