The Carbon Cycle - MsPetersensScienceScholars
advertisement

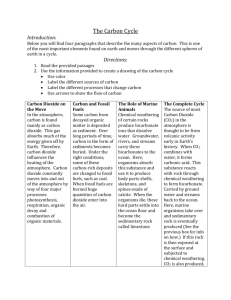
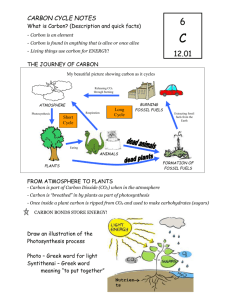
March 11, 2013 Q-2 Pg. Daily Goal: We will be able to explain why we never run out of carbon. Homework: Complete your daily carbon cycle log (to be passed out this class period). Science Starter: 1. Draw a picture of a flower and label the following parts: stem, roots, leaves, petals, anther, stamen, pistil, ovary, stomata, guard cells. 2. List all the ways that you can think of that the flower would interact with its environment. Include biotic and abiotic factors, and processes. You should be able to think of at least 8. What is matter? The Law of Conservation of Matter - matter cannot be created or destroyed, only rearranged or recycled Are rocks matter? How do rocks get rearranged or recycled? One characteristic of living things is that they carbon are ________________ based. Raise your hand if you can name the element that should go in the blank! Carbon is important because all life on Earth is based on carbon. The Carbon Cycle – a series of processes through which all of the carbon atoms in the world recycle All Carbon is found in the atmosphere (the air) and oceans as the gas carbon dioxide (CO2). life on earth is based on carbon. Open burning Photosynthesis Respiration Atmospheric CO2 Respiration Fuel Combustion Fuel Combustion Photosynthesis Dissolved CO2 Respiration Death and decay Death and decay Fossil fuels What is one process that we already know of that puts carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere? Respiration BOTH plants and animals release CO2 into the air through cellular respiration For example: Humans breathe in oxygen and breathe out CO2. What is one process that we already know of that takes carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere? Photosynthesis CO2 is taken out of the air by plants through photosynthesis. Plants “breathe in” or exchange CO2 and “breathe out” O2. It’s a cycle! Who can explain how this cycle is evidence of the Law of Conservation of Matter. CO2 O2 Decomposition – bacteria, fungi, and other organisms breakdown dead plants, animals and waste into carbon dioxide gas and solid carbonates Fossil Fuels – when living things decompose and the carbon atoms DO NOT find oxygen atoms to bond with, they turn into fossil fuels The fossil fuels we use now formed from the bodies of prehistoric organisms that were buried under layers of sediment. Fossil fuels include: Coal Petroleum Natural Gas Coal was formed from prehistoric trees, ferns and mosses. There are large deposits of coal in the Appalachian region. Where is the Appalachian region? Petroleum and natural gas are from prehistoric plankton and bacteria. Fossil fuels can be burned by automobiles, releasing carbon back into the atmosphere. How does burning fossil fuels change the carbon cycle? (It’s helpful to draw it) What will happen if we burn all of the fossil fuels that we have? Are fossil fuels renewable resources? (Remember, a renewable resource is something that can be created as fast as we use it.) How does carbon move from the air to plants? How does carbon move from plants into the bodies of animals? Where is solid carbon found? Where is carbon dioxide gas found? How does carbon move back into the air from plants and animals? How do decomposers contribute to the carbon–oxygen cycle? Use the plant that you drew for the Science Starter. ANSWER: How is it part of the carbon cycle? DRAW: Diagram how the carbon cycle would work in relation to your plant.