Free Enterprise PowerPoint
advertisement

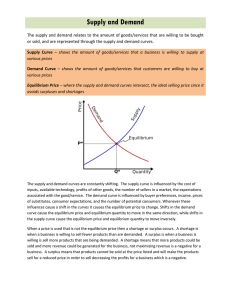
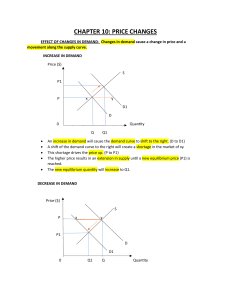
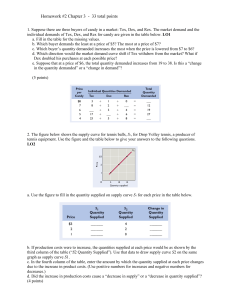
Free Enterprise System In Introduction to Economics Philosophy that our nation’s founders believe that individuals should have the freedom of choice. In theory, the free enterprise system encourages individuals to start and operate their own businesses without government involvement. Competition Struggle between companies for customers that is both healthy and vital to out free enterprise system. Price Competition Focuses on the sale price of a product. Non-price Competition Businesses choose to compete on the basis of factors that are not related to price. Competition, cont. Direct Competition Product or brand which competes in the same product category. Indirect Competition A product that is in a different category altogether but which is seen as an alternative purchase choice. Competition, cont. Monopoly Exclusive control over a product or the means of producing it. Are Monopolies Fair? Risk The potential for loss or failure. Profit The money earned from conducting business after al costs and expenses have been paid. Economic Benefits of Successful Firms Vs. Economic Cost of Unprofitable Firms The Role of Government: 1. Provide general services (fire, police, education) 2. Support business (SBA, loans for businesses) 3. Regulates business (worker, business protection) 4. Competes with small business (TVA, Mail, Amtrack) The Role of Consumers: 1. Pick the winners 2. Determine how much demand 3. Keep it a customer oriented society Economic Systems System by which a nation decides how to use its resources to produce and distribute goods and services. 3 Basic Economic Questions: What is produced? How is it produced? For whom is it produced for? Economic Systems, cont. By answering the 3 basic questions, you will fit into 1 of 2 categories. Market Economy No government involvement in economic decisions. Command Economy The government answers the economic questions. What countries economies are a pure market or pure command? Mixed Economies Capitalism The economic market system characterized by private ownership of businesses and marketplace competition. Socialist Increased amount of government involvement in order to reduce the differences between rich and poor. Communist Totalitarian--that means that the government runs everything. Mixed Economy, cont. Privatization Process of selling government-owned business to private individuals. Factors of Production Economist term for resources. Capital The money needed to start and operate a business, which also includes the goods used in the production process. Labor All the people who work in the economy. Land Refers to everything in its natural state. Entrepreneurhsip Refers to the skills of the people who are willing to risk their time and money to run a business. Production, cont. Infrastructure The physical development of a country, which includes the roads, ports, sanitation facilities, and utilities. Resources All the things used in producing goods and services. Scarcity The difference between needs and wants, and available resources. Unlimited Needs & Wants Limited Resources Scarcity Choices What How For Whom Economics Basics Demand Refers to consumer willingness and ability to buy products. Supply The amount of goods producers are willing to make and sell. Equilibrium Exists when the amount of product supplied is equal to amount of product demanded. Economics Basics, cont. Surplus Occurs when supply exceeds demand. Shortages Occurs when demand exceeds the supply. The Demand Schedule and Demand “Curve” for MP3 songs. Demand curve Demand schedule The demand curve slopes downward because of the law of demand $1.25 $1.00 Price Price $ 1.25 $ 1.00 $ 0.75 $ 0.50 $ 0.25 Quantity Demanded 8 14 20 26 32 $0.75 $0.50 D $0.25 $- 2 8 14 20 Quantity 26 32 The prices of related goods: Substitutes and Complements • • Substitutes are goods that are related in such a way that in increase in the price of one good leads to an increase in demand for the other good Complements are goods that are related in such a way that an increase in the price of one leads to a decrease in the demand for the other The Supply Schedule and Supply “Curve” for MP3s Supply curve $1.25 S $1.00 Price Supply schedule Quantity Price Supplied $ 1.25 28 $ 1.00 24 $ 0.75 20 $ 0.50 16 $ 0.25 12 $0.75 $0.50 The supply curve slopes upward because of the law of supply $0.25 $8 12 16 20 Quantity 24 28 Changes in Supply Changes in supply can be caused by changes in, Technology The prices of resources used in production (input prices = wages, interest, rent) Producer expectations The number of producers Market equilibrium “a snap shot” P D S In equilibrium, the plans of buyers match the plans of sellers Pe a.k.a. the market clearing price Qe Q Market Schedules and Equilibrium for MP3s Price $ 1.25 $ 1.00 $ 0.75 $ 0.50 $ 0.25 Quantity Supplied 28 24 20 16 12 Market schedules Quantity Surplus or Demanded Shortage 8 Surplus of 20 14 Surplus of 10 20 Equilibrium 26 Shortage of 10 32 Shortage of 20 Price Fall Fall Remain the same Rise Rise Business Cycle Reoccurring movement or changes in the economy that goes through four stages: Prosperity Period of economic growth. Recession Period of economic slowdown. Depression Period of prolonged and deep recession. Recovery Period of renewed economic growth. Productivity The output per worker hour. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) The measure of the goods and service produced using labor and property located in this country. Gross National Product (GNP) Everything produced by U.S. citizens here or abroad. Standard of Living Measurement of the amount of goods and services that a nation’s people have. Inflation Rising Prices. Consumer Price Index (CPI) Measures the change in price over a time of some 400 specific goods and services used by the average urban household.