Supply

The amount of a good or service that is available
Producers offer more of a good or service as its price increases and less as its price falls
Quantity supplied: how much of a good or service a producer is willing and able to sell at a specific price
Ceteris paribus, if a firm increases the price of a good or service, it will increase the firms profits When price goes up, suppliers recognize the chance to make money & more suppliers want to enter the market
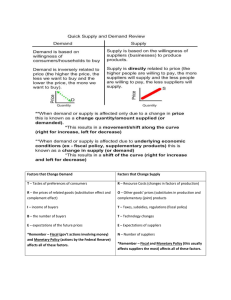
Shows the relationship between prices and quantity supplied
A graphic representation of the supply schedule
Similar to demand curve except now it measures the quantity of the
goods supplied not demanded
Measures how firms will respond to changes in the price of a good or service
How many workers do you hire?
Marginal product of labor: change in output from hiring one of labor increases as the number of workers increase
Specialization worker
Diminishing marginal returns: when adding more workers increases total output but at a decreasing rate Limited capital
Negative marginal returns: workers get in each others way, overall output decreases
Profit = Total revenue – Total cost
Several factors can cause a supply curve to shift
Number of suppliers
Government actions
Global events
But very important influence = suppliers’ input costs
Non-price determinants that alter supply shift the entire curve to the right or left
Subsidy: government payment that supports a business or market
Quota: Government imposed trade restriction
Excise Tax: tax on the production or sale of a good
Large share of goods and services consumed by Americans is imported
Supply is affected by conditions in other countries
Indian wages are raised, what happens to the supply of carpets made in India?
Which was does the curve shift?
The US imports oil from Russia,
Russia experiences a new oil discovery. What happens to the supply curve?
You’re a soybean farmer and you expect prices of soybeans to double next month, what would you do with the crops you just harvested?
How does that affect supply in the soybean market for this month?
Number of suppliers in the market
If more suppliers enter, supply rises
If suppliers leave the market, supply falls
When prices rise, people enter the market
Prices are affected by laws of supply and demand, and government action
The point at which supply and demand come together is called Equilibrium
Point of balance
Quantity demanded = quantity supplied
Buyers will by as much as firms are willing to sell
Quantity supplied is not equal to quantity demanded
Any other price than equilibrium
Shortage
Surplus
Shortage: (excess demand)
Quantity demanded > quantity supplied
Actual price is below equilibrium price
Surplus (Excess supply)
Quantity supplied > quantity demanded
Actual price of is higher than equilibrium price
Price ceiling: Government imposed maximum price that can be legally charged for a GorS
Price floor: Minimum price set by government that must be paid for a GorS
Changes in supply and demand upset market equilibrium
Markets tend towards equilibrium, meaning price & quantity will gradually move towards equilibrium