Chapter 27 - Ohio County Schools
advertisement

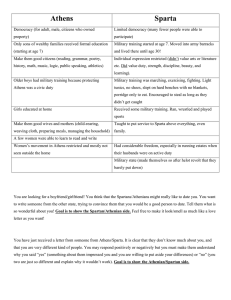
Chapter 27 Life in Two City-States: Athens and Sparta 27.2: Comparing Two CityStates • Athens o Located in Central Greece o Athenians liked to travel o They encouraged artists to come share their knowledge of art and architecture o Developed strong relationships with other citystates o Grew powerful through trade • Sparta o Was more isolated o Located on a plain between mountains • Peloponnesus o Suspicious of outsiders and their ideas o Grew what they needed around Sparta • Took what they didn’t have by force o Valued strength and simplicity • Taught sons and daughters to fight • Produced soldiers instead of artists and thinkers o Athens and Sparta were bitter enemies 27.3: Athenian Government • Democracy o Only free men could be citizens • all men over the age of 18 born in Athens were citizens o Every citizen could take part in the city’s government • Council of 500 met every day o Every year names of all citizens 30 years old and older were collected and 500 were chosen. • Ran day-to-day business of government and suggested new laws o Laws had to be approved by the Assembly • Met every 10 days • 6000 citizens had to be present for the meeting to take place • If not enough showed up, slaves would round up citizens o Assembly • Debated and voted proposed laws • Every citizen had the right to speak o Water clock was used to time • One cup was set above another with the water dripping in the bottom cup 27.4: Athenian Economy • Economy based on trade because land could not provide enough food • Traded with other city-states and foreign lands to get goods and other natural resources o Wood from Italy o Grain from Egypt • Bought and sold goods at the agora • Agora o Huge marketplace o Merchants sold goods in small stands o People bought lettuce, onions, olive oil, wine, and other foods o Bought household items like pottery, furniture, and clay oil lamps o Leather sandals and jewelry were very popular o Slaves were bought and sold • Coins o Made out of gold, silver, and bronze o Image on one side had a picture of Athena, the other side Athena’s favorite animal, the owl 27.5: Education in Athens • Main purpose o Produce good citizens • Boys and girls were educated differently o Boys • Until 6 or 7, were educated at home • 6-14, went to school o Teachers taught reading, writing, arithmetic and literature o Books were read aloud because they were expensive o The boys had to memorize everything o They used writing tablets o Coaches taught sports • Wrestling and gymnastics to strengthen muscles o Studied music • They learned to sing and play the lyre • At 18, they begin their military training • After their service, wealthy young men might study with private teachers o Charged high fees for lessons in debate and public speaking, which would help them to become political leaders o Girls • Did not learn to read or write • Grew up helping their mothers • Were taught to cook, clean, spin thread, and weave cloth • Some learned ancient songs and dances for religious festivals • Usually married around 15 o Wealthy families the father chose o Poorer families had more choice 27.6: Women and Slaves in Athens • Women were not considered citizens o o o o Had fewer rights than men Could not inherit or own much property Could not vote or attend the Assembly Most couldn’t even choose their own husband • Only a few had a job o Some sold goods in the market o Some were priestesses o Most spent their time in the home • Managing the household and bringing up the children • She had separate rooms and never went out alone • She would spin, weave, and supervise slaves • Educated her sons until 6 or 7 and her daughters until 15, when they married • Slaves o If person was not poor, owned at least 1 o Some were born into slavery o Others were captured in wars o Performed a variety of jobs • Ran households • Tutored children • Trained as craftsmen • Worked in farms or factories • Some worked as clerks • Unluckiest worked in the silver mines. o 10 hours a day o 300 feet below the surface 27.7: Spartan Government • Oligarchy o Even though there was an Assembly, all decisions were made by the Council of Elders • Council of Elders o Made up of 2 kings and 28 men o The kings inherited their power and shared equally o Other 28 members were elected by the Assembly • Men had to be at least 60 years old and from a noble family • Served for life o Held the real power o Prepared laws for the Assembly to vote on o Had the power to stop any laws passed by the Assembly • Assembly o Made up of male citizens o Met in a large outdoor area away from the center of the city o Had very little power o Did not debate issues o Could only vote “yes” or “no” on laws suggested by the Council of Elders 27.8: Spartan Economy • Relied on farming and conquering other people o Didn’t enough land to feed all its people o Took land they needed from neighbors o Used slaves and noncitizens to produce need goods o Turned conquered neighbors into slaves (helots) • Lived in their own villages, but had to give food they grew to the Spartans • Noncitizens o Called perioikoi o Free men, not slaves o Served in the army when needed, but couldn’t take part in the government o Made necessary items such as shoes, red cloaks, iron tools, and pottery • Discouraged trade o Feared contact with other city-states would lead to new ideas that would weaken the government. 27.9: Education in Sparta • Purpose was to produce men and women to protect the city-state o A baby that appeared weak might be left to die • Spartans valued discipline and strength o From the age of 7 all Spartan children were trained to fight o Girls even received military training o They learned wrestling, boxing, footracing, and gymnastics o Spartan boys lived in barracks • They were taught to read and write • Most important thing was to be a brave soldier o Spartan boys were taught to suffer any amount of physical pain without complaining o They marched without shoes o They were not fed well and were told to steal food o At 20, Spartan men were given a difficult test of fitness, military ability, and leadership skills • Pass become Spartan soldiers and full citizens o A man could not live with his wife and family until after he was 30 years old 27.10: Women and Slaves in Sparta • Spartan women lived the same simple life as Spartan men o Wore plain clothing with little decoration o Did not wear jewelry or use cosmetics or perfume o Were expected to be strong and healthy and ready to fight o Was expected to look after her husband’s property in times of war • Guard against invaders and slave revolts • Women’s rights o Free to speak with their husband’s friends o Own and control their own property o Could marry another man if their husband was away too long • Spartan slaves Called helots People conquered by the Spartans More helots than citizens Government sometimes declared war on the helots to stop a rebellion o Had some rights • Could marry whoever and whenever they wanted o o o o o Could pass their names on to their children o They could sell any extra crops after their master his share. o If they saved enough, they could even buy their freedom