2-Column Notes
advertisement
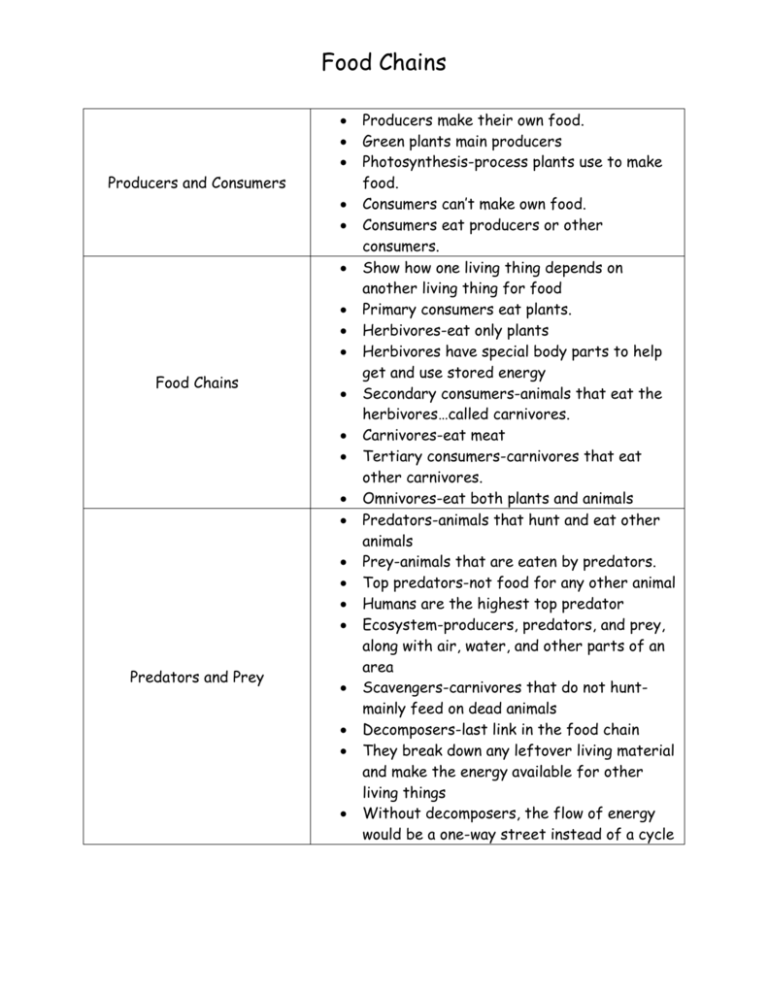
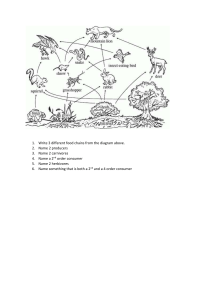
Food Chains Producers and Consumers Food Chains Predators and Prey Producers make their own food. Green plants main producers Photosynthesis-process plants use to make food. Consumers can’t make own food. Consumers eat producers or other consumers. Show how one living thing depends on another living thing for food Primary consumers eat plants. Herbivores-eat only plants Herbivores have special body parts to help get and use stored energy Secondary consumers-animals that eat the herbivores…called carnivores. Carnivores-eat meat Tertiary consumers-carnivores that eat other carnivores. Omnivores-eat both plants and animals Predators-animals that hunt and eat other animals Prey-animals that are eaten by predators. Top predators-not food for any other animal Humans are the highest top predator Ecosystem-producers, predators, and prey, along with air, water, and other parts of an area Scavengers-carnivores that do not huntmainly feed on dead animals Decomposers-last link in the food chain They break down any leftover living material and make the energy available for other living things Without decomposers, the flow of energy would be a one-way street instead of a cycle Food Webs Energy Pyramid Survival Food web is a complex web of relationships between living things Many food chains put together Ocean food webs, forest food webs Energy pyramids show how energy is lost as it passes from one part of a food chain ot food web to the next Only a fraction of the energy from one level is used at the next Energy is lost from movement, digestion and reproduction Less energy is available as you move up One-tenth of the energy is passes along at each level Need more producers than consumers More primary consumers than secondary consumers More secondary consumers than tertiary consumers Food chains can’t have too many links, 4 or 5 competition-fighting for the same resources each species have adaptations that help its members find what they need to survive adaptations-special body parts or behaviors changes in an ecosystem make it hard for living things to survive changes effect other levels in chain diseases, natural disasters, and human caused threats (oil spills, pesticides) can harm food chains invasive species-species introduced and do harm to an ecosystem (foxes in Alaksa)