IPsec – An Introduction
advertisement

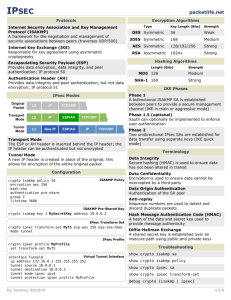
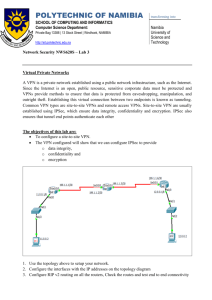
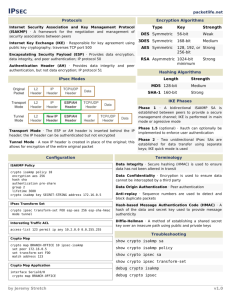
Configuration of a Site-to-Site IPsec Virtual Private Network Anuradha Kallury CS 580 Special Project August 23, 2005 IPsec – An Introduction IPsec is a suite of protocols used to create virtual private networks (VPNs) Creates encrypted tunnel between 2 private networks Authenticates both ends of the tunnel IPsec – An Introduction (Cont’d) Can choose what traffic to encrypt and how to encrypt it Encapsulates and encrypts IP data only (can use GRE for non-IP traffic) IPsec is composed of the following main protocols: Internet Key Exchange (IKE) protocol Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) protocol Authentication Header (AH) protocol IPsec - Fundamental Mechanisms Packet Encapsulation Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) - encrypts and authenticates data Authentication Header (AH) – authenticates data and header Tunnel mode - new IP header appended in front of original IP header of packet Transport mode - uses original IP header of packet Encryption Uses symmetric key algorithms DES or 3DES Integrity Checking Uses Message Authentication Codes using Hashing (HMAC) Hashing algorithms used are MD5 or SHA-1 IPsec Implementation LAN-to-LAN IPsec VPN Also called site-to-site IPsec VPN Merges 2 private networks across a public network Appears as one virtual network with shared resources IKE – An Introduction Responsible for negotiating the details of the IPsec tunnel between the 2 peers Main functions of IKE in IPsec: Negotiate protocol parameters Exchanging public keys Authenticate both ends Managing keys after exchange How IKE Works IKE is a two phase protocol Phase 1 Uses main mode or aggressive mode exchanges between peers Negotiates a secure, authenticated communication channel between the IPsec peers Phase 2 Uses quick mode exchanges between peers Negotiates security associations for the IPsec services IKE - Main Mode The main functions of the main mode (or aggressive mode) are: Agree on a set of parameters that will be used to authenticate the 2 IPsec peers Agree on a set of parameters that will be used to encrypt a part of the main mode and all of the quick mode exchange. Authenticate the 2 IPsec peers to each other Generate keys that can be used to generate the necessary data encryption keys after negotiations are done. IKE - Main Mode (Cont’d) All the information negotiated in main mode is stored as an IKE or ISAKMP security association (SA). There is only one SA between any 2 IPsec peers. IKE - Quick Mode The main functions of the quick mode are: Agree on a set of parameters for creating the IPsec SAs used to encrypt (for ESP) the data between the 2 peers If Perfect Forward Secrecy (FPS) is being used, performs another Diffie-Hellman (DH) exchange to generate new keys for generating the data encryption keys IKE Authentication Mechanisms Preshared Keys Digital Signatures Define the same key on both IPsec peers Simple but not scalable Uses public/private key pairs generated on both IPsec peers Public key is exchanged using a digital certificate that also contains sender info Certificate issued by a certificate authority (CA) server Encrypted Nonces Pseudo-random numbers are encrypted and exchanged by the IPsec peers IPsec Negotiation Using IKE IKE negotiates IPsec tunnels between IPsec peers using one of three main methods: 1. Main mode using preshared key authentication followed by quick mode negotiation 2. Main mode using digital signature authentication followed by quick mode negotiation 3. Aggressive mode using preshared key authentication followed by quick mode negotiation Configuration of LAN-to-LAN IPsec - Network Diagram Responder Initiator 192.1.12.5 192.1.12.20 10.1.1.0/24 Cisco Routers R1 and R2 both running IOS version 12.2.15T11 (including support for IPsec and 3DES) Cisco Catalyst Switch 3550-01 running IOS version 12.1.22(EA1a) 10.1.2.0/24 Configuration of LAN-to-LAN IPsec - Setup of Routers Step 1: Ensure that IKE is enabled Router(config)# crypto isakmp enable Step 2: Create the ISAKMP policy which defines the attributes negotiated between the peers for the IKE SA Router(config)# crypto isakmp policy 1 Router(config-isakmp)# encryption 3des Router(config-isakmp)# hash md5 Router(config-isakmp)# authentication pre-share Router(config-isakmp)# group 1 Router(config-isakmp)# lifetime 14400 priority Configuration of LAN-to-LAN IPsec - Setup of Routers (Cont’d) Step 3: Define the pre-shared key and the IP address of the IPsec peer Router(config)# crypto isakmp key 42DB72B3 address 192.1.12.20 Step 4: Define a transform-set for use with IPsec as follows: Router(config)# crypto ipsec transform-set myset1 esp-3des esp-md5-hmac Step 5: Define the mode associated with the transform-set (optional) Router(cfg-crypto-tran)# mode tunnel Configuration of LAN-to-LAN IPsec - Setup of Routers (Cont’d) Step 6: Define an access list which specifies the interesting traffic for IPsec Can be used to specify “interesting” traffic for IPsec Router(config)# access-list 101 permit ip 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 10.1.2.0 0.0.0.255 Step 7: Define a crypto map The crypto map links together all of the details of the IPsec configuration Router(config)# crypto map mymap1 ipsec-isakmp Configuration of LAN-to-LAN IPsec - Setup of Routers (Cont’d) Step 8: Within the identified crypto map, define the IP address of the IPsec peer Router(config-crypto-m)# set peer 192.1.12.20 Step 9: Within the identified crypto map, define which transform-set is to be used with this crypto map Router(config-crypto-m)# set transform-set myset1 Step 10: Within the identified crypto map, define which access list is to be used with this crypto map Router(config-crypto-m)# match address access-list 101 Configuration of LAN-to-LAN IPsec - Setup of Routers (Cont’d) Step 11: Assign the crypto map to the specific interface of the router on which IPsec traffic will flow Router(config)# interface Ethernet 0/0 Router(config-if)# crypto map mymap1 Step 12: Verify that the defined policy, transform-set, and pre-shared key are the same on both IPsec peers Configuration of LAN-to-LAN IPsec – Viewing IPsec attributes Assigned IPsec attributes can be viewed using following commands: Router# show crypto isakmp policy Router# show crypto isakmp sa Router# show crypto isakmp key Router# show crypto ipsec transform-set Router# show crypto map Router# show crypto ipsec sa Router# show crypto ipsec security-association lifetime Configuration of LAN-to-LAN IPsec – Screenshot1 of Router 1 crypto Configuration of LAN-to-LAN IPsec – Screenshot2 of Router 1 crypto Configuration of LAN-to-LAN IPsec – Screenshot1 of Router 1 config Configuration of LAN-to-LAN IPsec – Screenshot2 of Router 1 config Configuration of LAN-to-LAN IPsec – Screenshot3 of Router 1 config Configuration of LAN-to-LAN IPsec – Screenshot1 of Router 2 crypto Configuration of LAN-to-LAN IPsec – Screenshot2 of Router 2 crypto Configuration of LAN-to-LAN IPsec – Screenshot1 of Router 2 config Configuration of LAN-to-LAN IPsec – Screenshot2 of Router 2 config Configuration of LAN-to-LAN IPsec – Screenshot3 of Router 2 config Configuration of LAN-to-LAN IPsec Debug output on router 1 (initiator) Configuration of LAN-to-LAN IPsec Debug output on router 1 (cont’d) Configuration of LAN-to-LAN IPsec Debug output on router 1 (cont’d) Configuration of LAN-to-LAN IPsec Debug output on router 1 (cont’d) Configuration of LAN-to-LAN IPsec Debug output on router 1 (cont’d) Configuration of LAN-to-LAN IPsec Debug output on router 1 (cont’d) Configuration of LAN-to-LAN IPsec Debug output on router 2 (responder) Configuration of LAN-to-LAN IPsec Debug output on router 2 (cont’d) Configuration of LAN-to-LAN IPsec Debug output on router 2 (cont’d) References Network Security Principles and Practices by Saadat Malik Cisco IOS Security Configuration Guide, Release 12.2 Cisco IOS Security Command Reference, Release 12.2 Cisco IOS Configuration Fundamental Configuration Guide, Release 12.2 Cisco IOS Interface Command Reference, Release 12.2