Facultatea de Ştiinţe Economice şi Gestiunea Afacerilor Str. Teodor
advertisement
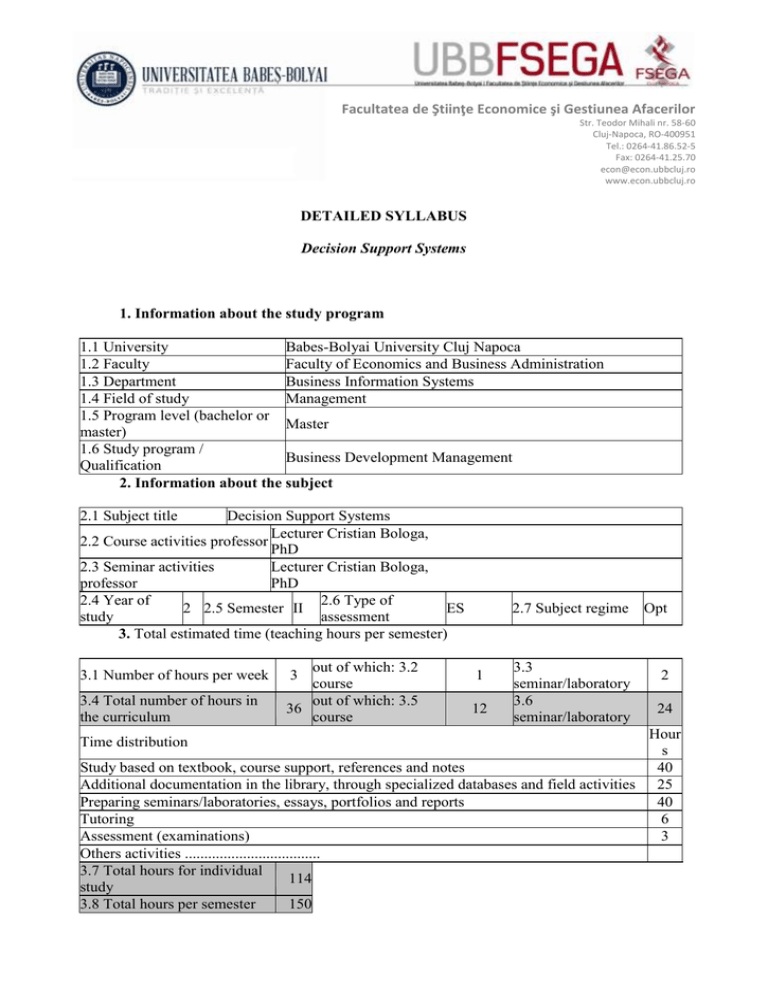
Facultatea de Ştiinţe Economice şi Gestiunea Afacerilor Str. Teodor Mihali nr. 58-60 Cluj-Napoca, RO-400951 Tel.: 0264-41.86.52-5 Fax: 0264-41.25.70 econ@econ.ubbcluj.ro www.econ.ubbcluj.ro Ă DETAILED SYLLABUS Decision Support Systems 1. Information about the study program 1.1 University Babes-Bolyai University Cluj Napoca 1.2 Faculty Faculty of Economics and Business Administration 1.3 Department Business Information Systems 1.4 Field of study Management 1.5 Program level (bachelor or Master master) 1.6 Study program / Business Development Management Qualification 2. Information about the subject 2.1 Subject title Decision Support Systems Lecturer Cristian Bologa, 2.2 Course activities professor PhD 2.3 Seminar activities Lecturer Cristian Bologa, professor PhD 2.4 Year of 2.6 Type of 2 2.5 Semester II ES study assessment 3. Total estimated time (teaching hours per semester) 3.1 Number of hours per week 3.4 Total number of hours in the curriculum out of which: 3.2 course out of which: 3.5 36 course 3 2.7 Subject regime Opt 1 12 3.3 seminar/laboratory 3.6 seminar/laboratory 2 24 Hour s Study based on textbook, course support, references and notes 40 Additional documentation in the library, through specialized databases and field activities 25 Preparing seminars/laboratories, essays, portfolios and reports 40 Tutoring 6 Assessment (examinations) 3 Others activities ................................... 3.7 Total hours for individual 114 study 3.8 Total hours per semester 150 Time distribution 3.9 Number of credits 6 4. Preconditions (if necessary) 4.1 Curriculum Not applicable 4.2 Skills Not applicable 5. Conditions (if necessary) 5.1. For course For course lectures there are necessary: video-projector, whiteboard, development Internet access 5.2. For seminar / For laboratories there are necessary: computer network, Internet access, laboratory video-projector, whiteboard development 6. Acquired specific competences Professiona • Participation in the development and implementation of software applications for l financial accounting competenc • Assist management in decision making es • Preparation of financial statements of the summaries, the reports made for various organizations and analyzes, summaries, forecasts and economic assessment Transversal • Knowledge, explanation and interpretation of ideas, processes, phenomena, competenc status and trends for specific economic activities and development of value es judgments grounded at micro and macro level • Use technology and modern tools for information processing and management of databases for specific economic and social activities 7. Subject objectives (arising from the acquired specific competences) 7.1 Subject’s general objective Understanding of the key technologies used in the management of information and organizations. 7.2 Specific objectives Knowledge of: • types of existing information systems that serve the decisionmaking process: accounting information systems, finance, human resources, sales and marketing, manufacturing and services • decision support systems • executive information systems • office automation systems • intelligent information Systems • e-commerce systems •integrated business management systems; customer relationship management systems; supply chain management systems 8. Contents 8.1 Course Introduction, data, information, knowledge, information society, decisions, types of decisions, the decision-making process Information system, features, components, role of information systems in business Teaching methods Lecture Lecture Observations One lecture One lecture Types of information systems, decision support systems, Lecture Two lectures characteristics, structure, stages of development of a decision support system, benefits Intelligent systems, features; expert systems Lecture One lecture E-business Systems, advantages, disadvantages, risks; Lecture Two lectures Models and categories of e-business, e-commerce categories; legislation on electronic commerce Integrated business management systems; customer relationship Lecture Two lectures management systems; supply chain management systems Data warehouse; On line analytical processing of data; Data Lecture Two lectures mining; Business Intelligence Manifestation of risks in information systems Lecture One lecture References: 1. Vicki L. Sauter -Decision Support Systems for Business Intelligence, Wiley, 2011 2. Simha R. Magal - Integrated Business Processes with ERP Systems, Wiley, 2011 3. France Belanger - Information Systems for Business: An Experiential Approach, Wiley, 2011 4. Marakes G.M., Decision Support Systems in the 21st Century, Second Edition, Prentice Hall, 2002. 5. James O'Brien, George Marakas - Management Information Systems, McGrawHill/Irwin Teaching 8.2 Seminar/laboratory Observations methods Practical aspects regarding the components of a computer system Discussions, One individual laboratory study Business Information Systems; examples Discussions, Two individual laboratories study Decision support systems; examples Discussions, Two individual laboratories study Intelligent systems, expert systems, examples Discussions, One individual laboratory study Ecommerce systems-examples Discussions, Two individual laboratories study Integrated business management-examples Discussions, One individual laboratory study Customer relationship management systems and vendors-examples Discussions, One individual laboratory study Data warehouses, multidimensional data analysis systemsDiscussions, One examples individual laboratory study Data mining, business intelligence -examples Discussions, One individual laboratory study References: 1. Vicki L. Sauter -Decision Support Systems for Business Intelligence, Wiley, 2011 2. Simha R. Magal - Integrated Business Processes with ERP Systems, Wiley, 2011 3. France Belanger - Information Systems for Business: An Experiential Approach, Wiley, 2011 4. Marakes G.M., Decision Support Systems in the 21st Century, Second Edition, Prentice Hall, 2002. 5. James O'Brien, George Marakas - Management Information Systems, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2010 9. Corroboration / validation of the subject’s content in relation to the expectations coming from representatives of the epistemic community, of the professional associations and of the representative employers in the program’s field. Expectations of business area regarding economics graduates conduct to the idea of knowledge of management and information technology used in business management. The role of this discipline is to familiarize students with the new technologies that are beginning to be implemented increasingly in Romanian companies and organizations. 10. Assessment (examination) Type of activity 10.1 Assessment criteria 10.4 Course 10.2 Assessment methods Knowledge about the concepts and Quizzes throughout the technologies presented in the course semester 10.3 Weight in the final grade 10% 40% Written exam with open questions. 10.5 The students has to develop an Seminar/laborat individual project based on ory laboratory activity Theory minimum mark: 5 Project 50% Laboratory minimum mark: 5 10.6 Minimum performance standard • It is necessary to obtain a minimum grade of 5 (five) in order to pass this subject; • The grades being granted are between 1 (one) and 10 (ten); • Students must approach each element (question, problem) within the exam sheet; • The exam is written and takes approximately 50minutes; Date of filling 13.01.2015 Signature of the course professor Lecturer Cristian Bologa, PhD Signature of the seminar professor Lecturer Cristian Bologa, PhD Head of department’s signature: Prof.dr. habil. Cosmin Gheorghe Silaghi Date of approval by the department 28.01.2015