Unit 3 * Evolution Lesson 1 * Mutations and Artificial Selection
advertisement

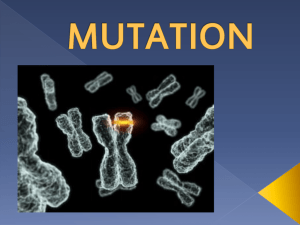
What is evolution and why is it important? The mechanism that drives evolution is natural selection. Natural Selection: the way in which nature favours the reproductive success of some individuals within a population over others. Genetic diversity must be present for nature to favour some individuals over other Mutations are the source of genetic variation What mechanisms have we studied that increases this genetic diversity? Substitution A substitution is a mutation that exchanges one base for another (i.e., a change in a single "chemical letter" such as switching an A to a G). -Such a substitution could cause a small change in the protein produced. For example,sickle cell anemia is caused by a substitution in the beta-hemoglobin gene, which alters a single amino acid in the protein produced. Heritable disease Codominant Chronic pain caused by RBCs moving through blood vessels. Stroke, other cardiovascular complications Insertion Insertions are mutations in which extra base pairs are inserted into a new place in the DNA. Deletion Deletions are mutations in which a section of DNA is lost, or deleted. Neutral mutation - a mutation that does not result in any selective advantage or disadvantage. Harmful mutation - any mutation that reduces the reproductive success of an individual and is therefore selected against; harmful mutations do not accumulate over time Beneficial mutations - are favoured by natural selection and accumulate over time Artificial selection - directed breeding in which individuals that exhibit a particular trait are chosen as parents of the next generation; artificial selection is used to produce new breeds or varieties of plants and animals 1. Choose a useful species that can be bred in captivity. 2. Breed a large number of individuals. 3. Choose a trait that you wish to favour, such as large size, a particular colour, or sweetness. 4. Identify individuals that exhibit the favoured trait most strongly. 5. Breed only these individuals to produce the next generation of individuals. 6. Repeat Steps 4 and 5 over many generations. Artificial Selection is limited by the genes that are present in the current population.