A+ Chapter 2 Motherboards and Processors_final
advertisement

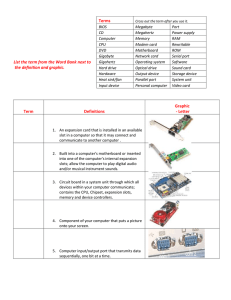
A+ Certification Guide Chapter 2 Motherboards and Processors Chapter 2 Objectives Students should be able to explain: – Motherboards and Their Components: • Form factors, integrated ports and interfaces, memory slots, and expansion slots, and demonstrate how to install and troubleshoot motherboards. – How to Install a Motherboard – How to Troubleshoot a Motherboard – Processors and CPUs: • CPU technologies • Installing and troubleshooting processors – CPU Cooling What Is a Motherboard? Main Printed Circuit Board (PCB) to which all other components are connected. – Has etched-out areas defining the copper data trails to/from: • CPU/clock generator • Northbridge – RAM – Video graphics card • Southbridge (depending on age of board) – PCI slots/USB connections – Com ports – On-board graphics controller – Flash ROM/BIOS Motherboard Similar to a transportation system in a large city: – Wide freeways for faster traffic – Mid-sized boulevards for slower traffic Businesses and neighborhoods send and receive traffic. Choosing a Motherboard What kind of slot does the CPU need? What kind of memory does the motherboard support? – How much memory does it require or can it use? – This question is also OS-dependent because Windows XP has a maximum of 3.2GB of RAM. How many PCI slots do I need? What kind of graphics processor will be needed? – Will the motherboard need a PCI x16 slot? – Is the onboard network adapter sufficient for the job? Am I planning to use this motherboard to support an HDMI output? How does the bus speed match up to the processor capabilities and to the memory that I might be using? Form Factor Motherboard Maximum Type Width Maximum Depth Maximum Number of Expansion Slots ATX 12 inches 9.6 inches Seven Full tower Mini-ATX 11.2 inches 8.2 inches Seven Full tower microATX 9.6 inches Four Mini tower Four Mini tower, small form factor FlexATX 9.0 inches 9.6 inches 7.5 inches Typical Uses RAM Random Access Memory Slots: – – – – Typically numbered from 0–3 (if four slots are included). Is connected directly to Northbridge for fast access to CPU. Data stored here is lost if power is interrupted (volatile). Current types include DDR, DDR2, and DDR3: • 240-pin slotted connector Memory Installation When installing RAM, the memory module should snap into position as it is seated firmly into the slot. – It is a tight fit to ensure connectivity. – Check to see if the “notch” is located properly. • If not, simply reverse the direction. Adapter Cards Different types of slots for different cards PCI (Peripheral Card Interconnect): – Sound cards AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port): – Older: On motherboards made before 2004 PCIe (PCI express): – Newer: Current standard: • PCIe x16 • Can perform 8Gbps Expansion for RAM and Cards Safe Installation of Adapter Cards Remember to avoid electrostatic discharge (ESD). Cards should “fit” the slot. Use gentle rocking rather than brute force: – Brute force can break the electrical traces underneath the motherboard. Attach any devices that the card was made to use: – Network connections/antennas – Printers – USB devices – Speakers Card Slot Configurations PCIe Card Sample Slot Type Performance Suggested Uses PCIe x1 v1 500MBps Network, I/O PCIe x2 v1 1,000MBps Network PCIe x8 v1 4,000MBps SLI video secondary card on older systems Video PCIe x16 v1 8,000MBps PCIe x1 v2 1,000MBps Network, I/O PCIe x2 v2 2,000MBps Network PCIe x8 v2 8,000MBps SLI video secondary card PCIe x16 v2 16,000MBps including SLI, CrossFire, and CrossFire X primary and secondary cards Video Including SLI, CrossFire, and CrossFire X primary and secondary cards Troubleshooting of Adapter Cards System does not recognize the card. – Is it plug ‘n’ play? – Is it properly seated? – Have you read the instructions? • Some need the driver to be installed before physical installation. Card causes problems with other devices. – Check for “resource conflicts.” Card does not perform beyond a basic level. – Check website for driver updates. Chipset Northbridge – Connects to the CPU and other high-speed components such as memory, PCIe, or AGP graphics Southbridge – Connects to lower-speed components: storage interfaces, PCI slots, USB ports, and CMOS Motherboard Installation Step 1. Determine which mounting holes should be used for brass spacers. Step 2. Install or remove brass spacers as needed to accommodate the mounting holes in the motherboard. Motherboard Installation (cont.) Step 3. Place the I/O shield into the opening at the back of the case. Step 4. Determine which holes in the motherboard have brass stand-off spacers beneath them, and secure the motherboard to the spacer. Motherboard Installation (cont.) Step 5. Connect front panel wires to the speaker, reset switch, drive activity light, and power light connectors on the motherboard. Motherboard Installation (cont.) Step 6. Connect the ribbon cables from the drives to the motherboard’s PATA and floppy disk drive interfaces (if present). Match the ribbon cable’s colored side to pin 1 on the interfaces. Step 7. Connect cables from the SATA drives to the SATA ports on the motherboard. Use SATA port 1 for the first SATA drive, and so on. Motherboard Installation (cont.) Figure 4-8 04fig08 Motherboard Installation (cont.) Step 9.Install the add-on cards The Role of the CPU Order of Operations (abbreviated): – – – – First, there must be a request to the CPU to “compute” something. Next, data must be delivered to the CPU to be computed (data input). The computation takes place. Finally, the result (data output) is delivered to some device, such as a monitor. Processors and CPUs Intel – – Land Grid Array (LGA) • LGA 775 • LGA 1155 • LGA 1156 • LGA 1366 Note protective cover Processors and CPUs AMD – – PGA • Pin Grid Array Sockets • 940 • AM2 • AM2+ • AM3 • AM3+ • F • FM1 CPU Technologies Hyperthreading Multicore Cache – for recently used process threads: – L1 – Processor Core – L2 – Processor Die – L3 – Processor Die – System checks L1 first, then L2, and then L3 Bus Speeds Overclocking 32 bit versus 64 bit Virtualization Support Integrated GPU CPU Cooling Passive and Active Heat Sinks Liquid Cooling Systems Choosing a CPU Scenarios in which a different CPU might be specified: – A graphics design company using Photoshop and 3D software. – A doctor’s office using office applications. – Local government servicing billing for water usage. – Server environment supporting 5,000 users with database access. Purchasing Planning Exercise Assume you work for a real estate management company. It asked you to investigate a new PC to replace its aging ones. It wants to run the latest Office applications and include the capacity for playing DVDs to show off itslistings. TItey needs 6 desktop machines for the office and 12 notebook computers for the salespeople. – What CPU speed will accomplish the job? – How much RAM will be needed? – What size hard drive should be adequate? – Based on the CPU you choose, what motherboard will work with it? Take a few minutes tosee what you come up with for this replacement project. Chapter 2 Summary Motherboards and Their Components: • Form factors, integrated ports and interfaces, memory slots, and expansion slots, and demonstrate how to install and troubleshoot motherboards. Installing a Motherboard Installing Adapter Cards: • Install video and sound cards, and how to troubleshoot common adapter card issues. Processors and CPUs: • Types of processors available, their architecture and technologies, and installing and troubleshooting processors. Next Lesson: Chapter 3