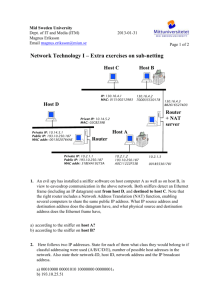
MAC address
advertisement

CCNA 1 v3.1 Module 10 Review 1 What is the address that is changed when a frame is received at a router interface? • MAC address 2 What OSI layer offers reliable, connection-oriented data communication services? • transport 3 What IP packet field will prevent endless loops? • time-to-live 4 Which processes occur each time a packet is switched from one router interface to another? • encapsulation • de-encapsulation 5 Which of the following are routed protocols? (Choose three.) • • • • • • IP BGP XNS RIP OSPF DECnet 6 How would you describe path determination at the network layer? • router compares available routing table information to select the best path 7 What do routers use to exchange topological information? • routing protocols 8 What are 3 metrics used with routing protocols? • delay • cost • reliability 9 What are 2 link-state routing protocols? • OSPF • IS-IS 10 What are 3 benefits of subnetting? • smaller broadcast domains • low-level security provided • increased address flexibility 11 Given a host with the IP address 176.42.75.23 and a default subnet mask, to which network does the host belong? • 176.42.0.0 12 A small company has a class C network license and needs to create eight usable subnets, each subnet capable of accommodating at least 14 hosts. What is the appropriate subnet mask? • 255.255.255.240 13 How many bits are available for Class B host IP addresses using the default subnet mask? • 16 14 What is true concerning the host bits of the network address and the broadcast address? • Host bits of the network address are all equal to 0. • Host bits of the broadcast address are all equal to 1. 15 How many usable subnets are created by applying the subnet mask 255.255.255.0 to a Class B network? • 254 16 What do you call the process that routers use to determine the subnet network address based upon a given IP address and subnet mask? • binary ANDing 17 Which statements describe the effects broadcast storms have on networking equipment? (Choose two.) • Switches forward broadcast storms. • Switches block broadcasts. • Switches handle broadcasts in similar fashion to routers. • Routers can be segmented to increase bandwidth. • Routers block broadcasts. • Routers and switches provide security and bandwidth control to overcome broadcast storms. 18 What information is listed in routing tables? (Choose three.) • • • • • • Protocol types Encapsulations Metrics MAC addresses Inbound interfaces Outbound interfaces 19 What is the routing metric for RIPv1? • hop 20 Which statements describe Layer 2 and Layer 3 packet address changes as the packet traverses from router to router? (Choose two.) • Layer 3 header is removed and replaced at every Layer 3 device. • Layer 2 and Layer 3 addresses do not change when the packet traverse. • Layer 3 source and destination addresses do not change when the packet traverse. • Layer 2 frame header and trailer are removed and replaced at every Layer 3 device. • Layer 2 source and destination addresses do not change when the packet travels. 21 What are two differences between routers and switches? • Routers make forwarding decisions using IP addresses, but switches use MAC addresses. • Switches forward broadcasts and routers do not. 22 What are two functions of a routing protocol? • provides processes for sharing route information • allows a router to communicate with other routers 23 How many usable class C subnetworks are created with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.240? • 14 24 Company XYZ uses a network address of 192.168.4.0. It uses the mask of 255.255.255.192 to create subnets. What is the maximum number of usable hosts in each subnet? • 62 25 Which are the network and broadcast addresses when given an IP host address of 198.101.6.55/27? • Network = 198.101.6.32 • Broadcast = 198.101.6.63 26