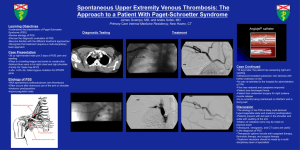
Towards a Meta-model for Description of Sociotechnical
advertisement

Towards a meta-model for the description of the sociotechnical perspective on ProductService Systems Christoph Hollauer, Julian Wilberg, Sebastian Maisenbacher, Mayada Omer Product Development © 2015 Prof. Lindemann Technische Universität München Towards a meta-model for the description of the sociotechnical perspective on PSS | Julian Wilberg | XX. Month 20145 1 Agenda Motivation Background Research Methodology Approach Result: Initial Metamodel for sociotechnical systems Conclusion & Outlook Product Development © 2015 Prof. Lindemann Technische Universität München Towards a meta-model for the description of the sociotechnical perspective on PSS | Julian Wilberg | XX. Month 20145 2 Motivation • Initial Situation – Product-Service Systems (PSS) combine products and services – Competitive advantage and potential for increased sustainability – Result: Increased complexity during development process – PSS represent sociotechnical systems (STS): Close coupling of social and technical systems that influence each other • Problems: – Additional complexity of sociotechnical systems in use phase – Technical and social systems need equal consideration in development phase – Difficulty analyzing sociotechnical systems: Lack of comparability Metamodel to describe sociotechnical system during use phase Product Development © 2015 Prof. Lindemann Technische Universität München Towards a meta-model for the description of the sociotechnical perspective on PSS | Julian Wilberg | XX. Month 20145 3 Background Layer 0 Layer 1 Layer 2 Layer 3 Product Development © 2015 Prof. Lindemann models modeling language meta²-model ... ... . . . Layer n • Metamodels Definition: „Model of a modeling language“ or „model of models (plural)“ Metamodels and its modeling languages are capable to describe all relevant aspects of a subject under consideration in describes conforms to metamodel in meta modeling language describes conforms to model meta² modeling language in modeling language represented by Subject under consideration (Sociotechnical Systems) [1],[2] Technische Universität München Towards a meta-model for the description of the sociotechnical perspective on PSS | Julian Wilberg | XX. Month 20145 4 Background • Ontologies Metamodels offer syntax, ontologies offer semantics for a modeling language „Formal, explicit specification of a shared conceptualization“ • PSS Integration Framework (PSSIF) PSSIF focuses on capturing different modeling approaches A Framework for the cross- disciplinary development of PSS Flexible and extensible Allows the transformation of various discipline-specific models Element * has Edge Attribute Node has 1-2 isConnected Product Development © 2015 Prof. Lindemann [3], [4], [5], [6] Technische Universität München Towards a meta-model for the description of the sociotechnical perspective on PSS | Julian Wilberg | XX. Month 20145 5 Research Methodology Literature-based approach • Research of existing approaches for modeling Literature Review Existing metamodels Root concepts and relationships „PSSycle“ Case Study Concrete Models Abstraction of concrete models Metamodel • Identification of root concepts and their relationships • Modeling of an academic PSS case study • Abstraction of created models Modeling approach Product Development © 2015 Prof. Lindemann Technische Universität München Towards a meta-model for the description of the sociotechnical perspective on PSS | Julian Wilberg | XX. Month 20145 6 Examples for existing PSS/STS Ontologies Roy et al. 2011 [7] • • • • • Kim et al. 2009 [8] Ontology on PSS research No Evaluation Relationships not fully detailed Some sociotechnical aspects addressed Different focus: Improve communication of toplevel PSS concepts • • Generic description of actors, not further elaborated Focus on representation of value, function, and structures as well as the relationships between them Müller & Sakao 2010 [9] • • • Nine “PSS design dimensions” Actors characterized briefly No concrete language elements for the modeling of PSS designs defined Alter 2009 [10] • Metamodel for sociotechnical systems • Different underlying understanding of sociotechnical systems more focused on individual-task relationship and work system Wu et al 2015 [11] • Framework for model integration • „STS element hierarchy“ • Technical system addressed, but not structured further • No PSS context: Services not explicitly addressed Product Development © 2015 Prof. Lindemann Technische Universität München Towards a meta-model for the description of the sociotechnical perspective on PSS | Julian Wilberg | XX. Month 20145 7 Results of Literature Review • Metamodels exist with focus on specific aspects – of PSS modeling – of STS modeling • Sociotechnical root concepts have been identified – E.g. Organizations, organizational layout etc. • Relationships between STS elements have not been addressed systematically yet • No PSS metamodel focuses on social subsystems • Lack of Stakeholder consideration in PSS development • Lack of overall focus on the sociotechnical perspective Bridging of PSS and STS modeling domains necessary Product Development © 2015 Prof. Lindemann [11] Technische Universität München Towards a meta-model for the description of the sociotechnical perspective on PSS | Julian Wilberg | XX. Month 20145 8 Case Study „PSSycle“ • Student project within the collaborative research centre „Sonderforschungsbereich 768 – Managing cycles in innovation processes“ • Concept of a pedelec sharing system • Focus on development of hardware components • Additional social subsystems and STS properties have been defined for modeling Product Development © 2015 Prof. Lindemann Technische Universität München Towards a meta-model for the description of the sociotechnical perspective on PSS | Julian Wilberg | XX. Month 20145 9 Model Abstraction Concrete Models Bike Frame Supplier Metamodel Elements Supply Chain Bike Frame Manufacturing Operations Insurance Supplier Bike Station Infrastructure Element Bike Maintenance Truck SysML 1.3 Product Development © 2015 Prof. Lindemann Implementationneutral Technische Universität München Towards a meta-model for the description of the sociotechnical perspective on PSS | Julian Wilberg | XX. Month 20145 10 Conceptual representation of metamodel Product Development © 2015 Prof. Lindemann Technische Universität München Towards a meta-model for the description of the sociotechnical perspective on PSS | Julian Wilberg | XX. Month 20145 11 Metamodel for the sociotechnical perspective on PSS • Class diagram – Abstract classes in italics <<Edge>> <<Edge>> InformationFlow MaterialFlow <<Edge>> <<Edge>> EnergyFlow MonetaryFlow <<Edge>> – Edges: Flows between elements – Nodes: Elements of STS • Design platform elements – Technical elements – Social elements/ subsystems Flow <<Node>> DesignPlatformElement <<Node>> <<Node>> InfrastructureElement PSSDesignElement <<Node>> <<Node>> PhysicalInfrastructureElement HardwareElement <<Node>> <<Node>> SupportNetwork ElectronicsElement <<Node>> <<Node>> OrganizationalSubElement MechanicsElement <<Node>> <<Node>> ValueChainElement SoftwareElement <<Node>> OrganizationalUnit <<Node>> Team <<Node>> StakeholderElement <<Node>> ServiceElement <<Node>> ProductServiceElement <<Node>> UserServiceElement <<Node>> Organization <<Node>> Individual Product Development © 2015 Prof. Lindemann Technische Universität München Towards a meta-model for the description of the sociotechnical perspective on PSS | Julian Wilberg | XX. Month 20145 12 Metamodel for the sociotechnical perspective on PSS • Hierarchical deconstruction and description of social subsystems • Description of relationships between PSS elements and STS elements InstanceOf <<Node>> SupportNetwork <<Node>> SupplyChainNetwork <<Node>> 1 Hardware 1…* consistsOf Element 1…* isSuppliedBy <<Node>> 1…* Supplier <<Node>> Provider InstanceOf 1…* isProvidedBy <<Node>> Organization <<Node>> Service Element 1 has 1…* <<Node>> Organizational SubElement 1 consistsOf 1…* <<Node>> Individual 1…* isPartOf Product Development © 2015 Prof. Lindemann <<Node>> Team 0…* Technische Universität München Towards a meta-model for the description of the sociotechnical perspective on PSS | Julian Wilberg | XX. Month 20145 13 Further Results • Complexity-based approach for stakeholder analysis (MDM and procedural model): Procedural model and tools – Literature-based checklists of stakeholder groups and –types – Checklist of generic stakeholder interests (25 items) • primary • secondary • external • internal • key • Undecided • Etc. • • • • Control Job security Stable relationships Env. Protection Product Development © 2015 Prof. Lindemann • Customers • Organizations • Management • Public and Media • Etc. Stakeholder Groups Stakeholder Types Stakeholder Is part of Is part of Has Stakeholder Groups Has relation to Has relation to (has) Stakeholder Types Has relation to Has relation to (has) MDM Interests Stakeholder Interests Conflicts with Technische Universität München Towards a meta-model for the description of the sociotechnical perspective on PSS | Julian Wilberg | XX. Month 20145 14 Conclusion and Outlook • Conclusion: – Contribution: Preliminary metamodel for modeling the sociotechnical perspective on PSS – Focusing on the social subsystems and their interaction with the technical subsystems • Outlook: – Implementation of full metamodel in a software tool for modeling – Extensions and Improvements, e.g. List of stakeholder attributes – Further elaboration of relationships – Evaluation by a broader spectrum of experts from research and practice Product Development © 2015 Prof. Lindemann Technische Universität München Towards a meta-model for the description of the sociotechnical perspective on PSS | Julian Wilberg | XX. Month 20145 15 Contact & Literature Contact: Julian Wilberg, M.Sc. wilberg@pe.mw.tum.de +49.89.289.15129 Dipl.-Ing. Christoph Hollauer hollauer@pe.mw.tum.de +49.89.289.15136 Institute of Product Development Technische Universität München Boltzmannstr. 15 85748 Garching, Germany [1] J.-M. Favre, “Foundations of meta-pyramids: Languages vs. metamodels Episode II: Story of thotus the baboon,” Lang. Eng. Model. Softw. Dev., vol. 4101, pp. 1–28, 2005. [2] P. Höfferer, “Achieving Business Process Model Interoperability Using Metamodels and Ontologies.,” ECIS, pp. 1620–1631, 2007. [3] A. Borshchev and A. Filippov, “From system dynamics and discrete event to practical agent based modeling: reasons, techniques, tools,” 2004. [4] T. R. Gruber, “A translation approach to portable ontology specifications,” Knowl. Acquis., vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 199–220, 1993. [5] K. Kernschmidt, T. Wolfenstetter, C. Münzberg, D. Kammerl, S. Goswami, U. Lindemann, and H. Krcmar, “Concept for an Integration-Framework to enable the crossdisciplinary Development of Product-Service Systems,” in Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE IEEM, 2013. [6] T. Wolfenstetter, K. Kernschmidt, C. Münzberg, D. Kammerl, S. Goswami, U. Lindemann, and H. Krcmar, “Supporting the Cross-disciplinary Development of Product-Service Systems Through Model Transformations,” in Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management, 2014. [7] R. Roy, Y. Xu, B. G. Annamalai, R. Hussain, M. Cakkol, S. Evans, and A. Tiwari, “An Ontology for Product-service Systems,” 2011. [8] Y. S. Kim, E. Wang, and M. W. Park, “Value-Function-Structure Modeling in an Ontological Representation of Product-Service Systems,” in International Conference on Engineering Design ICED, 2009, pp. 359–370. [9] P. Müller and T. Sakao, “Towards consolidation on product-service systems design,” in CIRP IPS2 Conference 2010, 2010, pp. 219–225. [10] S. Alter, “Metamodel for Understanding , Analyzing , and Designing Sociotechnical Systems,” Work. Pap. Inf. Syst., vol. 9, no. 2009. [11] Vasantha, G.V.A., Roy, R., Lelah, A., Brissaud, D., 2012. A review of product– service systems design methodologies. J. Eng. Des. 23, 635–659. doi:10.1080/09544828.2011.639712 Product Development © 2015 Prof. Lindemann Technische Universität München Towards a meta-model for the description of the sociotechnical perspective on PSS | Julian Wilberg | XX. Month 20145 16