Food Chains
advertisement

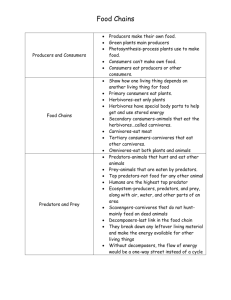
Created by Mr. Hemmert Science ALCOS L5.3 Tracing the flow of energy through a food chain Example: producer, first-level consumer, second-level consumer, and third-level consumer Food Chains Every organism needs to obtain energy in order to live. Plants get energy from the sun, some animals eat plants, and some animals eat other animals. Living things depend on one another to live. Food Chains consumer A food chain is the movement of food energy in a sequence of living things. producer consumer consumer consumer Food Chain Vocabulary Consumers that are eaten are called prey. A consumer that eats prey is a predator. Prey and Predators Predators limit the number of prey animals in a habitat. Ex. Wolves are predators of antelope. They keep the population of antelope from increasing too much, so the antelope don’t eat all of the producers. Predators often compete for the same prey. This limits the number of predators in a habitat. Level of Producers Primary Producers - Organisms that make their own food from sunlight. Primary producers are always the base (bottom) of the every food chain. Levels of Consumers First Level Consumers are animals that eat producers (plants). They are also called herbivores (planteaters) Levels of Consumers Second Level Consumers eat first level consumers. They are called carnivores (meat – eaters) and omnivores (animals that eat both animals and plants.) Levels of Consumers Third level consumers eat second level consumers. Practice What is the primary producer? _________________________ What is the first-level consumer? _________________________ What is the second - level consumer? ______________________ _ What is the third-level consumer? ________________________ Practice leaf bird Primary Producer: _______________ snail First-level Consumer: _____________ Second-level Consumer: __________ Third-level Consumer: ____________ fox Decomposer: ___________________ bacteria Resources Microsoft Online