Using Keele data to demonstrate efficiency and effectiveness
advertisement

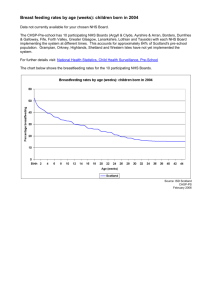
Using Keele data to demonstrate efficiency and effectiveness Jim Allison Background SCBMDN has to engage with the Keele benchmarking process. Improve the consistency of the data returned by Scottish labs Seek to influence the introduction of new questions within the Keele database Enable greater use of this data to plan service delivery Background : Background : National Pathology Benchmarking Service at Keele University Performance management tool. Peer comparison of key indicators. Internal comparison of year on year performance. Separate data collection and benchmark reports are offered for Clinical Biochemistry, Haematology/Blood Transfusion, Histopathology/Cytology, Immunology and Microbiology/Virology. Background : Keele Benchmarking – difficult and time consuming process. Questionnaires sent out electronically during April 2012. Completed questionnaires returned to Keele in June Data checking exercise undertaken. Data is processed at Keele, and a specialist panel - made up of clinicians from the relevant discipline - meet to discuss the data. Panel write a commentary on the findings, providing interpretation of the data which is included in the final report. Generic report produced in December for each participant, plus a separate analysis tool enabling you to drill down into the data further and create their own charts and tables. In January, participants are invited to a user group meeting, where the findings of the report are discussed, and the participants get the opportunity to influence future development of the programme Keele and the SCBMDN 1. What information /markers of efficiency and effectiveness Keele provides the SCBMDN. 2. Identify areas of inconsistency. 3. Recent interactions of the SCBMDN with Keele. 4. What the SCBMDN might do with Keele in the future. Keele Information: Workload Staffing Finance Efficiency & productivity Quality & effectiveness Engagement with Keele: SCBMDN questionnaire (Sept 2011); 8 out of 15 Health Boards responded. Efficiency and Productivity Cost per test and request Requests and Tests per WTE Effectiveness A&E turnaround times Other ideas Keele Information: Keele Information: Biochemistry is a local lab for local people. There’s no need for benchmarking here!!! Keele Information: Test Workload per 1000 Population Health Board Children Adults Total Ayrshire & Arran 63,210 299,850 363,060 Borders 19,840 92,050 111,890 Dumfries & Galloway 24,430 122,190 146,620 Fife 64,610 293,160 357,770 Forth Valley 53,670 232,770 286,440 Grampian 95,620 441,550 537,170 Greater Glasgow & Clyde 207,670 975,050 1,182,720 Highland 53,010 250,970 303,980 Lanarkshire 105,580 451,900 557,480 Lothian 140,450 676,880 817,330 Orkney 3,380 16,560 19,940 Shetland 4,220 17,940 22,160 Tayside 67,750 325,070 392,820 Western Isles 4,440 21,510 25,950 Keele Information: Workload: Like for Like U&E? Serum Creatinine Workload per 1000 Population Creatinine 500 400 300 200 Lab / Region NHS Tayside NHS Lothian WG St John's RIE NHS Lanarkshire NHS Highland NHS GGC Aberdeen Forth Valey Fife 0 Borders 100 Ayrshire & Arran Cereat Req /1000 pop 600 Keele Information: Workload: Like for Like TFTs? TSH & FT4 workload per 1000 Population Tests Per 1,000 GP Population: T4 (Free) 300 Tests Per 1,000 GP Population: TSH 200 150 100 Region NHS Tayside NHS Lothian NHS Lanarkshire NHS Highland NHSGGC NHS Grampian NHS Forth Valley NHS Fife 0 NHS Borders 50 NHS Ayrshire & Arran Req / 1000 Pop 250 Keele Information: Workload: Like for Like Lipids? Chol, Trig & HDL Workload Per 1000 Pop Triglyceride Cholesterol HDL (+D-LDL) 300 200 150 100 Region NHS Tayside NHS Lothian NHS Lanarkshire NHS Highland NHS GGC Aberdeen Fife Borders 0 Forth Valley 50 Ayrshire & Arran Req /1000 Pop 250 Keele Information: Workload: Like for Like HbA1c? HbA1c and Micro Alb Workload per 1000 Population 100 Albumin/Microalbumin (urine) 90 HbA1c 70 60 50 40 30 20 Region NHS Tayside NHS Lothian NHS Lanarkshire NHS Highland Aberdeen Forth Valley Fife Borders 0 NHS GGC 10 Ayrshire & Arran Req /1000 Pop 80 Keele Information: Staffing All Teaching Non Teaching Total Medical Staff (including Trainees) -14.76% -13.63% -19.39% Total WTE Biomedical Scientists -3.47% -4.48% -1.78% WTE MLA / Support Workers -3.05% -1.29% -6.23% Total WTE Clinical Scientists -12.24% -10.73% -15.99% % Change 2010-2011 Lab / Region Western Isles 70 Tayside 80 Western General 90 St John's Hospital 100 RIE RHSC NHS Lanarkshire Highland South Glasgow North Glasgow Clyde Elgin Aberdeen Forth Valley Fife Borders Ayrshire and Arran Numbers of Staff Keele Information: Staffing Lab Staff AfC band 4 and Below + Band 5 and Above Total Staff: AfC Band 4 and Below Total Staff: AfC Band 5 and Above 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 0 Lab / Region Western Isles Tayside Western General 3 St John's Hospital RIE RHSC NHS Lanarkshire Highland South Glasgow North Glasgow Clyde Elgin Aberdeen Forth Valley Fife Borders Ayrshire and Arran pay cost/ test (£) Keele Information: Finance Total Pay Cost Per Test 3.5 Total Pay Cost Per Test 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 Lab / Region Western Isles Tayside Western General 0.8 St John's Hospital RIE NHS Lanarkshire Highland South Glasgow North Glasgow Clyde Elgin Aberdeen Forth Valley Fife Borders Ayrshire and Arran pay cost/ test (£) Keele Information: Finance Total Pay Cost Per Test 0.9 Total Pay Cost Per Test 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 Lab / Region Western Isles Tayside Western General 0.7 St John's Hospital RIE NHS Lanarkshire Highland South Glasgow North Glasgow Clyde Aberdeen Forth Valley Fife Borders Ayrshire and Arran pay cost/ test (£) Keele Information: Finance Total Pay Cost Per Test 0.8 Total Pay Cost Per Test 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 Keele Information: Finance Biomedical Scientists Out of Hours Payments (Including Trainees) £1,200,000 Biomedical Scientists Out of Hours Payments (Including Trainees) £1,000,000 £600,000 £400,000 £200,000 Lab / Region Western Isles Tayside Western General St John's Hospital RIE RHSC NHS Lanarkshire Highland South Glasgow North Glasgow Clyde Elgin Aberdeen Forth Valley Fife Borders £0 Ayrshire and Arran Cost (£) £800,000 Keele Information: Efficiency and Productivity i) Efficiency – Cost per test and cost per request. ii) Productivity - Number of tests per WTE. Keele Information: Cost per Request PMS says …. No! Lab /Region Western Isles Tayside WG 4.5 St John's RIE RHSC Lanarkshire Raigmore Oban Caithness Belford South Glasgow North Glasgow Clyde Elgin Aberdeen Forth Valley Fife Borders Ayrshire and Arran Cost (£) Keele Information: Efficiency Total Pay and Non Pay Cost per Test Total Pay Cost Per Test Total Non Pay Cost Per Test 4 Grand Total 3.5 3 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 Keele Information: Efficiency Total Pay and Non Pay Cost per Test Total Pay Cost Per Test Total Non Pay Cost Per Test 1.2 Grand Total 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 Lab /Region Tayside WG St John's RIE Lanarkshire South Glasgow North Glasgow Clyde Aberdeen Forth Valley Fife Borders 0 Ayrshire and Arran Cost (£) 1 Lab/Region Western Isles Tayside Western General 200000 180000 160000 140000 120000 100000 80000 60000 40000 20000 0 St John's RIE RHSC Lanarkshire Oban South Glasgow North Glasgow Clyde Elgin Aberdeen Forth Valley Fife Borders Ayrshire and Arran Tests /Total WTE Keele Information: Productivity Tests Per Total WTE Staff Tests Per Total WTE Staff Keele Information: Productivity Tests Per Total WTE Staff 180000 160000 Tests Per Total WTE Staff 120000 100000 80000 60000 40000 20000 Lab/Region Tayside West Gen St John's RIE Lanarkshire South Glasgow North Glasgow Clyde Aberdeen Forth Valley Fife Borders 0 Ayrshire and Arran Tests/WTE 140000 Keele Information: Efficiency and Productivity These workload variations do not impact significantly on Keele efficiency and productivity figures. Tot Tests Tot Expend Total WTE Cost / Test Tests / WTE Average Lab 5,000,000 £3,500,000 48 £0.70 104,166 Plus extra 80,000 FT4, 50,000Trigs and 30,000HbA1C 5,160,000 £3,540, 000 48 £0.69 107,291 Keele Information: Quality & Effectiveness Accreditation status A&E TATs Keele Information: Effectiveness Keele - U&E TAT for A&E What is the target TAT for U&E requests from A&E? What proportion of A&E requests for U&E are reported within this target? 0 Lab Location Western Isles Tayside WG St John's RIE RHSC Lanarkshire Raigmore Oban Caithness Belford South Glasgow North Glasgow Clyde Elgin Aberdeen Forth Valley Fife Borders U&E Target TAT for A&E 140 120 100 70 80 60 60 50 40 40 30 20 20 10 0 % Within Target Ayrshire & Arran TAT (Min) Keele Information: U&E TAT for A&E Target TAT for U&E % of requests reported within this target 100 90 80 Keele Information: Future Inclusion of RCPath KPIs KPI: A&E blood sciences turn-around-times Baseline: Percentage of core investigations, i.e. renal function, liver function tests and full blood counts from A&E completed within 1 hour of receipt, including out of hours Challenge: 85% by Apr 2012 increasing to 90% by Apr 2014. The standard will move to 1 hour from sample collection by April 2015. SCBMDN: Agreement to adopt this RCPath KPI. Keele Information: Effectiveness Vetting Work Referred to Outside Laboratories Identifying Duplicate Requests and Standard Rejection Procedure Providing Requestors with Key Performance Indicators Participation in Training Events for Requestors and Utilisation of Order Comms for Education Disease/Symptom-specific Profiles, Requestor/Gradespecific Testing, Clinical Pathway Development Processes to Improve the Efficiency and Quality of Service Does your clinical biochemistry laboratory have a formal risk management policy ? Quality and Effectiveness SCBMDN engagement with Keele Engagement with Keele: SCBMDN New Questions in Keele Availability of clinical advice. Repertoire of tests available on an emergency basis? Communication of critical results; timeliness and number/ frequency. Number of urgent/emergency requests processed in last year? What percentage of reports contain interpretative comments? Number of complaints /critical incidents SCBMDN & KEELE Availability of Clinical Advice Q2-5-1 Which member(s) of staff provide clinical interpretative advice? UA When does this service operate? Is this 24 hours per day, 365(6) days per year? If no please state start and finish time (please use the format HH:MM) Start time Finish time Q2-5-2 Monday to Friday UA 09:00 17:00 Q2-5-3 Saturday UA 09:00 17:00 Q2-5-4 Sunday UA 09:00 17:00 Q2-5-5 Public Holiday UA 09:00 17:00 SCBMDN & KEELE Plasma/Serum/Blood Test Name Column 1 Total Tests Inhouse Column 2 Number of Tests Performed for Primary Care Column 3 Column 4 Tests Referred Out (change to 'yes' only if you refer the test out) Is Test Provided as an Emergency (change to 'yes' only if available 24/7, 365) 1,25 Hydroxy Vitamin D UA No No 11-Deoxycortisol UA No No 17 Hydroxy Progesterone UA No No 25 Hydroxy Vitamin D UA No No ACTH UA No No Adrenaline UA No No Albumin UA No No Alcohol (Ethanol) UA No No UA Ongoing Dialogue with Keele Getting more out of the existing questionnaire Incorporating further markers of effectiveness Invitation to David Holland to attend SCBMDN meeting later this year. END Example of Improvement in Clinical Effectiveness of Laboratory Service NHSG Primary Care – ongoing problem with spurious hyperkalaemia due to long transportation times. Jan 2010, <20% of SST samples from primary care spun at source. Centrifugation of SST tubes in primary care practices introduced in July 2010. Jan 2011, 95% of SST samples from primary care spun at source Clinical Effectiveness Retrospective audit conducted to review the impact on patient care of introduction of centrifugation in primary care: a) Pre-GP centrifugation Jan – June 2010 b) Post-GP centrifugation Jan – June 2011 Classification of follow-up of hyperkalaemia Appropriate admission: Genuine hyperkalaemia in a GP sample resulting in admission to acute medical receiving where the hyperkalaemia has been confirmed Appropriate GP follow-up: Genuine hyperkalaemia in a GP sample resulting in a repeat sample from the GP where the hyperkalaemia has been confirmed Inappropriate admission: Pseudohyperkalaemia in a GP sample due to delay in sample centrifugation resulting in admission to acute medical receiving where the follow-up serum potassium is within the reference interval Inappropriate GP follow-up: Pseudohyperkalaemia in a GP sample due to delay in centrifugation resulting in a repeat sample from the GP where the follow-up serum potassium is within the reference interval Effectiveness of follow-up of primary care patients with hyperkalaemia Sample centrifugation in primary care locations in NHSG has proven to be an excellent example in improving the clinical effectiveness of an existing laboratory investigations, whereby the same test deployed now secures a greater health gain for patients from the available resource.