here
advertisement

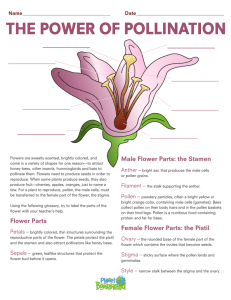
Lesson #3 Reproduction of Seed Plants Date November 10, 2014 Subject/Grade Level Science 7/8 Time Duration 40 min Unit Plants for Food and Fibre Teacher Bailey Thorson OUTCOMES FROM ALBERTA PROGRAM OF STUDIES General Learning Outcomes: Specific Learning Outcomes: 2. Students will investigate life processes and structures of plants, and interpret related characteristics and needs of plants in a local environment 2.1. describe the general structure and functions of seed plants (e.g., describe the roots, stem, leaves and flower of a common local plant) 2.5. describe life cycles of seed plants, and identify example methods used to ensure their germination, growth and reproduction (e.g., describe propagation of plants from seeds and vegetative techniques, such as cuttings; conduct a germination study; describe the use of beehives to support pollination) LEARNING OBJECTIVES Students will: 1. Identify the parts of a flower and explain their functions. 2. Describe the steps of plant reproduction. 3. Explain the function of a fruit. 4. Explain how pollen can get from one flower to another. ASSESSMENTS Observations: Key Questions: Products/Performances: I will observe student responses as they come up to the Smartboard and drag labels to plant structures I will observe students as they participate in a discussion surrounding seed plants and prior knowledge Fill out worksheet Put labels in appropriate place at desks LEARNING RESOURCES CONSULTED Alberta Program of Studies Science in Action 7 Textbook Unit Plan Learn Alberta MATERIALS AND EQUIPMENT Computer Smartboard Worksheets Flower diagram Lilies Exacto knives? PROCEDURE Prior to lesson Attention Grabber Expectations for Learning and Behaviour Advance Organizer/Agenda Introduction Hand out lilies to make observations about it. Write down observations in partners and we will discuss after. Stay on task Actively engage with material Fill out worksheet when asked Not talking while someone else “has the floor” Do some questions to get you thinking about plant reproduction. We will then come together and do an interactive activity on the Time 5 min Assessment of Prior Knowledge Transition to Body Learning Activity #1 Teacher Notes: Assessments/ Differentiation Learning Activity #2 Smartboard, where you will write down answers to worksheet questions as we go. We will be looking at the process of pollination (how the plant reproduces) and the structures involved. Guiding questions: Are the things sticking out of the middle the same size or different? What do you notice on top of them? Feel them. What happens? Does anybody want to cut one open and see what is inside? Begin with picture of flower up on board, unlabeled. Think back to when we went over plant structure. Is this a gymnosperm or angiosperm? (angiosperm, flowering plant). Can you name any of the parts of your flower? Today we are learning about reproduction of seed plants, and we will be looking specifically at how the parts of a flower like this contribute to propagation of plants (making more of). Body Gizmo Activity – students will work as a group with the interactive pollination lesson, filling out their worksheet along the way. Students will work with vocabulary regarding reproductive structure and learn about the process that occurs in both self-pollination and crosspollination. Assessment: Observation and inquiry-based assessment (can they answer the questions I ask?). Students will hand in worksheet after for formative assessment to point out areas that need to be revisited. Labelling Activity – Students will have a picture of a flower sitting in front of them with labels and be able to write down answers that we will check together on the board. After that, they will work independently to match the structure with its function and finish the questions. Time 20 min 10 min After complete and discussed, we will quickly look at the life cycle of a plant. We will then do the review questions together on Gizmo. Teacher Notes: Assessments/ Differentiation Consolidation of Learning: Feedback From Students: Feedback To Students Transition To Next Lesson Sponge Activity/Activities Reflections from the lesson Assessment: Observation and group check Closure In the last 5 minutes of class, we will do the review questions after Gizmo together. Students will vote for which answer they think we should choose. Tell students that there will be a quiz tomorrow on labelling the plant. I will also take in worksheets to mark tomorrow (can use to study tonight). Are there any questions? Tomorrow we will start the class with a quick quiz on what we learned today. We will then look at other ways plants reproduce! Fill out self-reflection on plant processes book Time 5 min Name: _____________________________ Date: ________________________ Student Exploration: Flower Pollination Vocabulary: anther, cross-pollination, filament, fruit, ovary, ovules, petal, pistil, pollen, pollen tube, pollination, self-pollination, sepal, stamen, stigma, style Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1. How may insects help a plant to reproduce? ______________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 2. Apples, oranges, and watermelons are all examples of fruits. How are they all alike? _________________________________________________________________________ 3. Based on your answer to question 2, do you think that a pumpkin is a fruit? How about broccoli? _________________________________________________________________________ Gizmo Warm-up 1. Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from the male part of a flower to the female part of a flower. Select the Pollination tab and then select Self-pollination. How many flowers are on the screen? __________________________________________ 2. Now select Cross-pollination. How many flowers do you see? __________________________________________ 3. How do you think cross-pollination may be different from self-pollination? __________________________________________ __________________________________________ Activity A: Pollination Question: How are self-pollination and cross-pollination the same and how are they different? 1. Observe: Follow the directions in the Gizmo to observe the steps of self-pollination. In your own words describe what happens in each step. 1 2 3 4 5 2. Think about it: Read the description of the last step carefully. Why do you think plants surround the seeds with a yummy fruit? _________________________________________________________________________ 3. Observe: Click Start over, then click Cross-pollination. Follow the directions to observe the steps of cross-pollination. How is cross-pollination different from self-pollination? _________________________________________________________________________ 4. Extend your thinking: In cross-pollination, pollen grains must get from one flower to another. What are some ways that this might happen? Discuss your answer with your teacher and classmates. _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ Activity B: Get the Gizmo ready: Flower parts and pollination Select the Identification tab. Click Start over. Check Show information. Goals: Identify the parts of the flower and describe the function of each. 1. Complete the diagram on the last page. When you are finished, review together on the board. 2. Test yourself: For each flower part below, write the letter of the correct description. Use the Gizmo to check your answers. ______ Anther A. A small leaf that protects the flower before it blooms ______ Filament B. They contain pollen ______ Ovary C. Tiny grains that contain sperm cells ______ Ovules D. The male part of the flower ______ Petal E. The part of the pistil between the stigma and the ovary ______ Pistil F. They grow from a pollen grain to an ovule ______ Pollen G. The female part of the flower ______ Pollen tube H. They contain the egg cells and develop into seeds ______ Sepal I. ______ Stamen J. A stalk that supports the anther ______ Stigma K. The sticky top of the pistil ______ Style L. The part of the pistil that contains the ovules A part of the plant that attracts insects 3. Make connections: How might having the anther atop a tall filament make it more likely that plants will be pollinated? _________________________________________________________________________ 4. Think and discuss: In some plants, the pistils don’t form until a few days after the stamens do. How might this keep a plant from self-pollinating? _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________