Imperialism Around the world
advertisement

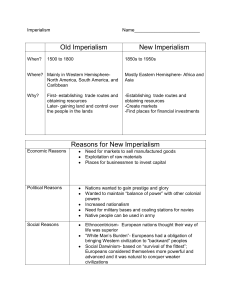
Imperialism Around the world Warm Up: Grab a Map, Color (in red) in all the colonies in Africa who were ruled by Britain. Use page 343 in the textbook or your map. Standard 10.4.2 - Discuss the locations of the colonial rule of such nations as England, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the Netherlands, Russia, Spain, Portugal, and the United States. 10.4.3 - Explain imperialism from the perspective of the colonizers and the colonized and the varied immediate and long-term responses by the people under colonial rule. Objective I will investigate the different countries who imperialized the world in the form of a jigsaw. I will also track the British Empire on my map. Jigsaw • • • • • • • • Work as a table Grab a textbook Read the section you have been assigned Answer the questions on your hand out as thoroughly as possible. The more information the better. Get the answers checked by Mr. Luyau Build your poster, YOU DO NOT NEED TO WRITE THE QUESTIONS (YOU WILL NOT HAVE SPACE). Make it colorful! You have 1 hour and 45 minutes to complete the project Warm Up: Silently Get into your groups and finish your poster. You have 15 minutes Standard 10.4.2 - Discuss the locations of the colonial rule of such nations as England, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the Netherlands, Russia, Spain, Portugal, and the United States. 10.4.3 - Explain imperialism from the perspective of the colonizers and the colonized and the varied immediate and long-term responses by the people under colonial rule. Objective I will summarize the Age of Imperialism through a gallery walk and discuss America’s role in Imperialism. Poster Gallery walk Grab your packet and a pen or pencil Put your poster on your table Move with your group from table to table and write the answers to the questions and color the map accordingly. Read the vocabulary (they may be on the test!). When you are finished, see Mr. Luyau You have 1 hour. Latin America After Independence Colonial Legacy Latin Americans worked for large land owners Could only use their vouchers at the owners supply store Known as peonage Debt accumulated and went from one generation to the next Landowners became wealthy Political Instability Caudillos controlled most of Latin America Juan Vincente Gomez Domingo Sarmiento Ruled Venezuela for 30 years (believed it to be his cattle ranch) Promoted education Faced little opposition because they were supported by wealthy landowners Economies Grow Under Foreign Influence Main trading partners with LA – Britain and US Old Products, New Markets Mostly dependent on exports Sent out beef, fruits and vegetables Imported a lot of US and British manufactured goods With technology the exports grew because of the steamboat and steam train Remained unindustrialized, leading to being imperialized Outside Investment and Interference Built schools, roads and hospitals with what they made from exports Borrowed a lot of money from Britain, France, US, and Germany Took over countries because they could not pay back their debts The Monroe Doctrine Most Latin American countries were independent by the 1800’s United States feared that Europe would try to conquer them James Monroe creates a document to protect the new colonies of the Americas “the American continents… are henceforth not to be considered as subjects for future colonization by any European powers.” United States did not provide a lot of help till Cuba in 1898 Cuba Libre! One of Spain’s last colonies in the Americas Fought a 10 year battle with Spain to gain independence (1868-1878) Failed to become free In 1895, Jose Marti tried to have a second attempt at freedom United States had a good business relationship with Cuba Monroe Doctrine enforced which begins the Spanish American War The US took the Philippines first from the Spanish Catches the Spanish off guard. Once the Philippines are taken, Cuba is taken next US installs a government and takes over Cuba Spain gives up Puerto Rico, Guam and the Philippines to the US for losing the war. Warm Up: What was the Monroe Doctrine and how was it used to start the Spanish American War? Explain it in full. Standard 10.4.2 - Discuss the locations of the colonial rule of such nations as England, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the Netherlands, Russia, Spain, Portugal, and the United States. 10.4.3 - Explain imperialism from the perspective of the colonizers and the colonized and the varied immediate and long-term responses by the people under colonial rule. Objective I will reinforce my knowledge of the age of imperialism through reading notes. Panama! Latin Americans began to call the United States “the Colossus of the North” Transcontinental railroad built from east to west of the United States, but slow The United States wanted a faster way to move product. Set sights on the country of Panama (who was owned by Colombia) Roosevelt offers 10 million + yearly payment but Colombia demands more. United States helps starts a revolution in Panama which is successful US gets 10 miles to build the canal United States controlled the bridge between the Atlantic and the Pacific Ocean Roosevelt Corollary United States had a lot of influence in many South American and Latin American countries for business related reasons Roosevelt issues an extension to the Monroe Doctrine (known as the Roosevelt Corollary) Gave the right for the US to be “an international police power” in the Western Hemisphere This was done to protect American investments Latin Americans did not want American troops in their country but could not protest due to being weak. Turmoil and Change in Mexico Antonio War Lopez de Santa Anna and the Mexican He fought for Mexican independence against Spain and was victorious! Became the first president of Mexico He tried to keep power any way he could (sometimes flip flopping his beliefs) He gave up his presidency to fight for the territory of Texas In the 1820’s, Mexico wanted Americans to move there to help the economy Gave them land if they would follow Mexican law Tensions grew as the population grew over slavery and religion Stephen Austin led a revolt against Mexico in 1835 Texas Revolt and the Fall of Santa Anna Santa Anna leads forces to try to hold Texas Beat the Americans at the Alamo Lost the Battle of San Jacinto Sam Houston releases Santa Anna after he agrees to give Texas independence Santa Anna’s troops were defeated and Santa Anna was captured Santa Anna lost his power upon returning to Mexico Fought with the US one more time over the border of Mexico and Texas Signed the treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo Gave the US the American Southwest and California Exiled after these losses Eventually came back and was forgotten