Gas - LWC Chemistry
advertisement

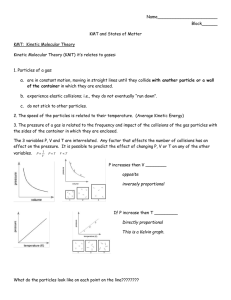
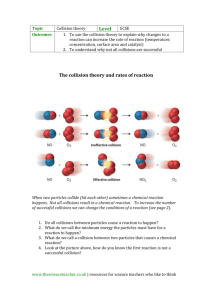
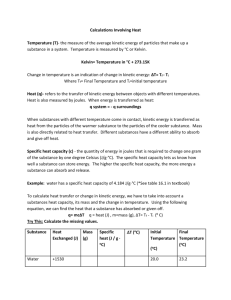
Matter: States of Matter (Gas) 3 States of Matter 1. 2. 3. 4. Solid Liquid Gas Plasma *** http://www.chem.purdue.edu/gchelp/liquids/character.html http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/physics/states-of-matter.html http://www.middleschoolchemistry.com/multimedia/chapter2/lesson5 Gas • Takes the shape and volume of the container • Easily compressed Gas Vs. Vapor • Gas and vapor are often used interchangeably, but there is a difference!! Gas Vs. Vapor • Gas • Substances that exist in the gaseous state at room temperature. • Vapor • A substance that is currently a gas, but normally is a liquid or solid at room temperature. Gas Vs. Vapor • Which is correct: “water gas”, or “water vapor”? Gas • Kinetic refers to motion • Kinetic energy - energy an object has because of it’s motion • Kinetic theory - tiny particles in all forms of matter are in constant motion! Gas #1. Gas is composed of particles • Small, hard spheres • Insignificant volume; far apart from each other #2. Particles in a gas move rapidly in constant random motion #3. Collisions are perfectly elastic- meaning K.E. is transferred without loss from one particle to another • Kinetic Energy and Temperature Kinetic Energy is related to temperature. The faster something is moving, the higher the temperature, the higher the K.E. that particle has. • Please rate the following from least to greatest amount of K.E. • Steam • Water • Ice Pressure • Gas Pressure – Force (F) of a gas per unit surface area –Due to: • F of collisions • # of collisions –No particles present = no collisions no pressure (a.k.a. vacuum) Pressure • Atmospheric pressure results from the collisions of air molecules with objects –↓as you climb a mountain because the air layer thins out as elevation increases Pressure • The SI unit of pressure is the pascal (Pa) –Other units: • kPa • mm Hg • atmospheres (atm)