Space Norm Line Timeline
advertisement
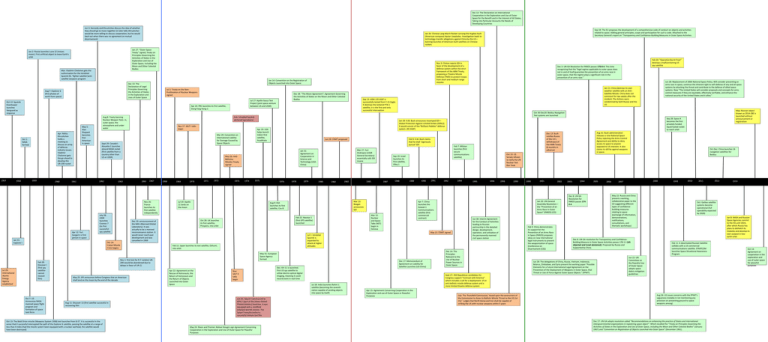
Dec 13: The Declaration on International Cooperation in the Exploration and Use of Outer Space for the Benefit and in the Interest of All States, Taking into Particular Accounts the Needs of Developing Countries Jun 3: Kennedy and Khrushchev discuss the idea of whether they should go to moon together (in later talks Khrushchev would be more willing to discuss cooperation, but he would back out when there was no agreement on mutual disarmament) Jan 26: Chinese Lang March Rocket carrying the Hughes-built (American company) Apstar-1explodes. Investigation leads to technology-transfer allegations against China by the US— banning launches of American-built satellites on Chinese rockets Jan 27: “Outer Space Treaty” signed; Treaty on Principles Governing the Activities of States in the Exploration and Use of Outer Space, including the Moon and Other Celestial Bodies Jan 2: Russia launches Luna 12 (misses moon). First artificial object to leave Earth’s orbit Mar: Vladimir Chelomei gets the authorization for the Istrebitel Sputnik (lit. ‘fighter satellite’)antisatellite weapons program Jul 1: Treaty on the NonProliferation of Nuclear Weapons signed Oct 12: Sputnik Eisenhower launches Vanguard as response Apr: Nikita Khrushchev holds a meeting to discuss an array of defense industry issues. Vladimir Chelomei gets the go ahead to develop the UR-200 rocket Oct 1: NASA formed 1957 1958 1959 1960 1961 Aug 8: Treaty banning Nuclear Weapon Tests in, outer space, the atmosphere and under water 1963 Nov 26: France launches its first satellite independently Apr 12: Yuri Gargarin is first person in space July 28: USSR launches Cosmos 7 (its first successful spy satellite Jan 31: Explorer I Jul 29: International Atomic Energy Agency established Oct 7: US Announces NASA manned space flight program and formation of space task force 1970 1971 1972 1973 1974 1975 Oct 13: The Bold Orion missile (Weapons System 199B) test launches from B-57. It is successful in the sense that it successful intercepted the path of the Explorer 6 satellite, passing the satellite at a range of less than 4 miles (had the missile system been equipped with a nuclear warhead, the satellite would have been destroyed) 1978 1979 1980 1982 Feb 22: Navstar 1 (first GPS satellite) launched Oct 28: UK launches its first satellite, Prospero, into orbit 1983 1985 1987 1988 1989 1990 1991 1992 1994 Mar 12: Nuclear and Space Talks (NST) begin in Geneva Jul 1: Istrebitel Sputnik is expanded to attack at higher altitudes May 31: European Space Agency formed Apr 22: Agreement on the Rescue of Astronauts, the Return of Astronauts and the Return of Objects Launched into Outer Space Nov: SALT II talks begin Dec 17: Memorandum of Agreement on Liability for Satellite Launches (US-China) Dec: KH-11 is launched. First US spy satellite to utilize electro-optical digital imaging, meaning it could record event in real-time Jul 18: India launches Rohini 1 satellite (becoming the seventh nation capable of sending objects into space by itself) Jun 25: Salyut 3 (announced as OPS-2 [part of the Almaz Orbital Piloted Stations) launches. It was equipped with a modified onboard aircraft cannon. The Salyut 3 would conduct a successful remote test fire. May 24: Nixon and Premier Aleksei Kosygin sign Agreement Concerning Cooperation in the Exploration and Use of Outer Space for Peaceful Purposes 1995 1996 1998 1999 Jun 30: Interim Agreement for the Conduct of Activities leading to Russian partnership in the detailed design, development, operation, and utilization of the permanently manned civil space station May 13: START signed Dec 14: The Principles Relevant to the Use of Nuclear Power Sources in Outer Space Sept 27: 350 Republican candidates for Congress support “Contract with America” which includes a call for a deployment of an anti-ballistic missile defense system and a more limited theatre defense system Apr 15: Agreement Concerning Cooperation in the Exploration and use of Outer Space or Peaceful Purposes Oct-Dec: China launches 16 navigation satellites for Beidou Oct 13: US Senate refuses to ratify the UN Nuclear Test Ban Treat 2000 2001 2002 Jan 20: UN General Assembly Resolution— the “Prevention of an Arms Race in Outer Space” (PAROS) (CD) Apr 7: China launches the Asiasat-1 Communications satellite (first commercial contract) Aug 31: Bush administration releases a new National Space Policy rejecting the Arms Control Agreement and ability to deny access to space to anyone opposed to US interests. It also claims to still be against weapons in space. Dec 13: Bush notifies Russia of the US’s withdrawal of the AMB Treaty (6 months in advance) Feb 7: Milistar launches (first secure communications satellite) Sep 19: Israel launches its first satellite, Ofeq 1 Mar 23: Reagan announces SDI Aug 9: ESA launches its first satellite, Cos-B Nov 1: first test for R-7 rockets( UR200 would be abandoned due to delays in favor of UR-2) Aug 11: Discover 13 (first satellite successful in recovering film 1976 Feb 11: Japan launches its test satellite, Oshumi, into orbit May 25: JFK announces before Congress that an American shall land on the moon by the end of the decade Mar 27: Yuri Andropov (USSR General Secretary) essentially calls SDI insane Jan 31: Agreement on Cooperation in Science and Technology (USAChina) Jul 20: Apollo 11 lands on the moon Dec 10: announcement of the MOL (Manned Orbital Laboratory). It was actually to be a manned reconnaissance station. It would never reach past development and was cancelled in 1969 Oct 14: Cuban Missile Crisis begins Feb 28: Discover I (first spy satellitecannot recover film) 1969 May: Russian object known as 2014-28E is launched without announcement or registration Sep 28: Space X becomes the first privately funded liquid fueled rocket to reach orbit Feb 9: H.W. Bush claims that he shall ‘vigorously pursue’ SDI Jun 29: START proposed May 26: AntiBallistics Missiles Treaty signed 1968 Jan 11: China destroys its own weather satellite with an AntiSatellite Missile. China does not comment for two weeks after the incident. The Actions were condemned by both Russia and the US Jan 29: H.W. Bush announces revamped SDI— Global Protection Against Limited Strikes (GPALS) It would consist of the “Brilliant Pebbles” defense system. (KE ASAT) Apr 19: USA helps launch India’s first satellite, Aryabhata Mar 29: Convention on International Liability for Damage Caused by Space Objects 1967 Jun 28: Replacement of 2006 National Space Policy. Will consider preventing an arms race in space, continue the inherent right to self-defense of any and all space systems by attacking the threat and contribute to the defense of allied space systems. Now “The United States will consider proposals and concepts for arms control measures if they are equitable, effectively verifiable, and enhance the national security of the United States and it allies.” Oct 30-Dec20: Beidou Navigation Test systems are launched Nov 17: SALT I talks begin 1965 Feb 20: “Operation Burnt Frost” destroys a malfunctioning US spy satellite Dec 3: UN GA Resolution for PAROS passes 178-0-4. This time recognizing that the “legal regime applicable to outer space does not in and of itself guarantee the prevention of an arms race in outer space, that the regime plays a significant role in the prevention of an arms race.” Sep 13: ASM-135 ASAT is successfully tested from F-15 Eagle. It destroys the Solwind P78-1 satellite, it is the first and only successful interception Feb: Istrebitel Sputnik declared operational Sept 29: Canada’s Alouette 1 launches aboard NASA rocket (first satellite from a country other than US or USSR) 1962 Dec 18: “The Moon Agreement”; Agreement Governing the Activities of States on the Moon and Other Celestial Bodies Jul 17: Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (joint space venture between US and USSR) Apr 24: PRC launches its first satellite, Dong Fang Hong-1 May 5: Alan Shepard becomes first American in space Nov 3: Clinton rejects SDI in favor of the development of a defense system within the strict framework of the ABM Treaty, proposing a Theatre Missile Defense (TMD) to protect troops from short and medium range missiles Jan 14: Convention on the Registration of Objects Launched into Outer Space Dec 13: The Declaration of Legal Principles Governing the Activities of States in the Exploration and Uses of Outer Space Aug 7: Explorer 6 (first photos of earth from space) Sep 18: The EU proposes the development of a comprehensive code of conduct on objects and activities related to space. Adding general principles, scope and participation for such a code. Attached to the Secretary General’s report on “Transparency and Confidence-Building Measures in Outer Space Activities July: The ‘Rumsfeld Commission,’ based upon the assessment of the Commission to Asses to Ballistic Missile Threat to the US (Jul 15),” judges that North Korea and Iran shall be capable of striking the US with nuclear weapons within 5 years Feb 9: China demonstrates its support for the Prevention of an Arms Race in Space (PAROS) proposes ideas on new international legal instruments to prevent the weaponization of space (Conference on Disarmament [CD]) 2003 2004 2005 2006 2008 2007 May 22: Russia and China present a working, collaborative paper to the CD suggesting different types of confidencebuilding measures relating to space (exchange of information, demonstrations, notifications, consultations, and thematic workshops) Dec 8: UN GA Resolution for PAROS passes 1740-4 Dec 8: UN GA resolution for Transparency and ConfidenceBuilding Measure in Outer Space Activities passes 178-1-1 (US objected and Israel abstained). Proposed by Russia and Supported by China. Jun 28: The delegations of China, Russia, Vietnam, Indonesia, Belarus, Zimbabwe, and Syria present the working paper “Possible Elements for a Future International Legal Agreement on the Prevention of the Deployment of Weapons in Outer Space, that Threat or Use of Force Against Outer Space Objects “ (PPWT) 2009 2010 2011 2012 2014 Oct: Galileo satellite systems become operational (full operability expected by 2020) Jan 8: NASA and Russian Space Agencies commit to the ISS until 2024, after which Russia has plans to dethatch its modules and develop its own outpost in lowearth orbit Feb 11: A deactivated Russian Satellite collides with a US commercial communications satellite. STRATCOM launches Space Situational Awareness Program Jun 15: UN Committee on the Peaceful Use of Outer Space adopts space debris mitigation guidelines Aug 26: US issues concerns with the PPWT’s vagueness (notably in not mentioning any provision on preventing ground to space weapons among) Dec 17: UN GA adopts resolution called “Recommendations on enhancing the practice of States and international intergovernmental organizations in registering space object”. Which recalled the “Treaty on Principles Governing the Activities of States in the Exploration and Use of Outer Space, including the Moon and Other Celestial Bodies” (January 1967) and “Convention on Registration of Objects Launched into Outer Space” (December 1961). Oct 14: Agreement on cooperation in the exploration and use of outer space for peaceful purposes Article IV States Parties to the Treaty undertake not to place in orbit around the Earth any objects carrying nuclear weapons or any other kinds of weapons of mass destruction, install such weapons on celestial bodies, or station such weapons in outer space in any other manner. The Moon and other celestial bodies shall be used by all States Parties to the Treaty exclusively for peaceful purposes. The establishment of military bases, installations and fortifications, the testing of any type of weapons and the conduct of military maneuvers on celestial bodies shall be forbidden. The use of military personnel for scientific research or for any other peaceful purposes shall not be prohibited. The use of any equipment or facility necessary for peaceful exploration of the Moon and other celestial bodies shall also not be prohibited.






