Chapter 22 Test Review
advertisement
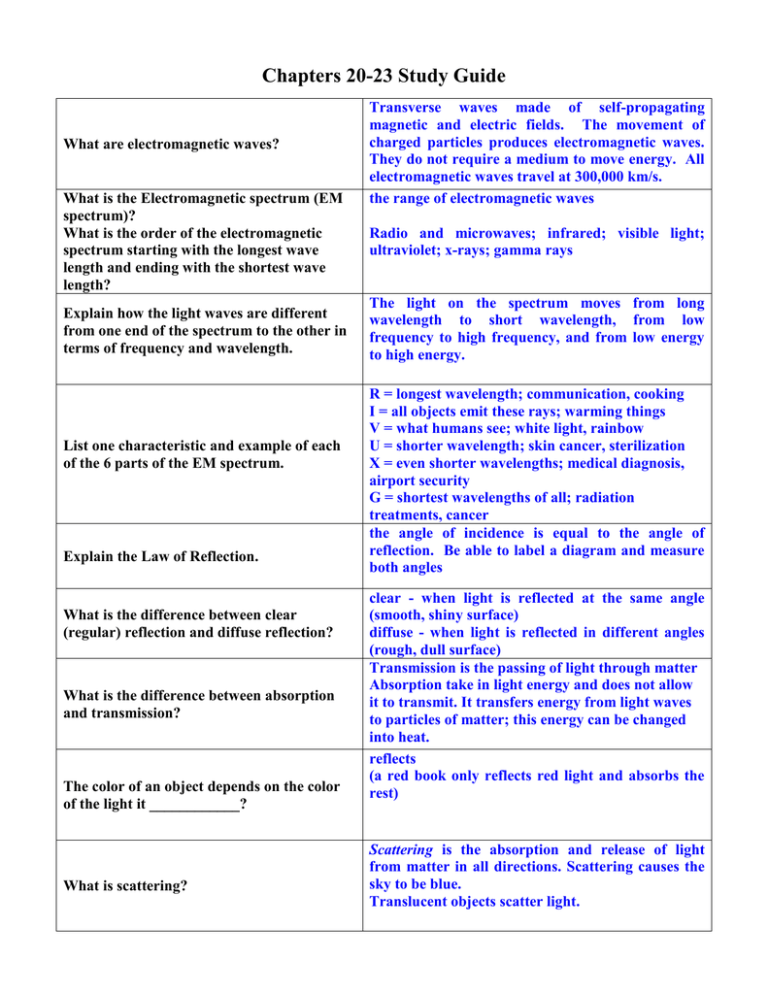
Chapters 20-23 Study Guide What are electromagnetic waves? What is the Electromagnetic spectrum (EM spectrum)? What is the order of the electromagnetic spectrum starting with the longest wave length and ending with the shortest wave length? Explain how the light waves are different from one end of the spectrum to the other in terms of frequency and wavelength. List one characteristic and example of each of the 6 parts of the EM spectrum. Explain the Law of Reflection. What is the difference between clear (regular) reflection and diffuse reflection? What is the difference between absorption and transmission? The color of an object depends on the color of the light it ____________? What is scattering? Transverse waves made of self-propagating magnetic and electric fields. The movement of charged particles produces electromagnetic waves. They do not require a medium to move energy. All electromagnetic waves travel at 300,000 km/s. the range of electromagnetic waves Radio and microwaves; infrared; visible light; ultraviolet; x-rays; gamma rays The light on the spectrum moves from long wavelength to short wavelength, from low frequency to high frequency, and from low energy to high energy. R = longest wavelength; communication, cooking I = all objects emit these rays; warming things V = what humans see; white light, rainbow U = shorter wavelength; skin cancer, sterilization X = even shorter wavelengths; medical diagnosis, airport security G = shortest wavelengths of all; radiation treatments, cancer the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Be able to label a diagram and measure both angles clear - when light is reflected at the same angle (smooth, shiny surface) diffuse - when light is reflected in different angles (rough, dull surface) Transmission is the passing of light through matter Absorption take in light energy and does not allow it to transmit. It transfers energy from light waves to particles of matter; this energy can be changed into heat. reflects (a red book only reflects red light and absorbs the rest) Scattering is the absorption and release of light from matter in all directions. Scattering causes the sky to be blue. Translucent objects scatter light. What material allows all light to be transmitted and no light to be absorbed? Give an example. What material allows some light to be transmitted and absorbed? Give an example. Transparent – clear glass filled with water Translucent – tissue paper or white paper Opaque – black paper or rocks What material allows no light to be transmitted and all light to be absorbed? Give an example. What are the primary colors of light? What are the primary pigments? Primary colors: Red, green and blue will combine to produce white light. Pigments: yellow, cyan and magenta. Pigments absorb some light and reflects others. Black What color do you have if all colors are absorbed and no light is reflected? What is an object that produces light? What is an object that reflects light? Luminous Non-luminous List the 4 properties of light. Light travels in a straight line. Light travels much faster than sound. We see things because they reflect light into our eyes. Shadows are formed when light is blocked by an object. How does the electromagnetic spectrum change from one end to the other? Wavelengths are long and frequency is low at the radio waves end of the electromagnetic spectrum and become short wavelengths and high frequency at the gamma rays end of the spectrum. How do convex mirrors and lenses curve? How do concave mirrors and lenses curve? Which lens or mirror diverges? Which converges light into a single point? curve out curve in Convex lenses & concave mirrors – converge light (bends it in) Concave lenses & convex mirrors – diverges light (bends it out) A concave mirror Light rays refract inward because of the lenses so the focus is on the back of the eye (retina) and a person can see clearly. What type of mirror magnifies? How does refraction through lenses help a person who wears glasses to see? (how do the light rays bend) What are the 5 steps in how light is produced? Explain what a photon is. 1.Electrons move around the nucleus. 2.Electrons absorb energy and jump to a new position. 3.This new position is unstable, so electron returns to its original position. 4.Electrons release a photon when it jumps back to its original position. 5.A stream of photons from the movement of electrons is thought to be EM waves. A photon is a particle-like packet of radiant or light energy. What do waves transfer? Transfer energy from one place to another What is interference? Wave interaction that occurs when 2 or more waves overlap What is the crest of one wave overlapping the crest of another wave producing a larger wave? Give an example. What is the crest of one wave overlapping the trough of another wave producing a smaller wave? Give an example. What is wave interaction in which waves bend around barriers? Give an example. What is the bending of a wave as it passes at an angle from one medium to another? Constructive interference Loud sound, bright light What is when a wave bounces back after striking a barrier? Reflection What is the section of a wave where matter being squeezed together? What is the section of a wave where the particles are less crowded? What type of wave is sound and how is sound produced? What is the difference between a standing wave and a propagating wave? Give an example of each. In what medium is sound fastest? Slowest? How frequency is perceived and how high or low sound is Destructive interference Soft sound, dim light Diffraction hearing sound around a corner Refraction-rainbow, pencil in water Compressions (longitudinal waves only) Rarefactions Sound is a longitudinal, mechanical wave (requires a medium). Sound is produced by vibrating matter. Standing wave does not move. Propagating wave moves. Guitar string and sound in air Fastest in solids like steel / slowest in gases like air; Increases with temperature Pitch If you have a low frequency, what type of pitch will there be? High frequency has what pitch? If you have high amplitude, what type of sound will you have? Low pitch High pitch The larger the amplitude, the louder the sound (in decibels) What is the apparent change in frequency of a wave created by a moving object? Doppler Effect An approaching object like a car will have -Short wavelength and have high frequency = high what type of wavelength and pitch? When it pitch moves away what wavelength and pitch will -Long wavelength and low frequency = low pitch it have? What is the reflection of sound called? What adaptation have some animals Echo developed where they reflect sound waves to Echolocation detect objects and locate food? Study your previous wave and sound quiz. Be able to identify and label both types of waves. Any question on that quiz may (and probably will be) on the test.







