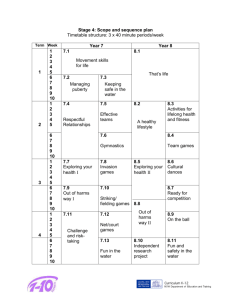
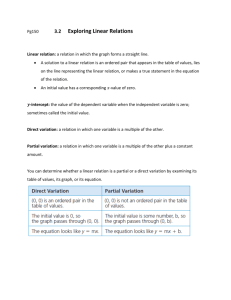
Section 1 Exploring the World of Business (cont'd.)

The World of Business and Accounting
Making Accounting Relevant
Owning and operating a business takes special skills and traits.
What skills do you think are important for the person who owns and operates a business?
Section 1 Exploring the World of
Business
What You’ll Learn
Profit and risk-taking.
The free enterprise system.
Starting and running your own business.
Three types of business operations.
Three forms of business organization.
Section 1 Exploring the World of Business (cont'd.)
Why It’s Important
In order to participate in the world of business, you’ll want to understand how businesses are formed, organized, and operated.
Section 1 Exploring the World of Business (cont'd.)
Key Terms
free enterprise system
profit
loss
entrepreneur
capital
service business
merchandising business
manufacturing business
sole proprietorship
partnership
corporation
charter
Section 1 Exploring the World of Business (cont'd.)
The Environment of Business
In a free enterprise system people are free to produce the goods and services they choose.
Nike
IBM
local video rental store
clothing boutiques
local grocers
Tower Records
Section 1 Exploring the World of Business (cont'd.)
The Need for Profit
The amount of money earned over and above the amount spent to keep the business operating is called profit.
Businesses that spend more money than they earn operate at a loss.
The Need for a Risk-Taker
Entrepreneurs transform ideas for products or services into real-world businesses.
Section 1 Exploring the World of Business (cont'd.)
Entrepreneurship: Who Me?
Have you ever considered owning a business?
Pros
Cons
You are your own boss
You probably need to work long hours.
You create opportunities for earning money.
You create and control your work schedule.
You lose the security of steady wages and medical benefits an employer provides.
You choose the people you serve.
You market your own services or products.
You select the people who work with you.
You pay for your own operating expenses.
You benefit from the rewards of your own hard work.
You must be motivated and energetic each day.
You choose your own work hours.
You face the possibility of losing money.
Section 1 Exploring the World of Business (cont'd.)
Types of Business Operations
Service Businesses
Merchandising Businesses
Manufacturing Businesses
Section 1 Exploring the World of Business (cont'd.)
Forms of Business Organizations
Sole proprietorship
Partnership
Corporation
Section 1 Exploring the World of Business (cont'd.)
Sole Proprietorship
A business owned by one person.
Advantages:
Easy to set up
Disadvantages:
Limited expertise
All profits go to owner Hard to raise money
Owner has total control Owner has all the risks
Few regulations to follow
Hard to attract talented employees
Section 1 Exploring the World of Business (cont'd.)
Partnership
A business owned by two or more persons, who agree to operate the business as co-owners.
Advantages:
Easy to start
Skills and talents are pooled
More money available
Disadvantages:
Conflicts between partners
Profits must be shared
Owners share all risks
Section 1 Exploring the World of Business (cont'd.)
Corporation
A business organization that is recognized by law to have a life of its own.
Advantages:
Easier to raise money
Easy to expand
Easy to transfer ownership
Losses limited to investment
Disadvantages:
Costs more to start up
Complex to organize
More regulations
Higher taxes
Section 1 Exploring the World of Business (cont'd.)
Check Your Understanding
Would you say that the advantages of being an entrepreneur outweigh the disadvantages or vice versa? Why?
Section 1 Exploring the World of Business (cont'd.)
You work as a sales clerk at the Gap. The fall merchandise has come in, and the store manager has asked you to price the crewneck sweaters at
25% over cost. A sweater costs 15 wholesale. What is the retail price? With a 6 percent sales tax, what is the cost of the sweater to the customer? If the
Gap sold 100 sweaters at that price, what would the profit be?
Section 2 Accounting: The
Universal Language of
Business
What You’ll Learn
How the accounting system works.
Who uses financial accounting reports.
Who uses management accounting reports.
How accounting is used to help make business decisions.
What assumptions provide the foundation for accounting systems.
Section 2 Accounting: The Universal Language of
Business (cont'd.)
Why It’s Important
Understanding accounting systems is the key to understanding business.
Key Terms
accounting system
manual accounting system
computerized accounting system
GAAP
financial reports
financial accounting
management accounting
business entity
accounting period
going concern
Section 2 Accounting: The Universal Language of
Business (cont'd.)
The Accounting System
Designed to collect, document, and report on financial transactions affecting the business.
manual accounting system
computerized accounting system
generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP)
financial reports
Section 2 Accounting: The Universal Language of
Business (cont'd.)
How the Accounting System
Works
Inputs
Source
Documents
Checks
Invoices
Sales
Slips
Receipts
Processing
Tasks
Analyzing
Classifying
Recording
Outputs
Financial and
Management
Accounting
Reports
Financial condition
Results of operations
Investments by and distributions to owners
Section 2 Accounting: The Universal Language of
Business (cont'd.)
Using Accounting Reports for
Making Business Decisions
There are two groups that use accounting reports:
individuals outside the business who have an interest in the business
individuals inside the business
Section 2 Accounting: The Universal Language of
Business (cont'd.)
Financial Accounting
Financial accounting focuses on reporting information to external users.
Who Uses Financial Accounting
Reports?
potential investors
individuals and institutions, such as banks, that loan money to a business
local, state, and federal governments
workers, consumers, union leaders, and competitors
Section 2 Accounting: The Universal Language of
Business (cont'd.)
Management Accounting
Management accounting focuses on reporting information to management.
Managers
Section 2 Accounting: The Universal Language of
Business (cont'd.)
Accounting Assumptions
business entity – the business records are held independently of personal financial activities
accounting period – most common is one year
going concern – assumes the business has the ability to survive and operate indefinitely
Section 2 Accounting: The Universal Language of
Business (cont'd.)
Check Your Understanding
Consider creating an “accounting system” for your personal finances.
1.
How would you organize the system?
2.
What inputs would there be?
3.
How might you record your activities?
4.
How might you report on those activities?