Unit 10: Evolution
advertisement

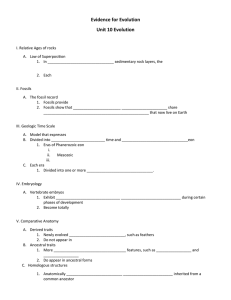
UNIT 10: EVOLUTION BIOLOGY CP WARM UP • Present Day Giraffes are believed to have evolved from ancestors that resembled a horse. There have been different theories about how this could have occurred. The two main ideas are listed on your handout. • Which of these 2 theories do you agree with most? Explain your position in as much detail as possible. GALLERY “WALK” • Each group will be given 2 minutes to look at each of the following diagrams (to be provided by teacher). • For each diagram you need to record one thing about evolution you know or observe from the diagram. You must also write a question or comment relating to what you want to know about evolution in relation to the diagram. • Pass the given table with the corresponding diagram to the next group. Group # 1 2 3 4 5 What do you know? What do you want to know? TIMER http://www.timeanddate.com/timer/ MISCONCEPTION VIDEO https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mZt1Gn0R22Q WHO IS THE FATHER OF EVOLUTION? Why, that’s CHARLES DARWIN, of course!! Evolution Darwin on the HMS Beagle A. Darwin’s role 1. Naturalist i. Collect biological and geological specimens 2. Companion to the captain Evolution The Galápagos Islands A. Darwin collected mockingbirds, finches, and other animals on the four islands 1. Noticed different islands seemed to have slightly different varieties of animals A. Almost every specimen that Darwin had collected on the islands was new to European scientists B. Populations from the mainland changed after reaching the Galápagos • http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/darwin/origin/inde x.html ADAPTATIONS https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-IiP-9VzY9w DARWIN OBSERVATION GAME Are you as observant as Charles Darwin? I have removed an object from the classroom, see if you can determine what has been removed! WARM UP 1: EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION 1. 2. 3. 4. What are fossils? What is the geologic time scale? When was the origin of the earth? Which layer of rock is the oldest, which is the youngest? EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION UNIT 10 EVOLUTION I. RELATIVE AGES OF ROCKS A. Law of Superposition 1. In horizontal sedimentary rock layers, the oldest layer is at the bottom 2. Each upper layer (higher layer) is younger than those below II. FOSSILS A. The fossil record 1. Fossils provide a record of species that lived long ago 2. Fossils show that ancient species share similarities with species that now live on Earth III. GEOLOGIC TIME SCALE A. Model that expresses major geological and biological events in Earth’s history B. Divided into Precambrian time and Phanerozoic eon 1. Eras of Phanerozoic eon i. ii. iii. Paleozoic Mesozoic Cenozoic C. Each era 1. Divided into one or more periods IMAGINE GEOLOGIC TIME SCALE AS A FOOTBALL FIELD (WE WILL USE THIS LATER) FOSSIL ROCK ANTHEM • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ClJ5lwl_wM0 IV. EMBRYOLOGY A. Vertebrate embryos 1. Exhibit homologous 2. structures during certain phases of development Become totally different structures in the adult forms EMBRYOLOGY ACTIVITY http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/evolution/guessembryo.html • In this activity we will try and determine which adult animal matches an embryo V. COMPARATIVE ANATOMY A. Derived traits 1. Newly evolved features, such as feathers 2. Do not appear in the fossils of common ancestors B. Ancestral traits 1. More primitive features, such as teeth and tails 2. Do appear in ancestral forms V. COMPARATIVE ANATOMY CONT. C. Homologous structures 1. Anatomically similar structures inherited from a common ancestor E. ANALOGOUS TRAITS E. Analogous structures 1. that have similar form or function, but were not present in the last common ancestor of those groups **** write at bottom of notes V. COMPARATIVE ANATOMY CONT. D. Vestigial Structures 1. Structures or reduced forms of functional structures (little to no purpose) GEOLOGIC TIME SCALE ACTIVITY • You and your table partner will be working as a pair to determine where on the geologic time scale (football field) different events in time are located. • You will be taking turns making a human bar graph (1 partner at a time will stand on the “football field” and estimate where you think these events occurred. WARM UP 2: EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION ** (Earth= 4.6 billion years old) 1. What is the geologic time scale? 2. What is a derived trait? Give an example. 3. What is an ancestral trait? Give an example. 4. What is the difference between homologous and analogous structures? NATURAL SELECTION I. NATURAL SELECTION A. B. C. Individuals in a population show variations D. Variations that increase reproductive success will have a greater chance of being passed on Variations can be inherited Organisms have more offspring than can survive on available resources II. VARIATIONS A. Variation: any difference between individuals of the same species III. TYPES OF ADAPTATIONS A. Adaption 1. Trait shaped by natural selection 2. Increases an organism’s reproductive success B. Types 1. Camouflage 2. Mimicry 3. Other coloration patterns IV. FITNESS A. Fitness 1. Measure of relative contribution an individual trait makes to the next generation MICE VIDEO http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/making-fittest-naturalselection-and-adaptation WARM UP 3: ANGRY BIRD LAB 1. What was the variation seen in the Angry birds? 2. Which bird was best fit for the environment (think about the adaptations)? As stated in the lab, many people think that adapting to the environment and evolving are a choice. Based on this lab, were you able to change or adapt by choice? 3. What happened to the birds that were not able to get enough food (2 or less seeds)? 4. What happened to the animals that were able to get a lot of food (10 or more seeds)? 5. How does this affect the future population? ** Have vocab and angry bird out and ready!! TYPES OF SELECTION EVOLUTION I. IMPORTANT TERMS A. Frequency 1. How often something is occurring B. Mean 1. Average THINK ABOUT Does Natural Selection act on the individual or the population? II. SEXUAL SELECTION A. evolution within a population 1. observable change in the allele frequencies 2. can result from natural selection III. NORMAL DISTRIBUTION A. graphs as a bell-shaped curve. 1. highest frequency near mean value 2. frequencies decrease toward each extreme value B. A population follows a normal distribution when: 1. Traits not undergoing natural selection have a normal distribution. IV. TYPES OF SELECTION A. Directional selection favors phenotypes at one extreme. 1. Ex. Bacteria and high drug resistance IV. TYPES OF SELECTION A. Stabilizing selection favors the intermediate phenotype. 1. Ex. Size of gall fly CHECK FOR UNDERSTANDING How might the extinction of the woodpecker affect the phenotypic distribution of the gall fly? IV. TYPES OF SELECTION C. Disruptive selection favors both extreme phenotypes. 1. Ex. Body color in male lazuli buntings CHECK FOR UNDERSTANDING If bluish brown coloring became advantageous for young males, what type of selection would likely occur? WARM UP 4: TYPES OF SELECTION 1. 2. Describe an organism and the environment it lives in. What is one trait that natural selection works upon in this organism? What is doing the selecting ex: predator or temperature (basically, what is causing these organisms to be successful or die off)? 3. What type of selection distribution is occurring? 4. Draw out a graph of the selection distribution for your organism. I. GENETIC DRIFT A. change in allele frequencies due to chance, causes a loss of genetic diversity. B. How it works 1. It is most common in small populations. 2. Due to a chance event allele frequencies are increased, decreased, or even eliminated I. GENETIC DRIFT A. Genetic drift has negative effects on a population. 1. Decreases genetic variation 2. Less likely to have some individuals that can adapt 3. Harmful alleles can become more common due to chance SURVIVAL OF THE SEXIEST https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4Ezc3aO4RSk II. SEXUAL SELECTION A. occurs when certain traits increase mating success and become common in the population B. How it works 1. Females preferentially mate with males that display certain traits 2. Those traits are passed on to offspring and become exaggerated each generation. SAGE GROUSE https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1KdOvNSDxws II. SEXUAL SELECTION C. There are two types of sexual selection. 1. 2. intrasexual selection: competition among males intersexual selection: males display certain traits to females SEXUAL SELECTION DOCUMENTARY https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4j7GSu99LmY WARM UP 5: GENETIC DRIFT/ SEXUAL SELECTION 1. 2. What are the 2 types of sexual selection? In sexual selection why do males have the exaggerated traits and not females? 3. What is genetic drift? 4. Genetic drift decrease ___________ _________ 5. Genetic drift usually occurs in these types of populations. ** Turn in make your own species SPECIATION I. SPECIATION A. The rise of two or more species from one existing species 1. Isolated populations adapt to their own environments a. Isolated = no gene flow 2. Genetic differences can add up over generations to make new species II. TYPES OF ISOLATION A.Reproductive isolation 1. members of different populations cannot mate successfully 2. final step to becoming separate species II. TYPES OF ISOLATION B. Behavioral isolation 1. Differences in courtship or mating behaviors prevents reproduction between populations a. Examples: 1. Firefly and light patterns 2. Bird dances 3. Whale songs BEHAVIORAL ISOLATION http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nS1tEnfkk6M II. TYPES OF ISOLATION C. Geographic Isolation 1. physical barriers divide a population into two or more groups a. Example: Isthmus of Panama separating Pacific and Atlantic Oceans GEOGRAPHIC ISOLATION http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WDPsZPKSEFg II. TYPES OF ISOLATION D. Temporal Isolation 1. timing of reproductive periods or courtship prevents reproduction between populations a. Example: Different flowering/pollination times in plants BILL NYE, ANYONE? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=svHQ4BQY__o