WHI: SOL 5c
advertisement

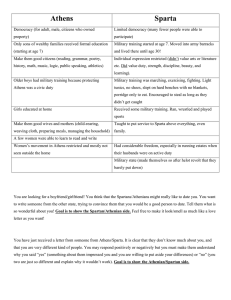
WHI: SOL 5c Sparta Life in Athens • Men participated in government and politics • Women had no role in government, but had a very public role in religion • Women ran the households • Weaving, spinning, caring for children, preparing food • Women could not go out in public unescorted Education • Girls received little or no education • Boys learned to read and write, studied poetry, music, practiced public speaking • Boys received military training and participated in athletic competition but were encouraged to explore many areas of knowledge • **Athenians placed emphasis on a welleducated man in government Sparta • Oligarchy (rule by a small group) – Two kings and a council of elders – An assembly made up of all citizens approved all major decisions • Rigid social structure • Militaristic and aggressive society Education • Babies were evaluated at birth, those too small or weak were left to die • Boys were taken from their families at age 7 and moved into barracks – They ate coarse food, wore minimal clothing, and no shoes – Trained to fight daily, encouraged to steal food, severe beatings for transgressions • At age 20 a man could marry but he had to continue living in the barracks for another 10 years and eat there for another 40 years Women • Women were expected to be the mothers of strong Spartan soldiers • Girls and women were required to exercise and strengthen their bodies • Women could inherit property • While men were at war, women often ran households and businesses Spartan Military • Developed the phalanx- a tactical formation of heavily armed foot soldiers • Sparta was isolated from other city-states • Travel was forbidden to their citizens • Spartans looked down on wealth and trade, had no use for the arts or new ideas