If a human skin cell with 46 chromosomes divides by mitosis, each
advertisement
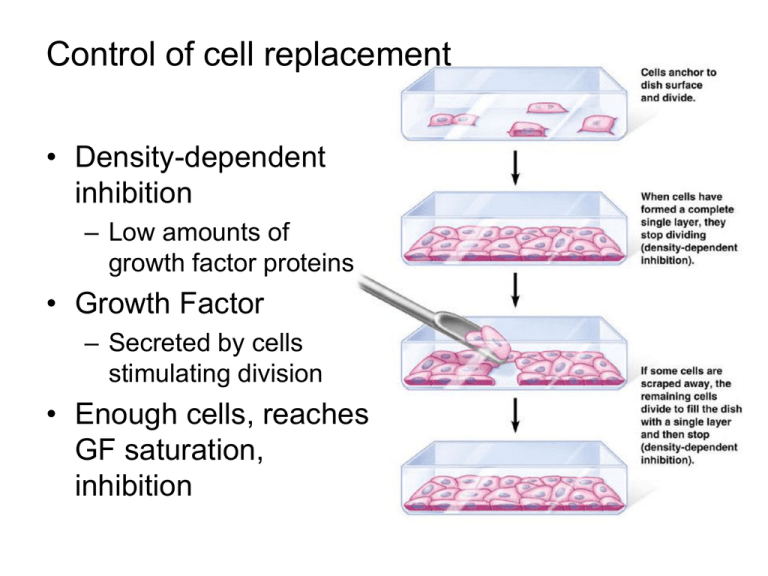
Control of cell replacement • Density-dependent inhibition – Low amounts of growth factor proteins • Growth Factor – Secreted by cells stimulating division • Enough cells, reaches GF saturation, inhibition Cancer - Disease of the cell cycle • Excessive division (out of control); tumor – Benign; removed if pushing against vital organs – Malignant; disrupts normal tissue & organ function • Metastasis; spreads to other tissues via bloodstream & lymph • Carcinoma – Epithelial cells (e.g. skin, intestinal lining) • Sarcoma – Connective or supportive tissue • (e.g. bone, cartilage, muscles, fat, blood vessels) • Leukemia – Blood or bone marrow; specifically WBC’s • Lymphoma – Originates in lymphocytes (immune cells) Chromosomes, sex cells, and meiosis • Somatic cells (typical body cell) have 46 chromosomes, or 23 matched pairs • Homologous chromosomes or homologues – Both have genes that code for the same characteristics – Will be at the same location or locus – e.g. if we think chromosomes as sets of instructions or manuals, we have two versions, and loci would be chapters Why do we have two versions? • We inherit one from each parent • of the 23 pairs in humans – 22 pairs are autosomes – 1 pair are sex chromosomes • XX females • XY males If we have two sets, than how do our gametes only have one set? • Tetrad = homologues come together, synapsis, (each with sister chromatids) • Crossing over = mixing or exchange of genes between homologues • Note: no Interphase – No duplication of chromosomes Fertilization of sperm and egg produces variety of offspring • 3 places for variation – Tetrad formation and crossing over • Prophase I – Independent assortment • Depends on orientation of chromosomes during Metaphase I & II – Random fertilization • Preferably outside of family • Sites of crossing over = chiasma – Prophase I Karyotype = inventory of chromosomes in mitotic metaphase Karyotyping process • centrifuge? • Purpose / result of hypotonic solution? • Digital arrangement of chromosomes by size & shape • Stained and compared Meiotic abnormalities • Trisomy 21 Down Syndrome Cause? Nondisjunction chromosome pair does not seperate Nondisjunction can also affect sex chromosomes • XXY: male with some female characteristics and underdeveloped sterile testes • XO: female, typically sterile, shorter, decreased development (treated with estrogen supplements)






