Weeds Lecture 3
advertisement

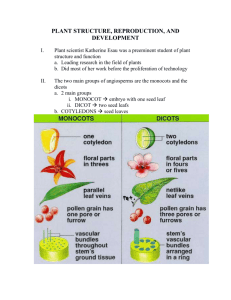
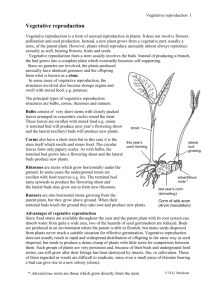
Weed life cycles Types of reproduction in plants Vegetative reproduction Production of new plants from vegetative structures Clones=daughter plants=ramets Genetically identical to the parent plant Sexual reproduction Production of new plants from seeds Allows for genetic mixing/diversity in offspring (genets) Five life cycle categories for weeds Summer annual Germinate in spring and summer and mature before winter Problems in spring and early summer planted crops, open sites, winter cereal crops, edges of natural areas Lambsquarter, redroot pigweed, bedstraw, wild buckwheat, green foxtail, wild oat Winter annual Germinate in the late summer, fall, and winter (in warmer regions) Mature in spring or early summer Problems in late summer and fall planted crops, open sites, bare spots in pastures In colder regions, winter annuals may be summer annuals Shepherd’s purse, field pennycress, downy brome Five life cycle categories for weeds Biennial Live for two growing seasons Seeds germinate and plants grow vegetatively as rosettes the first year Exposure to cold in winter causes the rosette to bolt in the spring The biennial then flowers, matures its seed, and dies during the summer or fall of the second growing season Usually a problem in perennial fields; not in fields that are disturbed in fall Henbit, houndstongue Perennial Survive indefinitely (3+ years) Flowering doesn’t trigger senescence Underground structures continue to live Five life cycle categories for weeds Simple perennials Start from seed, grow vegetatively Root and crown survive indefinitely Shoots periodically produce flowers and seeds Form a crown of tissue at or below the soil surface on the upper end of a taproot What is the purpose of seeds? Found in perennial crops, undisturbed areas, no-till fields Spotted knapweed Creeping perennials Reproduce from vegetative structures and seed Vegetative reproductive structures are the major means of localized spread, competition, and survival Creeping roots, rhizomes, stolons, bulbs, tubers Have large amounts of stored food and numerous buds Field bindweed, quackgrass, Canada thistle Vegetative reproductive structures Rhizomes Elongated horizontal underground stems with nodes, internodes, and modified leaves Root and new shoot growth always originates from buds at the nodes Tubers Thickened underground stems borne on rhizomes Internodes are shorter than those on a rhizome Root and new shoot growth always originates from buds at the nodes Vegetative reproductive structures Bulbs Modified leaf tissue borne on a small stem plate Roots and new bulbs develop from this stem plate Stolons Horizontal aboveground stems Leaves produced at the nodes are green Food storage not a major function Vegetative reproductive structures Creeping roots No leaves, nodes, or internodes Can grow downward and horizontally Can produce shoots along their length Tend to penetrate deeper than other vegetative reproductive structures and are harder to control Shoot Regeneration in Weed Species Shoot regeneration All plants have a growing point from which they can regenerate shoots Any practice that destroys the plant below the lowest growing point will kill the plant The position of shoot regeneration on a plant and the resistance of a plant to destruction depends on the life cycle Annuals Broadleaves The bud in the axil of the cotyledons in the lowest point from which an annual broadleaf can regenerate a new shoot Any action that destroys the weed below that point should kill it Grasses The growing point, or crown, is just below the soil surface Annual grasses need to be damaged under the soil surface for complete kill Shoot regeneration Biennials Rosette stage difficult to control As the seed stalk begins to elongate (bolt) the meristems raise aboveground Simple Perennials Crown is 1 to several inches below soil surface Crown and taproot survive and generate new shoots even after substantial damage How would you go about trying to control a simple perennial (mechanically?) Creeping Perennials Numerous well-protected buds capable of generating new shoots Large amounts of stored food and many buds Usually 6 in belowground, sometimes several feet Severe disturbance usually helps them regenerate Need repeated action to deplete the plant of energy reserves Questions! 1. Summer and winter annuals germinate in spring and summer and mature before winter. True or False? 2. _______________ weeds are most troublesome in perennial and no-till cropping systems. 3. a. Perennial b. Annual c. Biennial d. Centennial What stage of a biennial weed is most difficult to control? Why? Field pennycress Scientific name: Thlaspi arvense Family: Brassicaceae Life cycle: Annual Where found: Cropland Physical description: Seed: fingerprint pattern Cotyledon: oval with long petiole True leaves round to spatulate, then oblong to oval Forms a basal rosette at first, then alternate when flowering Early leaves have long petioles; later stem leaves are sessile, clasping around stem Leaves without hair, in contrast to shepherd’s purse Growth habit: erect Interesting facts: Seed pods are disc-shaped with a distinct notch at tip Distinct, garlic-like odor when brushed Latin name describes flat pod Thlas=to crush or flatten Shepherd’s Purse Scientific name: Capsella bursa-pastoris Family: Brassicaceae Life cycle: Annual Where found: Cropland Physical description: highly variable Seed: small, sticky when wet Cotyledon: ovate, apex may be indented Growth habit: basal rosette; flowering stem alternate True leaves oval, then elliptic to oblanceolate, most becoming pinnately divided Stem leaves lanceolate Early leaves have long petioles; later stem leaves are sessile, clasping around stem Leaves are sparsely hairy Interesting facts: Seed pods heart-shaped, flattened Latin name describes seed pods caps=small box bursa= purse, pastor=shepherd