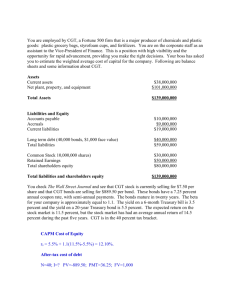
Succession Planning: Tax Reliefs & Estate Taxation
advertisement

Chartered Tax Consultant Stage 3 Module 6 Succession Planning Presenter Name – Carol Hogan 24th & 25th August 2012 Chartered Accountants House www.charteredaccountants.ie EDUCATING SUPPORTING REPRESENTING Learning Objectives • • • • Tax reliefs on transfers of assets? Succession Planning Structures Marriage and marriage breakdown Taxation of estates and post death planning Friday Afternoon • • • • • • • • Favourite Business Relief Nephew/Niece Relief Agricultural Relief Dwelling House Relief CAT/CGT Set Off Retirement Relief Transfer of site to child Consanquinity Relief Young Trained Farmer’s Relief Saturday • Share valuations • Trusts – Bare trusts – Fixed Income trusts – Discretionary trusts • • • • Family Partnerships Companies Taxation of Estates Marriage Breakdown Introduction • Transfer on wealth to next generation/spouse gift/inheritance/marriage break-up • Personal Wealth v Business • Role of family members in the business • Building up fund outside the business • Impact all tax heads CAT – Key Point Refresher Gift & Inheritance Tax @ 25% Group Thresholds Spouse transfers exempt Beneficiary liable Aggregate from 5th Dec1991 Annual exemption €3,000 Date of the gift = Date of inheritance = Sec 2 CATCA 2003 “On a death” Beneficially entitled in possession Date of death - disponer/LT Relevant for certain reliefs Valuation date relevant for: Valuation date for gift = Valuation date for inheritance = Can have < 1 VD per estate Agricultural and Business Reliefs Date of gift Earliest of three dates •Date of retainer •Date benefit retained •Date of delivery/payment/discharge CGT and SD Key Points CGT Stamp Duty Tax on Vendor/Transferor Tax on Purchaser/Beneficiary 25% Rate SD paid on MV Gain = Proceeds/MV – Cost MV imposed on gifts Shares 1% Commercial Property 1%-6% Annual exemption €1,270 Residential Property 1%/2% No CGT on death No SD on death –exceptions CAT Business Relief Business Relief • S. 90 to102A CATCA 2003 • 90% reduction in taxable value • Taxable Value = MV less liabilities, costs, expenses, consideration • Applies to gifts and inheritances • Limited or remainder interests • S. 91CATCA 2003 – no relief from DTT Relevant Business Property • S. 93(1) CATCA 2003 • Agricultural Relief has priority • S. 93(1)(a): Sole trader/partnership “property consisting of a business or an interest in a business” • S. 93(1)(b)-(f): Shares and securities • S. 93(1)(e): Land & buildings, P&M held personally and used in business Shares – Ownership Tests Beneficiary must satisfy one test Test 1 Beneficiary controls > 25% voting rights Test 2. Beneficiary has s. 27 CATCA ‘03 control a) Controls > 50% voting power b) Controls (or could obtain capacity to control) board of directors c) Receives (or has right) >50% dividends d) Owns >= 50% of nominal shares Shares – Quoted and Unquoted • Quoted shares – unquoted when acquired by donor or 23rd May 1994 (later of) • No requirement for company to be Irish registered or incorporated • Ownership tests to be satisfied by donee Control – Aggregate Shares • Beneficiaries shares aggregated with • Shares of relatives • Shares of his nominees and nominees of relatives • Shares of trustees of settlement where beneficiary or his relatives are objects Who is a relative of Beneficiary? S. 2(4) CATCA 2003 a) Spouse b) Parent, child, uncle or aunt c) Children and grandchildren of above stepchildren, grandchildren, cousins, siblings d) Spouse of relative at (b) or (c) e) Grandparent f) Company controlled by beneficiary Shares – Ownership Tests Test 3. 10% and Full time working test: • Beneficiary owns >=10% of nominal value issues share capital and • Has worked full time in the company (or group) for 5 years ending on date of gift/inheritance Land, Buildings, P&M • Owned personally by disponer • Used wholly for purposes of business controlled by disponer • Used wholly in partnership if disponer a partner • Control = majority of voting power held by disponer • Assets must be transferred to same beneficiary at same time as shares or partnership interest Qualifying Business S. 93(3) CATCA 2003 • Non-qualifying business • “..consists wholly or mainly of “ • Dealing in currencies, securities, stocks or shares, land or buildings or • Making or holding on investments • “Wholly or mainly” = >50% • 50% of what? Turnover, profits, assets? Revenue CAT Manual • Ratio of asset value and profit to trading and investment • Ratio of turnover to investment income • Employees engaged on trading and investment sides • Commercial reason for low trading profits • Use of investment income • Description of activity in directors’ report Business Relief • Wholly or mainly test met if business not excluded • Taxable value of any relevant business property relating to investment assets excluded • Holding company – wholly or mainly holding non excluded subsidiaries • Ignore value of any subsidiaries carrying on excluded businesses “Business” S. 90 CATCA 2003 • Includes exercise of profession or vocation • Does not include business not carried on for a gain • Broader meaning than trading “Business” • Smith v Anderson – “anything which occupies the time and attention and labour of a man for the purpose of profit” • Town Investments v DOE – “denotes the carrying on of a serious occupation” “Business” • Does the receipt of rental income consist of a business? • Case law – distinction between business carried on by individual and company • AE v Revenue Commissioners • Conacre letting held to be a business • Landowner obligations Minimum Ownership Period S.94 CATCA 2003 • Two years prior to date of inheritance taken on death of disponer • Five years prior to date of gift or inheritance in other case – Spouse period of ownership included – S.96 CATCA 2003 – ownership period runs from date of death for inheritance – Include pre incorporation ownership S.600 TCA 97 CGT Relief Example Mary gifts 100% of shares in qualifying company to her two children 50:50 The company was set up 10 years ago by Mary and her husband 50:50 She inherited 50% of her shareholding from her husband two years earlier • What is Mary’s period of ownership? • What shares meet the five year ownership requirement for gift tax business relief? Example Julie inherited shares from her grandfather who died in July 2009 Valuation date was March 2011 following litigation Julie died in August 2011 and left the shares to her son • What is the period of ownership of the shares for business relief? • Is the ownership period met for BR? Replacement Property S. 95 CATCA 2003 • Take period of both assets into account where relevant business property replaces other RBP • RBP and replaced RBP – 5/6 years for gift tax and 2/3 years inheritance tax • Where value of replacement property >property replaced then restrict value Ownership – Successive benefits • • • • Disposition 1st beneficiary who dies Death < 2/5 years after first benefit 1st beneficiary 2nd beneficiary 2nd beneficiary will qualify if earlier benefit qualified for BPR • Restriction for 2nd benefit • MV 2nd Benefit x Taxable value 1st Benefit Market Value 1st Benefit Calculation of Relief • S.92 CATCA 2003 - 90% reduction of taxable value of RBP • Taxable Value = MV-Liabilities, Costs, Expenses, Consideration • S.100 CATCA 2003 - exclude excepted assets • Mandatory efiling - online Return calculates tax • Calculate tax manually too BPR - Formula 1 MV of RBP – include excepted assets 2 Deduct Liabilities, Costs, Expenses and Consideration 3 Taxable Value 4 MV Excepted Assets 5 Value of RPB (3-4) 6 Replacement Property/Successive Benefits not eligible 7 RPB on which relief granted (5-6) 8 Calculate limited interest 9 10 BPR – 90% of 7 or 8 Taxable Value (7 /8 – 9) 11 Taxable value all assets (4+6+10) 12 Add 11 to non business property 13 Deduct small gain exemption Calculation of Relief • All assets owned/used wholly or mainly for business • All business liabilities • Each account looked at • Savings v Working Capital accounts Partnership • Partnership assets and liabilities Liabilities • Deduct business liabilities from business & assets Consideration • Deduct general debts and consideration paid IT 39 from non-business assets • Mortgage on business property • Surplus liabilities deducted as appropriate from business/non-business assets Sole Trader Example Non-Business Assets €000 Business Assets Deposit Account House 20 250 MV Liabilities/Costs Incumbrance Free Value Consideration Taxable Value €000 270 (20) 250 Shop Stock and Machinery Goodwill Business A/c MV Business Liabilities Taxable Value 250 20 50 10 330 (180) 150 (50) 200 BPR @ 90 % Taxable Value (135) 15 Excepted Assets • • • • • • • S.100 CATCA 2003 Not used wholly & exclusively for business For last 2 or 5 years Used for personal benefit of disponer or relative Deducted from qualifying RBP Calculate Relief @ 90% Added back to taxable value of RBP Asset not wholly or mainly used S. 100(5) CATCA 2003 • Relief only for part of land or building used wholly or mainly for business • IT 39 – apportion mortgage • “Flat above shop” • Part of building let Example • Non-business assets include flat €300,000 • Apportion mortgage - €30,000 to flat • Reduce non-business assets by liabilities costs and expenses of €20,000 • Reduce business assets by mortgage €120,000 and debts to suppliers Clawback of Relief No.1 • Sec 101 & 102A CATCA 2003 • Business ceases to qualify within 6 years and not rectified within 1 year • Notional gift test – s.101(2)(a) • No clawback if bankruptcy or bona fide winding up Clawback of Relief No.2 • S. 101(2)(b) – sale, redemption or compulsory acquisition of business within 6 years • Unless business replaced within 1 year by other RBP • Proportionate clawback if MV RBP replaced < MV original RBP • No clawback on death of beneficiary or life tenant but subsequent beneficiary may have clawback Clawback of Relief No. 3 S.102A TCA 1997 • Extension of clawback period from 6 to 10 years for development land • Development value treated as not qualifying for RBP • Relief given on CUV only • Includes shares in a company deriving value from development land • Only applies to a disposal Clawback of Relief 3 • • • • • Development Land @ date of gift/inheritance and date of disposal No provision for reinvestment DL definition – MV > CUV DL = MV - CUV Applies to gifts or inheritances taken on or after 2nd February 2006 CAT Agricultural Relief Agricultural Relief S. 89 CATCA 2003 • MV of “agricultural property” reduced by 90% • Benefit comprised of agricultural property at date of gift/inheritance and valuation date • Beneficiary is a “farmer” at valuation date Agricultural Property S. 89(1)(a) CATCA 2003 • Agricultural land, Pasture and Woodland in EU State • Crops, trees and underwood on land • Farm Buildings, farm houses and mansions • Farm machinery, livestock and bloodstock on land Farmer S. 89(1) CATCA 2003 • An individual • 80% of gross assets on valuation date comprise agricultural property in EU State • “Farmer” test is a financial test • No “working farmer” test • Off farm PPR – deduction for mortgage Example Farmhouse €000 Non Agricultural Prop 250 House (net)* Farmlands 1,250 Car Agricultural Prop Stock & Machinery Welsh Farm Total €000 345 10 70 Cash 15 300 Shares 30 1,870 Total 400 Farmer Test 1,870 x 1870/(1,870+400) = 82% *Without deduction of mortgage on PPR, farmer test would not be met Farmer Test – Anti Avoidance S. 89(1) CATCA 2003 • Interest in expectancy included • DT settled by beneficiary - include MV of property • Deals with “temporary” transfer of assets by beneficiary to another person • Prevents transfer of assets by beneficiary to DT Valuation Date • Farmer test must be met on Valuation Date • Acquire or dispose of assets prior to date of gift? • Scope for planning between date of death and valuation date? • Benefit must comprise AP at date of gift/inheritance and valuation date • S. 89(2) CATCA – conditional gifts “gift overs” Calculation of Relief 1 Market Value of Agricultural Property 2 90% Reduction of 1 3 Agricultural Value (2-1)* 4 Liabilities, Costs and Expenses – apportioned *10% 5 Incumbrance Free Value (3-4) 6 5 x Limited Interest Factor 7 Deduction for consideration x 10% 8 Taxable Value * Contrast with BPR – 90%* Taxable Value Liabilities, Costs & Expenses • Deductible first from residue • Exception for debts charged on assets • Apportion between agricultural and non agricultural assets – residuary beneficiary • Deduction for 10% against agricultural property Example Non-Agricultural Assets Deduction Allowed NIL Agricultural Assets Total Deduction Allowed No apportionment 90% Restriction Farm Debt €30,000 €30,000 x 10% = €3,000 Apportionment €15,000 x €80,000/€1,940,000 = €619 Apportionment and Admin €10,000 90% Reduction €15,000 x €1,860,000/€1,940,0 00 x 10% = €1,438 Clawback of Relief No1 S. 89(4) and 102A CATCA 2003 • Disposal or compulsory acquisition within 6 years and no reinvestment within 1 year (6 for comp acquisition) • Partial clawback of full proceeds not reinvested • Purchase of property from spouse/civil partner not treated as reinvestment Clawback of Relief No.2 • • • • • • Similar to BPR clawback for DL Extension of 6 year period for development land Disposal after year 6 and before year 10 Taken on or after 2nd February 2006 CAT recalculated – AR only on CUV Applies where DL on valuation date and sale of that DL Clawback of Relief No.3 • Where beneficiary not resident in Ireland in any of 3 years immediately following year of assessment of VD • Beneficiary need not be resident in year of gift/inheritance or VD Trees and Underwood • No need to meet “Farmer Test” • Sale or compulsory acquisition does not trigger a clawback of relief • Timber can be sold without underwood - no clawback • No requirement to be resident in 3 years following gift/inheritance • Death of beneficiary - no clawback BPR on Agricultural Property • • • • • • Farmer Test not met BPR applies if other tests met Farmhouse – must be used W&E for business Agricultural Relief takes precedence Planning for BPR prior to valuation date Why claim BPR? BPR v Agricultural Relief Business Relief Agricultural Relief Taxable Benefit x 90% MV x 90% & Costs & Expenses x 90% Liabilities, costs and expensesreduce non-business assets first Liabilities, costs and expenses apportioned Minimum ownership period No minimum ownership period No business test for beneficiary Test for shares in company Farmer Test Restrictions on letting Land can be let Farmhouse – relief only if W&E “Character appropriate” farmhouse Compulsory acquisition – replacement within 1 year Compulsory acquisition – replacement within 6 years Clawback if control of co broken Clawback only on sale No residence requirement 3 year resident requirement Reinvest in any qual business Reinvestment in Agricultural Property Favourite Niece/Nephew Relief Favourite Nephew Relief • Para 7, Part 1 Schedule 2 CATCA 2003 • Group A applies to BPR and Agricultural Relief where favourite niece/nephew relief applies • Nephew/niece in blood • Requirement to work substantially on a full time basis for 5 years Favourite Nephew Relief • Requirement to work substantially on a full time basis for 5 years • Ending on date of cessation of donor’s interest • Carrying on trade, business or profession of disponer or company controlled by disponer – >24 hours per week or – >15 hours per week – beneficiary, donor and spouse carry on business Favourite Nephew Relief • Property used in connection with trade, business, profession or employment/office of disponer • Shares in company owning such property • Business property definition wider than BPR • Assets used in trade, business or profession Favourite Nephew Relief • Shares must be in PTC controlled (s. 27) by disponer who is a director • Group A applies to business or agricultural assets • Group B for other assets • Group A may apply with or without BPR/AR – reliefs not interdependent • Mandatory e-filing Dwelling House Relief Dwelling House Relief • • • • • • S. 86 CATCA 2003 Dwelling house exempt where conditions met 3 year occupation prior to gift/inheritance No entitlement to other dwelling house Must occupy dwelling during “relevant period” No deduction for liabilities, costs expenses against other assets Conditions for Gifts S. 86(3A) CATCA 2003 1. Disponer must own dwelling house for 3 year period preceding gift and 2. Period during which donee occupies house that was disponer’s PPR is disregarded unless disponer depends on services of donee due to old age or infirmity (>65) Affects transfers where no tax avoidance is in play i.e. siblings, co-habiting couples etc Civil Partners entitled to CAT exemption Clawback • • • • Beneficiary must occupy property for 6 years Not applicable to over 55s Property sold during relevant period No clawback where – house sold due to long term medical care – house sold and replaced within 1 year and occupied for 6 years falling within 7 years of date of gift/inheritances CAT/CGT Set Off CAT/CGT Set Off S.104 CATCA 2003 • CAT and CGT arising on “same event” • Disposal for CGT of “same property” • Gift of asset • Distribution of asset from trust • Clawback of agricultural/business relief and CGT retirement relief CAT/CGT Set Off • • • • • • • CGT paid is credited against CAT CGT paid by disponer CAT payable by beneficiary where > CGT Example - gift of shares CGT €4,683 CAT €15,948 - €4,683 CAT due €11,265 CAT/CGT Set Off • efiling • Temporary credit for CGT allowed where CAT due before CGT Clawback S.104(3) CATCA 2003 • Clawback if transferee sells asset within 2 years • Introduced to counter tax use of set off where land gifted by parents to children with immediate sale to developer • Impact on appointment of assets from trusts CGT Retirement Relief CGT Retirement Relief • • • • • • • • S. 598 and 599 TCA 1997 S. 599 - disposal to child No limit on consideration S. 598 - disposals to other persons Limit of €750,000 Disposal of qualifying assets Main purpose must not be to avoid tax Anti avoidance S. 598(8) TCA 97 CGT Retirement Relief • Annual exemption €1,270 cannot be claimed • Disponer must be at least 55 years • Qualifying assets must be held for 10 years • TB 60 - disposals in 12 months to 55th birthday considered where due to ill health Qualifying Assets • Chargeable business assets • Certain shares and securities • Certain agricultural assets Chargeable Business Assets • Owned by individual for 10 years • Chargeable business assets throughout 10 years • 10 year condition not applicable to tangible moveable property eg plant and machinery • Assets used for trade, profession, office or employment • Carried on by individual or his family company - or member of trading group Chargeable Business Assets? • • • • Land & Buildings Plant & Machinery Goodwill Shares and investment assets • Stocks, Debtors, Cash Family Company Individual must hold: • at least 25% of voting rights or • at least 10% voting rights and together with family hold at least 75% voting rights Family = individual’s spouse, relatives of the individual and his spouse Relative = brother, sister, ancestor, lineal descendant Shares or Securities • Shares in a trading or “family company” • Shares in member of trading group of which the holding company is the individual’s family company (75% subs) • Held for at least 10 years Shares or Securities • Working director for at least 10 years • Full time director for at least 5 years – devoting substantially whole of his time in managerial or technical capacity • 10 year ownership to include reconstruction or amalgamations Assets owned personally • Lands, buildings, plant & machinery • Owned personally for at least 10 years • Used by family company throughout 10 year period • Disposed of to same person and at same time as shares • Treated as qualifying assets Disposal by Sole Trader Example • Gain on qualifying business assets €480,090 • Sale proceeds €660,000 (<€750,000) • CGT payable on warehouse not owned for 10 years • CGT retirement relief €120,023 • CGT payable €2,955 Disposal of Shares • Sale Proceeds x Chargeable Business Assets Total Chargeable Assets Example Proceeds on CBA €727,612 CGT on Shares €134,775 CGT on CBA (Retirement Relief) €130,752 CGT payable €4,023 €750,000 Limit • No CGT where sale proceeds <= €750,000 • Aggregate limit • Withdrawal of relief – assessment or additional assessment • Time limit of 10 years • Proceeds from qualifying disposals to children not aggregated Marginal Relief • Proceeds marginally above €750,000 • Tax limited to : (Proceeds – €750,000) x 50% (€800,000-€750,000)x 50% = €25,000 CGT payable €175,456 Marginal Relief €150,456 Spouses/Civil Partners • • • • • • • Include spouse’s period of ownership Include period of use of deceased spouse S. 1028(5) TCA 97 - “no gain/no loss” S. 598(6) TCA 97 - anti avoidance Part disposals of asset by spouses @mv Prevents both spouses availing of €750,000 Consider transfer of business assets between spouses pre 55th birthday S. 599 TCA – Disposal to Child • “Child” includes foster children • Includes nephew/niece working full time for 5 years prior to disposal in trade, business, profession, employment • No limit to sales proceeds • Clawback – disposal within 6 years • Child liable for CGT on both disposals • No rollover provisions Transfer of Site to Child Transfer of Site to Child • • • • • • • CGT Relief S. 603A TCA 97 Site ≤ 1 acre MV site ≤ €500,000 Site used for child to build house for occupation No CAT relief – Group A threshold No Stamp Duty relief (abolished in FA 2011) Transfer of Site to Child • Clawback if land sold before house built or house not occupied as PPR by child for 3 years • CGT arises to child on disposal • Where clawback, parent can claim relief on another qualifying transfer • Concession if site is subsequently transferred to joint names of child & spouse • CAT could arise under “gift splitting” Consanguinity Relief Consanguinity Relief • Sch 1 Para 15 SDCA • SD at half normal rate - excludes residential property, shares, stocks, marketable securities and leases • Adjudication required • All parties must be related • No clawback of relief • No SD on inter-spousal/CP transfers Young Trained Farmer Young Trained Farmer - SD S. 81AA SDCA 1999 • Exempts transfers of agricultural land • Farm buildings, farmhouses and mansions • EU Single Farm Payment Supplements • Applies to sales and gifts • Right of residence support and maintenance Young Trained Farmer - SD • Power of revocation not allowed • Aged < 35 years • Completed qualifying course in qualifying institution listed on form SD2B • Application on Form SD2B • Intention to own lands and working 50% farming land for 5 years Young Trained Farmer - SD • • • • • Relief extended to 2012 Qualifications obtained within 4 years Clawback within 5 years if land sold efiling mandatory Penalties of 125% SD if false information provided plus interest Share Valuation Share Valuation • • • • • Different methods – earnings, asset, turnover Combination may be used CGT and SD – Market Value CAT – MV CAT exception – controlling interest in private company CAT Share Valuation • S. 26 CATCA 2003 • Market Value - including non controlling interest in private company • To obtain best price for vendor • Unquoted shares - assumption of willing vendor and arm’s length • Revenue CAT manual Part 21 CAT Manual Part 21 Shareholdings ≤ 25% Realistic dividends paid Value by reference to dividends Shareholdings ≤ 25% No dividends paid Discounted earnings Discount 50%-75% Shareholdings 25%-50% Discount 35%-40% Shareholdings > 50% 50% 51%-74% >75% Value of company less discount Discount 20/30% Discount 10/15% None – 5% at most Controlling Interest Private Cos S. 27 CATCA 2003 • Beneficiary “controls” company after taking gift or inheritance • Private Co – under control of not more than 5 persons • Control – S.27(4) CATCA 2003 • Beneficiary’s shares aggregated with relatives, nominees, trustees, controlled companies Private Company Shares • • • • • • Company under “control” of beneficiary Shares valued as part of group of shares Shares of beneficiary and relatives/others No discount for minority interest Valued as proportion of group Discount may be given – CAT Manual Part 21 Surcharge for Undervaluation S.53 CATCA 2003 • Submitted Value v Agreed Value • Right of appeal • Interest due on surcharge MV as % of Ascertained Value Surcharge 0% <40% ≥ 40% <50% 30% 20% ≥50% < 67% 10% Stamp Duty Valuations S. 30 SDCA 1999 • Voluntary Dispositions inter vivos • MV - same rate as conveyances or transfers on sale • S 19 SDCA 1999 – Revenue valuation of property as sec 26 CATCA 2003 • Same discounts as CAT Stamp Duty Valuations • No special rules for minority interests • Different valuations for CAT, SD and CGT • S.44(1) SDCA 1999 – conditional or deferred consideration • S. 15 SDCA 1999 undervaluation surcharge MV as % of Ascertained Value ≥15% <30% ≥ 30% <50% ≥50% Surcharge 25% 50% 100% Capital Gains Tax • S. 547 TCA 1997 - MV where transaction not at arm’s length • S. 548 TCA 1997 - MV for transfers between connected persons • S. 547(1) TCA 1997- acquisitions • S. 547(4) TCA 1997 - disposals Capital Gains Tax • S. 547(1) TCA 1997 – MV on acquisition • Otherwise than arm’s length bargain – includes gifts • Distribution in respect of shares – includes winding up • Consideration wholly or partly unascertainable, connected with loss of office/employment, past services Capital Gains Tax • • • • S. 547(4) TCA 1997 – MV on disposal Otherwise than at arm’s length including a gift Where consideration is unascertainable S. 547(3) TCA 1997 – MV not imposed on acquisition • No corresponding disposal & less than MV paid • Issue of shares by company, goodwill Connected Parties - Anti Avoidance • MV on connected parties – CGT • No MV connected party rules for CAT/SD • Anti avoidance – CAT and SD CAT Anti Avoidance • S. 8 CATCA 2003 - Connected Gifts • Gift Splitting • Gifts given through person to ultimate beneficiary to gain higher thresholds • Deems ultimate beneficiary to receive from original disponer • Applies where second gift happens 3 years before or after first gift CAT Anti Avoidance S.38 CATCA 2003 - enlarging value • Prevents valuable assets being split and disposed of separately • Property taken which increases value of other property from same disponer • Increase in value taxable at time of second disposition • Applies to gifts and sales CAT Anti Avoidance • Applies to all property • Parties need not be connected • Disposal by beneficiary of first benefit in 5 years prior to taking second benefit • Deemed to be beneficially entitled in possession if sold for less than full consideration or disposal to private company under control of beneficiary CGT Anti Avoidance • S.549 TCA 1997 • Connected persons – MV • S.10 TCA 1997 – definition of connected persons • Meaning of control – S. 432 TCA 1997 Sec 10 TCA 97 Individual Husband or wife, relative, husband or wife of relative of individual or spouse; Relative Brother, sister, ancestor, lineal descendant, uncle, aunt, niece or nephew Sec 10(4) Trustees Connected with settlor or persons connected with settlor Connected with trustees if close co and shareholders Include trustees or beneficiary of settlement Sec 10(4) Company Sec 10(5) Partners Person connected with partners and partner’s relatives unless bf transaction Sec 10(6) Companies Same person has control of both Person has control of one and connected persons have control of other Group controls each co – same persons or connected persons Sec 10(7) Companies Company connected with person controlling it Persons acting to control of co connected Sec 10(8) Connected Persons • • • • S. 549 TCA 97 Restrictive covenants imposed on assets Disregard restriction – give little weight Lower of MV of right/restriction or amount by which extinction would enhance value • Ignore rights/restrictions reducing value to nil • Avoids artificial loss creation • Exception – disponer indifferent to sale proceeds Series of Disposal • S. 550 TCA 97 • Series of transactions between transferor and same connected person or persons • Assets deemed disposed for greater value • S. 602 TCA 97 – exemption for tangible moveable property eg chattels • Anti avoidance • Prevents breaking up of assets < €2,450 limit Stamp Duty Anti Avoidance • Deed must contain “transaction certificate” or “finance act certificate” for lower rates • Cert states that transaction no part of larger or series of transactions • Revenue guidance notes • Interdependence • Auction sales – AG v Cohen Stamp Duty Anti Avoidance • • • • S. 45 SDCA 1999 Apportionment of consideration Property purchased in separate lots Each deed stamped based on MV of property • Residential and non residential property Succession Planning Structures Succession Planning Structures • Trusts – Bare trusts – Fixed Income trusts – Discretionary trusts • Family Partnerships • Companies Bare Trust • Bare or Simple Trust • Trustee holds asset for beneficiary as nominee • Trustees do not have discretion • Express instructions of beneficial owner • Beneficiary has absolute entitlement to asset • Transparent for tax purposes Bare Trust • • • • Minors - no legal capacity At 18 beneficiary has control Privacy for owner – legal owner in CRO Tax on transfer of assets in hope that value will appreciate • No tax at transfer when 18 Bare Trust Income Tax • Absolute right to income - beneficiary assessed directly on trust income • S.795 TCA 1997 anti-avoidance • Applies to all trusts - minor children • Attribution of income of gains to settlor • Irrevocable trusts with accumulate income outside anti-avoidance • 20% surcharge on undistributed income Bare Trust CGT • CGT on transfer of asset to trust if change in beneficial ownership • S. 567(2) TCA 1997 - acts of trustees treated as acts of person entitled as against the trustee • Trustees deemed guardians - infant, under disability • Residence of beneficial owner • No CGT on transfer of asset to beneficiaries Bare Trust CAT • CAT on beneficiary on transfer of asset to bare trust • Threshold – disponer and beneficiary • No CAT on transfer of asset to beneficiary e.g minor now 18 Bare Trust SD • Beneficiary liable for SD on transfer of asset to trust • SD on value of asset on date of transfer • Consanguinity Relief applies • No SD on asset called on by minor at 18 Fixed Trust • Interest in possession or life interest trust • Entitlement to trust income/property for life or period certain • Interest in possession • Life tenant or tenant for a period certain • Remainderman • Settlor has control of assets Fixed Trust Income Tax • Beneficiary assessed on income • Appointments of income liable to IT on trustee if not mandated to beneficiary • IT at standard rate – Form R185 • Beneficiary liable at marginal rate under Sch D Case IV • Trustees cannot claim credits or allowance for individuals only • Capital payments more tax efficient? Fixed Trust CGT • CGT treatment the same as for other trusts that are not bare trusts • Discretionary Trusts • S 5 TCA 1997 – settled property • S 567 TCA 1997 property excluded (bare trust) • Property held by trustee in bankruptcy excluded CGT Settled Property • S.10 TCA 97 – settled property • Any disposition, trust, covenant, agreement, arrangement, transfer of money or other property • Boothe v Ellard – retention of right to direct trustees • Tomlinson v Glynns Executor – interest contingent on children reaching 21 CGT Settled Property • S. 574(1) TCA 97 • Trustees are a single and continuing body of persons • Distinct from persons who are trustees • Taxed as a body of persons • Not individuals • No entitlement to annual €1,270 exemption Creation of Settlement S. 575 TCA 97 • CGT on settlor when assets transferred into trust • Disposal of entire property – even where donor has interest as a beneficiary or is a trustee • Applies where settlor settles property on himself for life with reminder to others • MV applies – bargain not at arm’s length Administration of Settlement S. 568(2)TCA 1997 • Trustees primary liable for CGT • Appointment of asset to beneficiary • Disposal to third party • Base cost = MV at date acquired by trustees • Beneficiary liable to CAT/SD • CAT/CGT set off Life Interest S. 576 TCA 1997 • CGT on trustees when beneficiary becomes absolutely entitled as against the trustees to trust property • Trustees deemed to dispose and immediately reacquire the asset • No CGT if remainderman becomes entitled to asset on death of life tenant and asset passes out of trust Deemed Disposal • S. 576(1) TCA 1997 • A person becoming absolutely entitled as against the trustee to trust assets • Deemed disposal by trustee – asset reacquired in capacity as trustee • Minor becoming of age • Exception for the same event on death of life tenant Reliefs and Exemptions - Trustees • S. 604(10) TCA 97 – PPR Relief • Main residence of individual entitled to occupy it • S. 577A TCA 97 – Retirement Relief • Life tenant over 55 years and assets in beneficial ownership of LT for 10 years CAT Fixed Trust • CAT on creation of fixed trust where beneficiary has an interest in possession • Settlor of trust is disponer - unless funds provided by another person • Life Interest • Incumbrance Free Value - Table A First Schedule CATCA 2003 • IFV = MV reduced by liabilities, costs and expenses before consideration and BPT/AR Life Interest Market Value Liabilities Costs and Expenses €250,000 €4,000 Incumbrance Free Value €246,000 Factor for Female age 45 = 0.8283 €203,762 Consideration €5,000 Taxable Value €198,762 Small Gift Exemption Taxable Value Group Threshold €3,000 €195,762 €33,208 Life Interest • Entitled to pay tax in 5 annual instalments plus interest • Remaining instalments waived on death of LT within 5 years • S. 54(5) CATCA 2003 • Deemed remaining instalments refunded • Applies also where life interest relinquished Interest for Period Certain • Exclusive right to use asset or right to income produced by asset • Sch 1 Table B CATCA 2003 • Factor for period applied to IFV • Contingencies – S. 29 CATCA 2003 • Asset subject to power of revocation • Beneficiary initially liable under S. 40 CATCA 2003 – life interest tables Interest for Period Certain • Interest taken is not for a full number of years 1. IFV x factor for higher number of years 2. IFV x factor for lower number of years 3. Subtract smaller value 4. Apportion difference to number of days or months Appointments of Income or Capital • CAT payable on appointments of income and capital • CAT/CGT set off – CGT paid by trustees available for beneficiary CAT • No CAT/CGT set off for income appointments • Structure payment out of capital? Appointments of Income or Capital • Payments out of income account treated as income for beneficiary • Payment out of capital account or accumulated capitalised income? • Character of payment in beneficiary’s hands • Regular v once off payments • Brodie’s Will Trustees v IRC • Stevenson v Wishart Stamp Duty • • • • • SD payable on transfer of assets into trust No consanguinity relief Trustees liable to SD on acquisitions No SD on cash appointments by trustees No SD on transfers if no beneficial interest passing - S. 30(5) SDCA 1999 • Assets appointed subject to mortgage - S 41 SDCA 1999 Discretionary Trust • • • • • • Class of beneficiaries Trustees have discretion to distribute Letter of Wishes Beneficiaries have no absolute right Change in status of trust liable to CGT Protection of minors, incapacitated persons Discretionary Trust Income Tax • Trustees liable to income tax on income earned • Standard rate tax - 20% • No personal credits, allowances or reliefs • S.802 TCA 97 - 20% surcharge on accumulated income • Distribute income within 18 months of end of tax year Discretionary Trust Income Tax • Undistributed income grossed up @ 20% • No deduction for tax already paid • Regular income payment to particular beneficiary? • Revenue may argue interest in possession created • CAT and Income Tax exposure for beneficiary Discretionary Trust Income Tax • • • • Beneficiary taxed on grossed up trust income Form R185 – Sch D Case IV Credit for tax paid by trust Beneficiaries taxed directly if interest in possession held eg Life Tenant • Williams v Singer – divs paid directly • Aikin v MacDonald’s Trustees – expenses out of capital Capital Gains Tax - DT • Same treatment as for fixed trusts • DT is settled property for CGT CAT Discretionary Trust • No CAT on settlement of asset to DT • Beneficiary does not have entitlement in possession • CAT on appointments of trust assets • Inheritance if benefit taken on death of settlor • Benefits from trust settled when settlor alive liable to Gift Tax (2 year rule) • No clawback of small gift exemption if settlor dies within 2 years Stamp Duty • Stamp Duty for Discretionary Trust • Same treatment as for Fixed Trusts Discretionary Trust Tax Covered in Stage 2 S. 2 CATCA 2003 • Broad definition - Trustees have power to accumulate or no beneficiary has in interest in possession in the income of the trust • 6% initial charge and 1% annual levy • Only applies to inheritances Family Partnerships • • • • • Vehicle for holding investments Partners generally parents and children Transfer of assets at today’s MV by parents Parents retain control of assets Increase in assets attributable to partners, including children • Popular during property boom • Less complex than trusts Family Partnerships • Similar to Bare Trust • Partnership Agreement • Parents retain control – assets/profit distribution/power of veto • CAT issues on transfer to children • Low initial tax charge – future growth in value accrues to children • Paperwork – ensure trust not created • Partnership Accounts Family Partnerships Income Tax IT payable by individual partners CGT Disposal of asset to partnership MV – connected parties Individuals liable on partnership disposals Retirement relief – business assets CAT on transfer of assets Small gift exemption Group A threshold CAT/CGT set off SD payable by partners No SD on cash SD on further acquisitions CAT Stamp Duty Companies • Back in fashion as asset protection mechanism • Legal pitfalls - bankruptcy and other legislation • Transaction void if made to defraud creditors • Facilitates faster debt repayment • 12.5% CT v 52/53/55% IT/USC/PRSI • Pension planning Companies - CGT • CGT on transfer of assets to company • S. 600 TCA 1997 • Deferral of CGT until shares in company disposed of • Double charge on disposal of assets – CGT on gain arising – Extraction of sales proceeds to pay CGT – Salary v Dividend v Liquidation ER 44% Companies Tax on Profits • Income and gains for company liable to corporation tax • Tax Rate on non-trading income is 25% • Close company surcharge of 20% (Module 1) Companies – Stamp Duty Transfer to company • SD on assets not passing by delivery • Stock, P&M, cash and bank accounts • Included in total consideration for SD rate Transfer from company • Purchase of company shares – 1% • Assets transferred – higher rates • No SD on distribution of assets in specie Companies - CAT • Subject to its Memo and Articles and Co Law • A company is a person and can make a gift • S. 43 CATCA 2003 – “look through” private company • S. 43(5) – settlor of DT is disponer where gift made • Gifts or inheritances taken by company – treated as separate DT Taxation of Estates Taxation of Estates • Assets taken over by personal representatives • Appointed by will or under Succession Act 1965 • Estate or administration period ends when all debts and liabilities paid and • Beneficiaries have received entitlements Taxation of Estates • Personal Reps appointed under Succession Act 1965 • Provision for minor children • Sec 57 Succession Act 1965 – creation of trusts in favour of minors • Sec 58 Succession Act 1965 – general powers on trustees under S 57 Taxation of Estates • • • • Estate is separate legal entity for tax Assets vested in personal reps Personal reps responsible for tax Administration period – date of death to time estate administered • VAT and CT issues if deceased was in business • Bare trustees where estate not wound up and holding assets - CGT Legal Issues • Succession Act 1965 • Revenue Form CA 24 – Inland Revenue Affidavit • Lodged in duplicate with probate office • Probate office liaise with Revenue • Financial position of deceased at date of death • S. 48(4) CATCA 2003 – Corrective Affidavit Legal Issues • Grant of Representation = Grant of Probate and Grant of Administration • Testate and Intestate • Personal reps can deal with assets with Grant of Representation issued by Probate Office • Valuation date for CAT – not always • S. 30 CATCA 2003 – benefit retained at earlier date Valuation Date S. 30 CATCA 2003 earliest of: 1. Date personal reps entitle to retain assets 2. Date asset retained 3. Date of delivery, payment, satisfaction or discharge VD – fixes pay and file date 2011 – VD in 12 month period ending 31st August has pay and file date of 30th September Estate Accounts • • • • Fiduciary duty of care to beneficiaries Detailed estate accounts to be kept Chaine-Nixon v Bank of Ireland Two sets of accounts – both Capital and Income • Pre death – up to date of death • Estate Account – period of administration • Includes income accrued to date of death forming part of capital Order of Entitlement • S. 46 Succession Act 1965 – Sch 1 • Solvent Estate • General costs and expenses firstly out of residue • Pro rata out of remaining assets • Testator may direct otherwise • Liability secured on asset Order of Entitlement S. 46 Succession Act 1965 – Sch 1 Insolvent Estate • Priority for funeral, testamentary and administration expenses, legal fees • Bankruptcy order of entitlement • Secured creditors • Preferential debts – tax/PRSI • Unsecured creditors – priority for pre death Estates – Income Tax • Residence Rules - Case Law • If all personal reps resident in Ireland estate taxable on worldwide income • If all personal reps not resident in Ireland estate liable on Irish source income • Dual residence – place of effective management to be determined Pre-Death Income S. 1047 TCA 1997 • Personal Reps can be held personally liable S. 1048 TCA 1997 – time limit • Grant of Representation extracted in year of death – 3 years • Grant of Representation extracted in year after death – 2 years Pre-Death Income • S. 67(2) TCA 97 – cessation of trade or profession • Death is a cessation • Revision of penultimate year? • Revenue concession if surviving spouse takes over business – absolute interest • “Sec 23” property - death = clawback Married Couples Sec 23 clawback • Inheriting spouse assessable person – No separate assessment in year of death – No separate liability on transfer • Deceased spouse assessable person – Surviving spouse chargeable on income from date of death – Two IT assessments – sec 23 loss in post death period – Revenue concession to allow in pre-death period • Tax Briefing No 8(2010) elect no clawback Post Death Income • Tax at 20% on estate income • S. 66 TCA 1997 commencement rules for business • Income paid to beneficiary grossed up @ 20% • Form R185 – credit for tax deducted • Specific legatees – no tax credit • Per Reps account for tax • Pass income bearing assets to beneficiaries as early as possible Estates -CGT S. 573(4) TCA 1997 • Personal reps take on deceased’s residence, ord residence and domicile at date of death • No CGT on assets passing to per reps • Per Reps are single continuing body of persons • Assets acquired at MV at date of death Estates -CGT • Personal Reps file and pay outstanding CGT relating to pre death period • €1,270 exemption available • Losses can be carried back to 3 years of assessment prior to year of death • No carry forward of losses post death • S. 573(5) TCA 97 – no CGT on asset appointed to legatee • Acquired by legatee at MV at date of death Estates -CGT • Sale of assets by personal reps • CGT on Sale Proceeds less MV at date of death • Sale of property on behalf of no resident beneficiary – secondary liability • CG50 where consideration > €500,000 • Non resident vendor – payment of CGT prior to issue of CGT clearance Post Death Planning • Deed of Family Arrangement • Agreement by beneficiaries to vary entitlements • No tax provision - not tax efficient • CAT and SD - variation treated as though original beneficiary took benefit and made gift • S. 573(6) TCA 1997 - CGT relief – Deed of family arrangement made within 2 years Post Death Planning • Deed of Family Arrangement • Agreement by beneficiaries to vary entitlements • No tax provision - not tax efficient • CAT and SD - variation treated as though original beneficiary took benefit and made gift Appropriation S. 55 Succession Act 1965 • Personal reps can appropriate property to a beneficiary • Notice served on beneficiaries and consent obtained • “Substitution” of property of equal value • Testator may expressly allow in will Appropriation Stamp Duty • SD applies unless express power of appropriation in will • No SD if between residuary legatees and no additional benefit is given • Include express power of appropriation in will Appropriation CGT • S. 573 TCA 97 and Revenue CGT Manual • No CGT on transfer of estate asset to legatee • No CGT on appropriation if express power in will • Personal reps liable to CGT if no express power of appropriation and no agreement with legatee • Base cost for legatee is MV at date of appropriation Appropriation CAT • Exercise of power of appropriation by personal reps • Asset treated as coming from deceased • S. 89(5) CATCA 2003 – appropriation of agricultural property • Treated as bequest from deceased • Maximises Agricultural Relief Disclaimers • A refusal to take an inheritance • Only effective where no interest taken in the relevant part of the estate • Not possible to disclaim part of a benefit or part of the residue • Disclaimed benefit follows succession rules • No direction can be given • Great care is needed with disclaimers Disclaimers • Testate Estate • Disclaimer of benefit falls into residue • Disclaimer of interest in residue – rules of intestacy • Other residuary beneficiaries do not benefit • Disclaimer of limited interest – accelerates remainder interest Disclaimers • Intestate Estate - passing on intestacy • Sec 72A Succession Act 1965 • Person disclaiming treated as dying immediately before death of intestate and • If that person is not spouse or direct lineal ancestor of intestate – as if he had died leaving no issue • Legal advice before disclaiming Disclaimers and CAT • S. 12 CATCA 2003 • Pure disclaimers with no direction • Person benefitting from disclaimer treated as taking benefit from original disponer • No CAT liability for person who made disclaimer • S. 12(3) CATCA 2003 – consideration for disclaimer • Consideration from disponer Marriage Breakdown Marriage Breakdown • • • • • Separation Agreement Judicial Separation Court Proceedings No separation agreement Divorce – living apart for 4 of last 5 years Marriage Breakdown • “Living apart” not defined Divorce Act 2006 • McA(M) v Mc(A)S 2000 – Living arrangements, holidays, financial – Services provided, other arrangements Income Tax Assessments • Joint Assessment – unless election for separate of single treatment • Single Assessment – either spouse can elect • Separate Assessment – must be claimed Independent assessment with right to share credits and rate bands on joint basis Marriage Breakdown • “Living together” unless • Separated under Court order or Deed of Separation or • Separated in such circumstances that separation is likely to be permanent Marriage Breakdown • Year of separation – deduction for legally enforceable maintenance payments and married credit • No married credit in subsequent years where maintenance payments claimed Marriage Breakdown • Year of separation • Where jointly or separately assessed • Assessable spouse taxed on joint income to date of separation – married SRB and credit • Non assessable spouse treated as single person from date of separation – single SRB and credit Election for Joint Assessment S. 1026 TCA 1997 • Both Irish resident • Divorced couple can elect • Divorce recognised as valid in Ireland • Neither spouse remarried • No single parent credit* if joint assessment claimed S. 462 TCA 1997 - €1,650 Maintain child under 18/over 18 full time education Maintenance Payments • • • • • S.1025 TCA 1997 Legally enforceable arrangement Separation or divorce Annual or periodic payments Payments to spouse – tax deductible for payor and taxable on receiving spouse • Payment for benefit of child – amount quantified – not tax deductible and not taxable Transfer of Assets • CGT exemption for transfer of assets between spouses living together • No CGT exemption for separated or divorced couples • S.1030 & 1031 TCA 1997 - CGT exemption for transfers on foot of: – – – – Deed of Separation Decree of Judicial Separation Family Law Act 1995 relief following dissolution Part of a divorce decree order Anti Avoidance Sec 1028(6H) • No spousal exemption where assets transferred to non resident spouse and • Non resident spouse not liable to Irish CGT on disposal of assets in same year • Kinsella v Revenue Commissioners • CGT exemption in Ireland/Italy DTA • Assets acquired from husband in same year CAT • • • • • CAT exemption for spouses Continues after separation S. 70 and 71 CATCA 2003 S. 88 CATCA 2003 - divorce Exemptions for gifts and inheritances only if made on foot of Court Order • Renunciation of succession rights - should be dealt with on separation Stamp Duty • Deed of separation or decree of judicial separation – no impact on SD exemption under Sec 96 SDCA 1999 • S. 97 SDCA 1999 – exemption not applicable where divorce, unless on foot of court order and no other party to deed Civil Partners and Cohabitants • F(no 3) A 2011 • Taxation measures of CPCROC Act 2010 • Civil Partnership Registration for same sex couples • Redress scheme for long-term opposite sex and same sex couples not married and not in CP Civil Partners – Income Tax • • • • Same as married couples Year of Registration Relief Income Tax on dissolution of CP Income Tax in Year of death Civil Partners – CGT • • • • • Same as married couples Joint Asst if living together CGT Losses allowed to other CP Assets transferred at “no gain/no loss” Dissolution of CP – same as marriage dissolution relief • Ownership and occupation of PPR passed from one CP to other Civil Partners – CAT • • • • S. 70/71 CATA 2003 Exemptions same as for spouses Exemption on dissolution of CP Group A threshold extended to child etc of CP • Group B threshold includes child of CP of brother/sister Civil Partners – CAT • CPs and children of CPs included in relatives - sec 27 CATCA 2003 • Surviving Spouse applies to surviving CP • Favourite nephew/niece relief includes child of a CP of a brother or sister Discretionary Trust Tax • • • • • • Principal Objects extended Disponer’s CP Children of CP Children of a predeceased child of CP Predeceased child’s CP’s children Children of CP of a deceased child of disponer’s CP Stamp Duty • • • • • S 96 SDCA 1999 spouse relief Applies to transfers between CP No other party to deed S. 97 SDCA 1999 – CP dissolution Consanguinity Relief – Sch 1 Para 15 SDCA 1999 • Transfer of non residential property • Transfer to CP, CP of parent or CP of lineal descendant Qualifying Cohabitants • Redress scheme for long-term cohabitants • Right to apply for financial provision from ex after relationship breaks down • 5/2 year period • Application to Court for maintenance order • Relief for maintenance payments and property transfers Qualifying Cohabitants • Income Tax – no similar marriage/CP treatment • Capital Gains Tax – S. 1031Q TCA 1997 – Court Order Sec 174 CPCROCA 2010 – Dissolution of relationship – No CGT on disposal of asset to ex – Ex acquires at original cost Qualifying Cohabitants Stamp Duty • S.97A SDCA 1999 • Exemption from SD on property transfers under S.174 CPCROCA 2010 CAT • S. 88A CATCA 2003 • Gift/Inheritance taken under Part 15 Order • Exempt from CAT • No change to thresholds Roundup • CAT – Business Property Relief and Agricultural Relief • 90% Reliefs • Conditions • Shares in company • Clawback • Dwelling House Relief • Favourite Nephew/Niece Roundup • • • • • • • CAT/CGT Set Off Clawback Retirement Relief PPR Relief Transfer of site to child – SD and CGT Consanguinity Relief – SD Young Trained Farmer Relief Roundup • • • • • • • • Share Valuation CAT, CGT SD CAT – exception to MV rule Control Private companies CAT anti avoidance Gift Splitting Splitting of property – increase in value Roundup • CGT – MV and connected person • Series of disposals – CGT anti avoidance • SD – Certificate re larger transaction or series of transactions Roundup • • • • • • • Succession Planning Trusts Family Partnerships Companies Taxation of Estates Marriage breakdown/CPCROC Act Post death planning – Deed of family arrangement – Appropriations – Disclaimers