Gymnosperms and Angiosperms - holyoke
advertisement

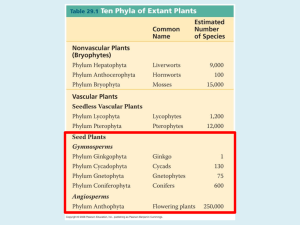
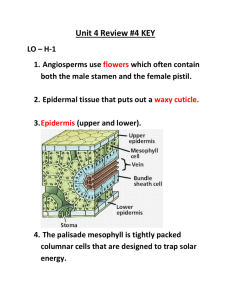
Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Biology 112 Presentation 4 Gymnosperms Include pines, spruce, juniper, fir and other cone bearing plants. Thin, needle-like leaves are a special adaptation to hot-dry summers and cold winters, with moderate rainfall. Needles retain moisture because of their thick waxy cuticle. Their roots extend over a wide surface area, as opposed to penetrating deep into the soil. Angiosperms Comprise more than all the other plant division combined (over 250 000 known.) Many angiosperms and insects have become completely inter-dependant. This process of joint evolution of two or more species is called coevolution. Common Characteristics of Flowers Stamen is the male part of the flower. It consists of: A thin stalk called a filament An anther where pollen is formed The carpel, or pistil is the female part of the flower. It consists of: The stigma – sticky part which pollen lands and grows The style – slender stalk pollen grains travel to ovary The ovary – contains ovule More Common Characteristics of Flowers Sepals – small green leaf-like structures that surround the carpel and stamen Petals – colorful part that attracts pollinators Nectary – small swelling at base of each petal Complete, or Incomplete Flowers Complete flowers contain carpels, stamens, petals, and sepals. I.e. lilies, tomatoes, etc. Incomplete flowers are missing at least one of these structures. In most species the petals die off after fertilization. Reproduction Refer to your handout for life cycle. Do worksheet. Monocots Monocotyledons is an angiosperm whose seeds have only one cotyledon or seed leaf. Vascular bundles distributed throughout stem Veins parallel Flowers in 3s or multiples of 3 Dicots Dicotyledon is an angiosperm whose seeds have two cotyledons or seeds leaves. Vascular bundles arranged in ring Veins netlike Flowers in multiples of 4s or 5s