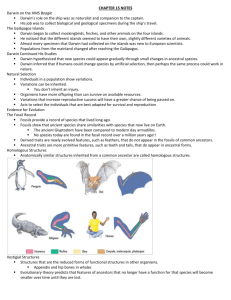
Evidence for Evolution Unit 10 Evolution
advertisement

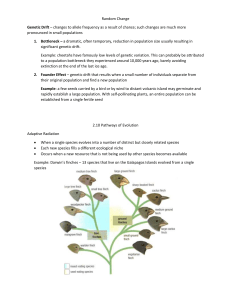
Evidence for Evolution Unit 10 Evolution I. Relative Ages of rocks A. Law of Superposition 1. In ________________________________ sedimentary rock layers, the 2. Each II. Fossils A. The fossil record 1. Fossils provide 2. Fossils show that _______________________ ______________________ share ___________________________________________________ that now live on Earth III. Geologic Time Scale A. Model that expresses B. Divided into __________________________ time and ________________________________eon 1. Eras of Phanerozoic eon i. ii. Mesozoic iii. C. Each era 1. Divided into one or more ________________________________. IV. Embryology A. Vertebrate embryos 1. Exhibit _______________________________ _____________________________ during certain phases of development 2. Become totally V. Comparative Anatomy A. Derived traits 1. Newly evolved ___________________________, such as feathers 2. Do not appear in B. Ancestral traits 1. More ___________________________________ features, such as _________________ and _________________ 2. Do appear in ancestral forms C. Homologous structures 1. Anatomically ___________________________ ________________________ inherited from a common ancestor D. Vestigial Structures 1. Structures or _____________________________ _________________________ of functional structures Cloze Notes: Types of Selection and Genetic Drift I. Natural selection A. Individuals in a population B. Variations C. Organisms have D. Variations that increase ____________________ ___________________ will have a greater chance of being passed on II. Variations A. Variation: III. Types of Adaptations A. Adaption 1. Trait shaped by 2. Increases an organism’s B. Types 1. 2. 3. Other IV. Fitness A. Fitness 1. Measure ______________ __________________ an individual trait makes to the I. Important terms 1. 2. II. Sexual selection A. evolution 1. __________________ change in the _______________ _______________________ 2. can result from III. Normal Distribution A. Graphs as a 1. highest frequency 2. frequencies decrease B. A population follows a normal distribution when: 1. Traits ____________________________________________________________________ have a normal distribution. IV. Types of selection A. Directional selection favors 1. Ex. Bacteria and high drug resistance B. Stabilizing selection favors 1. Ex. Size of gall fly IV. Types of Selection C. Disruptive selection favors 1. Ex. Body color in male lazuli buntings I. Genetic Drift A. Change in _________________ _______________ due to chance, causes a loss of B. How it works 1. It is most common in small populations. 2. Due to a chance event allele frequencies are ______________________, __________________, or ______________ II. Sexual selection A. occurs when certain traits B. How it works 1. Females preferentially mate 2. Those traits are passed on I. Genetic Drift A. Genetic drift has negative effects on a population. 1. Decreases 2. less likely to have some individuals 3. B. Genetic drift has negative effects on a population. 1. Decreases 2. less likely to have 3. harmful alleles can become II. Sexual Selection C. There are two types of sexual selection. 1. intrasexual selection: 2. intersexual selection: