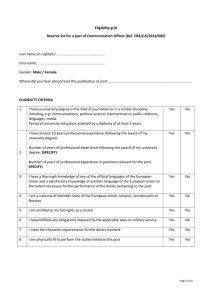
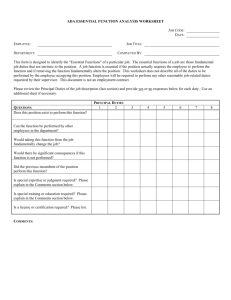
Chapter 4 Job Analysis and Job Design
advertisement

Chapter 4 Job Analysis and Job Design • • • • • • • Job versus Positions Job Analysis Data Sources and Data-Collection Methods Job Analysis and HR Legal Aspects of Job Specifications The Changing Environmental Job Design Copyright 2011 Health Administration Press Job Analysis • Cornerstone of SHRM • The process of obtaining information about jobs by determining the job’s duties, tasks, and activities • Foundation of job description and job specifications • Job description: summary of tasks, duties, and responsibilities • Job specification: personal qualifications required to perform the above duties and responsibilities Copyright 2011 Health Administration Press Data Sources and Methods • Data sources include the job analyst, the employee, and the supervisor • Methods of data collection: observation, interview, questionnaire, job performance, employee diary, technical conference, competency model, and the Occupational Information Network Copyright 2011 Health Administration Press Job Analysis and HR • Job analysis is the foundation for all HR activities. • Identify necessary skills and job relatedness for recruitment and retention. • Determine the relative worth of jobs. • Determine training. • Assess relevant job functions for performance appraisal. • Legal basis and defense for managing HR functions. Copyright 2011 Health Administration Press The Changing Environment • Future-oriented job analysis • Competency-based job analysis • General job analysis • Flexible and complex jobs require broader capabilities (i.e., intelligence, adaptability, and teamwork). Copyright 2011 Health Administration Press Job Design • The process of structuring jobs to enhance efficiency and job satisfaction • Increased job specialization in healthcare • Job enlargement: increasing the scope of jobs to provide greater variety (horizontal expansion) • Job enrichment: increasing autonomy and responsibility (vertical expansion) • Employee empowerment: allowing decisions to be made by those closest to the work • Work group redesign: different team structures Copyright 2011 Health Administration Press Work Schedule Redesign • Compressed workweek and reduction in the number of workdays while increasing the hours worked per day • Flextime: flexible employee starting and ending times • Job sharing: two part-time employees sharing one full-time job • Telecommuting: performing work away from the office through the use of technology • Contingent workers: independently contracted and on-call workers Copyright 2011 Health Administration Press